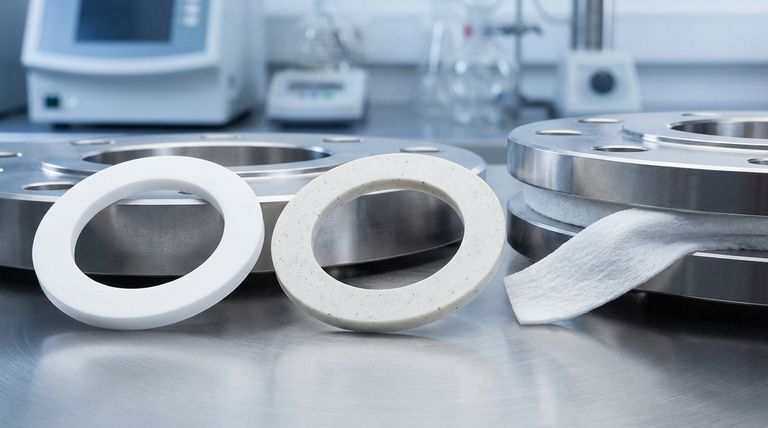
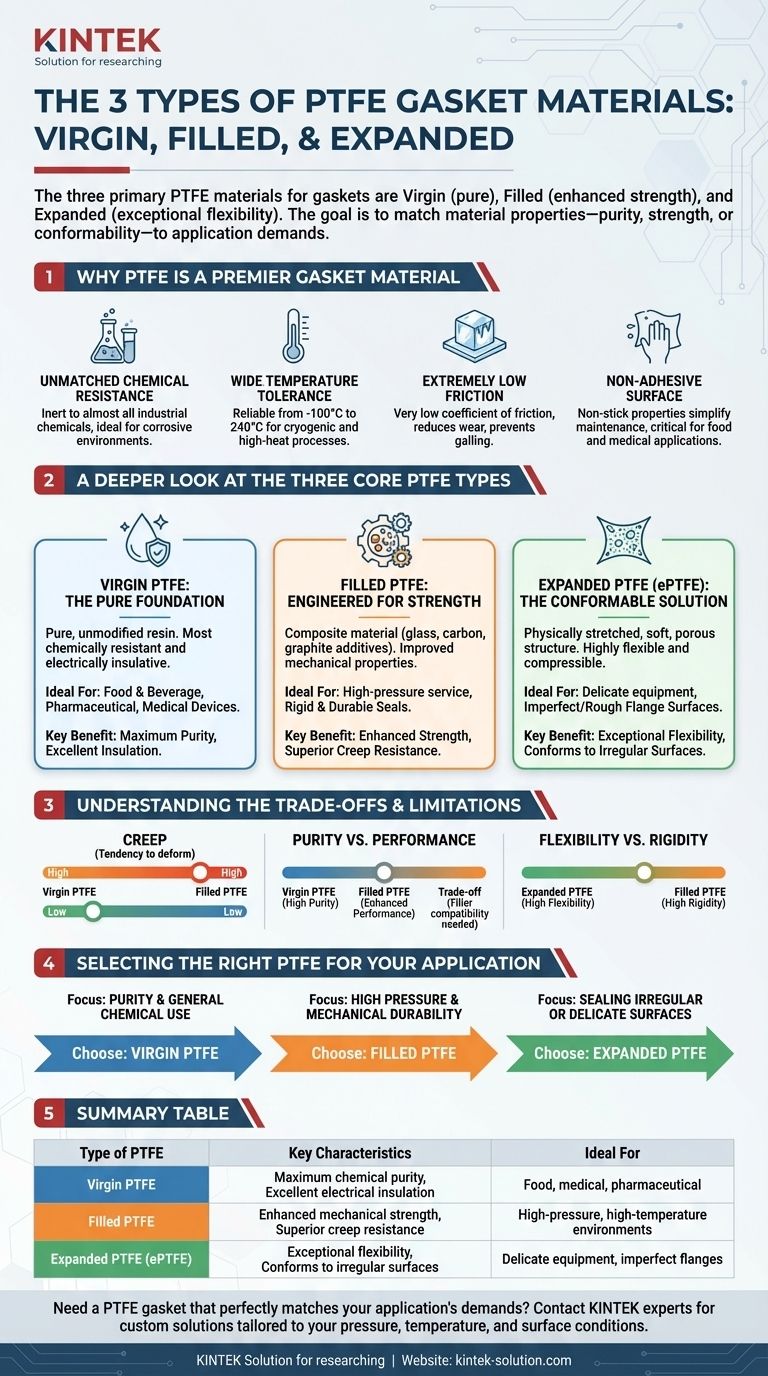
The three primary types of PTFE materials used for gaskets are Virgin (pure) PTFE, Filled PTFE, and Expanded PTFE. Virgin PTFE is valued for its chemical purity and electrical insulation, Filled PTFE is enhanced with additives for superior mechanical strength, and Expanded PTFE is engineered for exceptional flexibility and the ability to conform to irregular surfaces.
The core decision is not about finding the "best" type of PTFE, but about matching the specific material properties—purity, mechanical strength, or conformability—to the precise demands of your application's pressure, temperature, and surface conditions.

Why PTFE is a Premier Gasket Material
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance fluoropolymer chosen for sealing applications in demanding environments. Its unique molecular structure gives it a combination of properties that are difficult to find in any other single material.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals. This makes it an ideal choice for seals in aggressive chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and other corrosive environments.
Wide Temperature Tolerance
PTFE gaskets perform reliably across a broad temperature spectrum, typically from -100°C to 240°C (-148°F to 464°F). This allows them to maintain sealing integrity in both cryogenic and high-heat processes.
Extremely Low Friction
The material has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This reduces wear and tear in dynamic applications and prevents galling between metal flange surfaces.
Non-Adhesive Surface
PTFE's non-stick properties simplify maintenance and cleaning, as process media are less likely to adhere to the gasket surface. This is a critical advantage in food, beverage, and medical applications.
A Deeper Look at the Three Core PTFE Types
While all PTFE shares the core properties above, modifying its physical structure creates three distinct classes of gasket material, each with specific advantages.
Virgin PTFE: The Pure Foundation
Virgin PTFE is pure, unmodified material made directly from the resin. It is the most chemically resistant and electrically insulative of the three types.
Because it contains no additives, it is the default choice for applications where purity is non-negotiable, such as in food and beverage production or pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturing.
Filled PTFE: Engineered for Strength
Filled PTFE is a composite material created by adding substances to Virgin PTFE. Common fillers include glass, carbon, or graphite, each of which imparts different characteristics.
Adding a filler dramatically improves the gasket's mechanical properties, particularly its resistance to "creep" or cold flow under pressure and heat. This makes Filled PTFE ideal for high-pressure service or where a more rigid and durable seal is required.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE): The Conformable Solution
Expanded PTFE is produced by physically stretching Virgin PTFE, creating a soft, porous, and highly fibrillated structure. This process makes the material exceptionally flexible and compressible.
The key advantage of ePTFE is its ability to conform to rough, pitted, or damaged flange surfaces with very low bolt load. This makes it the perfect solution for sealing delicate equipment, such as glass-lined pipes, or in any situation where a tight seal is needed on an imperfect surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Choosing the right PTFE requires acknowledging the inherent trade-offs between the different material types.
The Challenge of "Creep"
The primary weakness of Virgin PTFE is its tendency to deform or "creep" under sustained mechanical load, especially at elevated temperatures. This can lead to a loss of bolt torque and potential leaks over time.
This limitation is the very reason Filled PTFE was developed. The additives act as a reinforcing matrix, significantly reducing creep and improving the gasket's dimensional stability.
Purity vs. Performance
While fillers enhance mechanical performance, they can compromise the material's absolute chemical resistance or purity. A filler that resists most acids might be attacked by a strong alkali, for example.
Therefore, selecting a Filled PTFE requires careful consideration of its compatibility with the specific process media to ensure it doesn't become a point of failure.
Flexibility vs. Rigidity
Expanded PTFE's softness and conformability are its greatest strengths, but this also means it lacks the rigidity of Filled PTFE. In extremely high-pressure applications, a more robust Filled PTFE gasket might be necessary to prevent extrusion.
Selecting the Right PTFE for Your Application
Your choice should be guided by the most critical demand of your sealing environment.
- If your primary focus is purity and general chemical use: Virgin PTFE is the most reliable and cost-effective choice for food, medical, and broad-spectrum chemical applications.
- If your primary focus is high pressure and mechanical durability: A Filled PTFE gasket, with its enhanced creep resistance, will provide a more robust and lasting seal in demanding service conditions.
- If your primary focus is sealing irregular or delicate surfaces: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) provides unmatched conformability, ensuring a tight seal even on damaged flanges with minimal bolt force.
By understanding these fundamental differences, you can select a PTFE gasket that provides not just a seal, but long-term operational integrity.
Summary Table:
| Type of PTFE | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | Maximum chemical purity, excellent electrical insulation | Food, medical, pharmaceutical applications |
| Filled PTFE | Enhanced mechanical strength, superior creep resistance | High-pressure, high-temperature environments |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Exceptional flexibility, conforms to irregular surfaces | Delicate equipment, imperfect flanges |
Need a PTFE gasket that perfectly matches your application's demands?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals and gaskets, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get a sealing solution that delivers long-term integrity, whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order.
Contact our experts today for a custom solution tailored to your pressure, temperature, and surface conditions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What industries are PTFE gasket envelopes suitable for? Find the Perfect Seal for Demanding Applications
- What are the uses of PTFE coatings in the semiconductor and electronics industries? Ensure Purity & Reliability
- What precautions should be taken when installing PTFE O-rings? Avoid Permanent Damage and Seal Failure
- How do fillers alter PTFE's machining properties? A Guide to Taming Abrasive Composites
- What are the key properties of PTFE that ePTFE gaskets retain? Superior Chemical & Thermal Stability
- How do PTFE and nylon differ in terms of water interactivity? Key Differences for Component Stability
- What makes expanded PTFE gaskets easy to handle and install? Achieve a Perfect Seal on Any Flange
- Why are PTFE gaskets suitable for the food and beverage industry? Ensure Purity, Hygiene & Performance



















