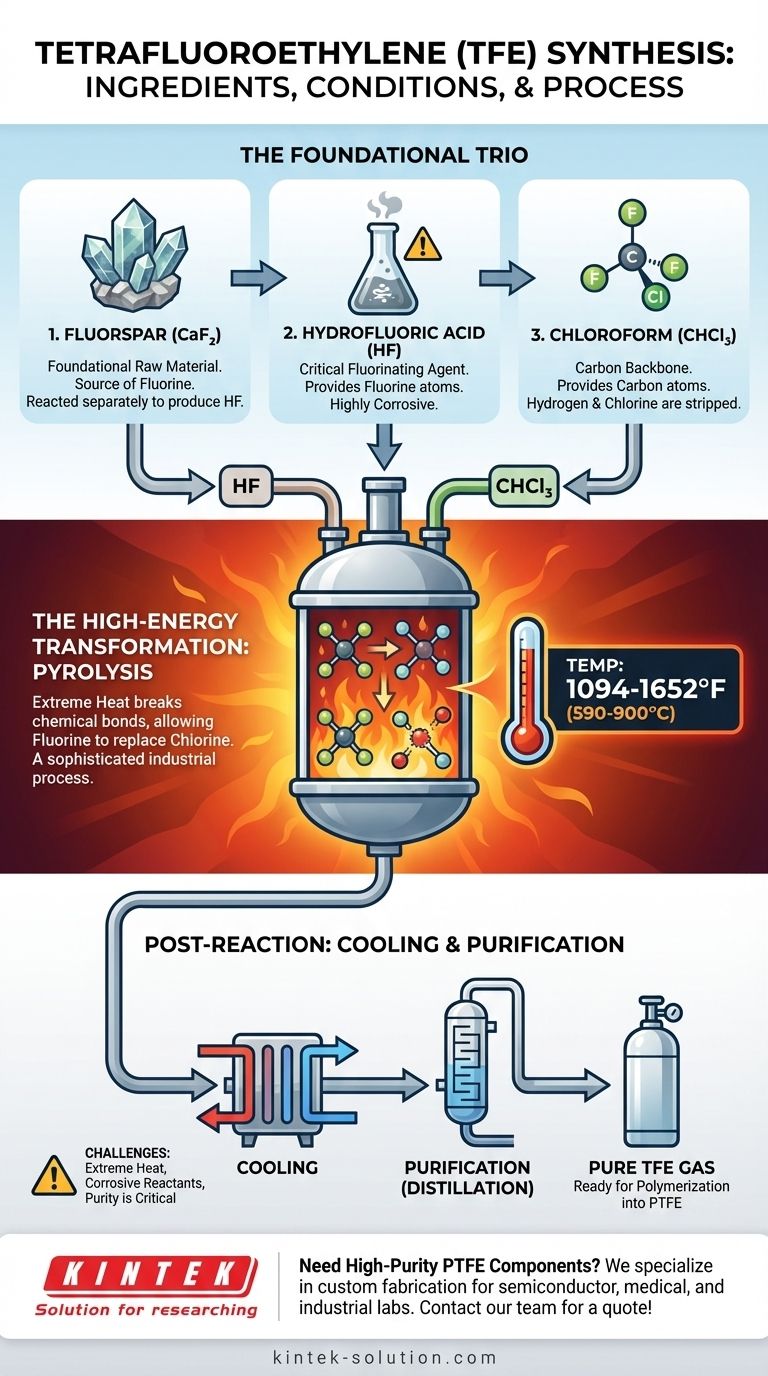
To synthesize Tetrafluoroethylene (TFE), the process combines chloroform and hydrofluoric acid within a reaction chamber heated to extremely high temperatures. While not a direct reactant in this final step, fluorspar is the essential mineral used to produce the hydrofluoric acid, making it the foundational raw material for the entire process. The reaction takes place between 1094-1652°F (590-900°C).
The synthesis of TFE is a high-energy chemical process known as pyrolysis. It involves reacting a carbon source (chloroform) with a fluorine source (hydrofluoric acid) at extreme temperatures to create the TFE gas, which must then be purified.

The Synthesis Process Explained
Understanding TFE synthesis requires looking at the role of each component and the specific conditions needed to force them to react. This is not a simple mixing of ingredients but a sophisticated industrial process.
The Role of Each Ingredient
Chloroform (CHCl₃) serves as the carbon backbone of the molecule. In this reaction, the goal is to strip away its hydrogen and chlorine atoms and replace them with fluorine.
Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) is the critical fluorinating agent. It provides the fluorine atoms that will bond to the carbon, transforming the precursor molecule into TFE.
Fluorspar (CaF₂) is the original source of the fluorine. It's important to clarify that fluorspar does not go directly into the TFE reactor with chloroform. Instead, fluorspar is first reacted with sulfuric acid in a separate process to produce the hydrofluoric acid needed for TFE synthesis.
The Critical Reaction Conditions
The reaction is conducted in a process called pyrolysis, which means using extremely high heat to break down molecules.
The mixture of chloroform and hydrofluoric acid is passed through a reactor heated to between 1094°F and 1652°F (590°C and 900°C). This intense heat provides the energy needed to break the chemical bonds in the chloroform and allow the fluorine atoms to take their place.
Post-Reaction Purification
The output from the reactor is a hot gas mixture, not pure TFE. This mixture contains TFE, unreacted starting materials, and other byproducts like hydrochloric acid (HCl).
This gas must be cooled and then purified through distillation. This final step separates the pure TFE gas from all impurities, making it ready for the next stage of production, typically polymerization into PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene).
Understanding the Inherent Challenges
The industrial production of TFE is a demanding process with significant technical and safety hurdles that must be overcome.
The Hazard of High Temperatures
Maintaining temperatures up to 1652°F requires a significant and continuous energy input. The reactors and associated piping must be constructed from specialized materials capable of withstanding this thermal stress without failing.
The Corrosive Nature of Reactants
Hydrofluoric acid is extremely corrosive and hazardous. It attacks glass, metals, and human tissue. All equipment in contact with HF must be made of resistant alloys, and rigorous safety protocols are mandatory for handling and transport.
The Importance of Purity
The final distillation step is not optional. Any impurities remaining in the TFE gas can interfere with the polymerization process, leading to a lower quality final product (like PTFE) or complete failure of the polymerization reaction.
Key Principles for TFE Synthesis
Understanding this process comes down to a few core principles depending on your focus.
- If your primary focus is the core reaction: The key transformation is the high-temperature substitution of chlorine atoms on a chloroform molecule with fluorine atoms from hydrofluoric acid.
- If your primary focus is the material supply chain: Recognize that fluorspar is the ultimate raw material, as it is the indispensable source for producing the required hydrofluoric acid.
- If your primary focus is engineering and safety: The central challenges are managing the extreme heat of pyrolysis and containing the highly corrosive reactants.
Ultimately, creating TFE is a precise and energy-intensive process that transforms common chemicals into a high-performance monomer.
Summary Table:
| Ingredient | Role in TFE Synthesis | Key Reaction Condition |
|---|---|---|
| Chloroform (CHCl₃) | Provides the carbon backbone | Pyrolysis reactor at 1094-1652°F (590-900°C) |
| Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) | Acts as the fluorinating agent | Reacts with chloroform at high temperatures |
| Fluorspar (CaF₂) | Raw material for producing HF | Processed separately to create the HF reactant |
Need High-Purity PTFE Components for Your Application?
The synthesis of TFE is a demanding process requiring precision and expertise—qualities that define KINTEK's approach to manufacturing PTFE products. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we transform high-quality monomers into reliable components like seals, liners, and custom labware.
We specialize in custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring the material integrity and performance your operations depend on.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our team today to get a quote or learn more about our capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of Teflon's softness? Unlock Superior Flexibility and Low-Friction Performance
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for high-performance applications? Unlock Extreme Performance
- How is FEP Teflon different from other types in terms of properties? The Key is Fabrication Flexibility
- What are some applications of PTFE due to its properties? Discover Its Versatility in Demanding Industries
- What precautions should be taken when using Teflon cookware? Essential Safety Tips for Non-Stick Pans
- What are the main material characteristics of PTFE? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Environments
- What types of clothing incorporate Teflon? Discover High-Performance Protective Apparel
- What makes PTFE plastic uniquely versatile across industries? The 4 Key Properties Explained



















