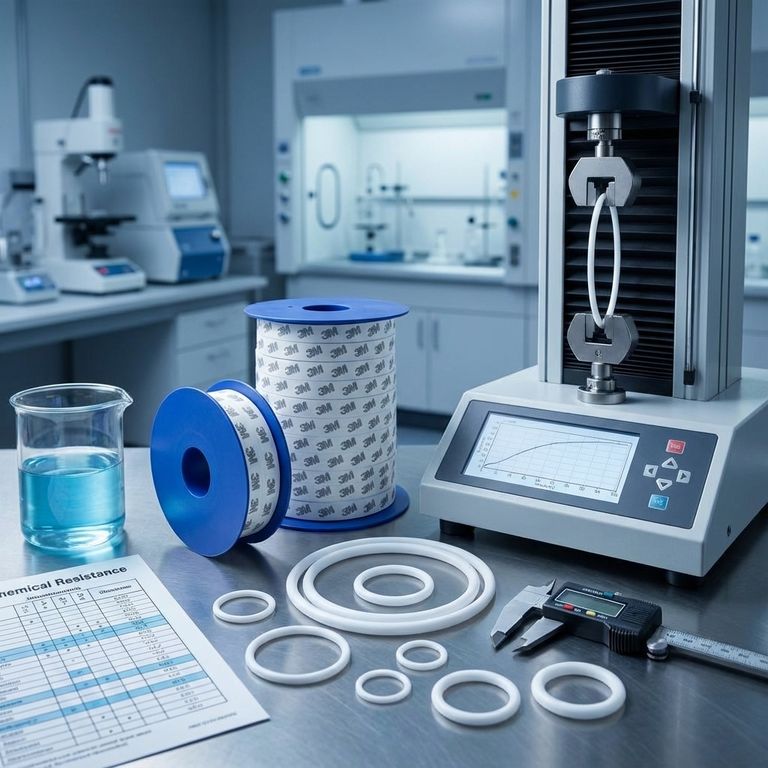
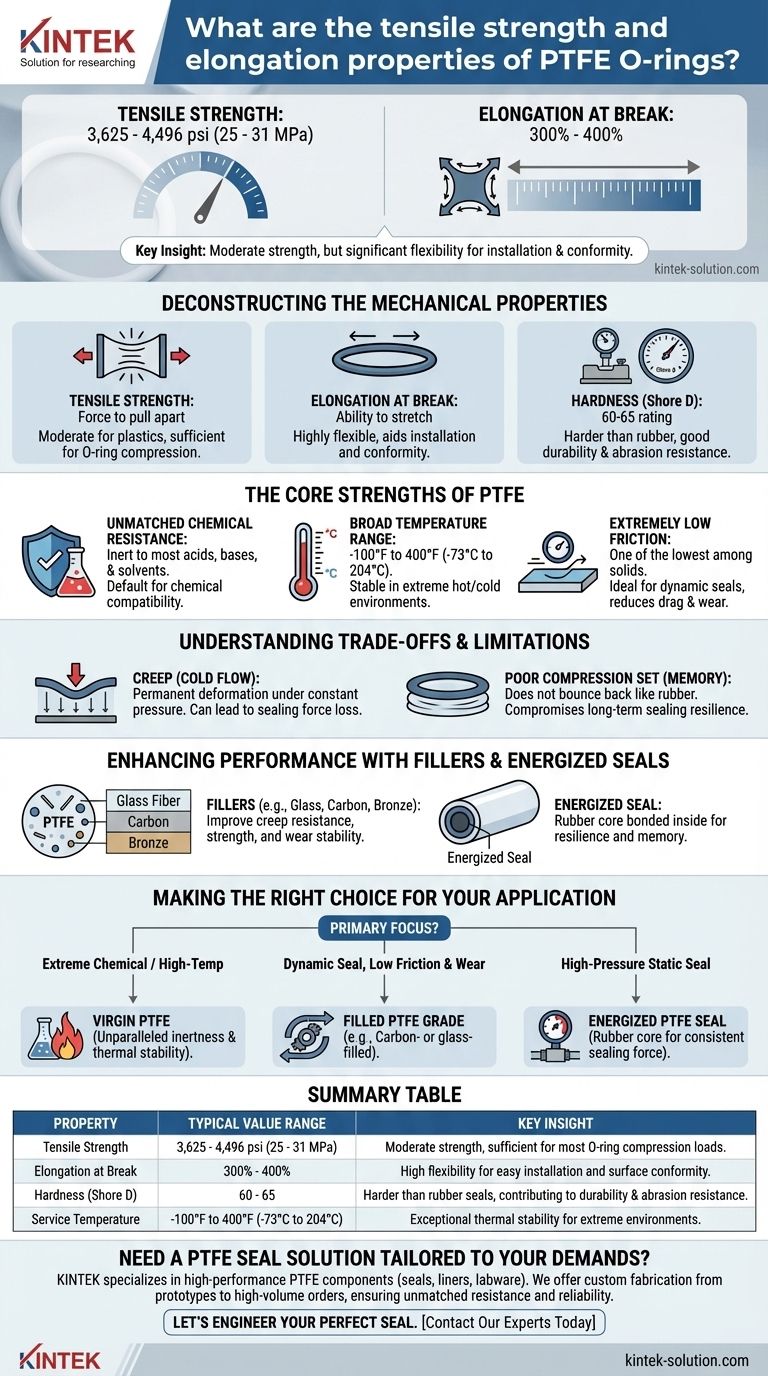
For Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) O-rings, the typical tensile strength ranges from 3,625 to 4,496 psi (25 to 31 MPa). Their elongation at break, which measures how much they can stretch before failing, is generally between 300% and 400%. These values indicate a material with moderate strength but significant flexibility.
While the numbers provide a baseline, they don't capture the full story. The decision to use PTFE is rarely based on its raw strength alone; it's driven by its unparalleled chemical inertness and performance across a vast temperature range, which often makes its mechanical trade-offs acceptable.

Deconstructing the Mechanical Properties
To properly evaluate PTFE for an application, we must understand what these core metrics mean in a practical context.
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures the force required to pull the material apart. The range of 3,625 to 4,496 psi places PTFE in a moderate category compared to many other engineering plastics.
However, for most O-ring applications, which primarily involve compression, this level of tensile strength is more than sufficient.
Elongation at Break
Elongation measures the material's ability to stretch without breaking. With a value of 300% to 400%, PTFE is highly flexible.
This flexibility is essential for an O-ring, as it allows the seal to be installed into grooves and conform to sealing surfaces effectively.
Hardness
PTFE O-rings typically have a durometer rating of 60-65 on the Shore D scale. This is quite hard compared to common elastomeric (rubber) seals, which are measured on the softer Shore A scale.
This hardness contributes to its durability and resistance to abrasion but means it requires more force to create an effective seal.
The Core Strengths of PTFE
The true value of PTFE is not in its mechanical strength but in its unique combination of other properties that make it a critical problem-solver in demanding environments.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert and resistant to almost all industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids, bases, and solvents. This makes it the default choice when chemical compatibility is the primary concern.
Broad Temperature Range
PTFE maintains its integrity across an exceptionally wide service temperature range, typically from -100°F to 400°F (-73°C to 204°C). This stability is critical for applications involving cryogenic fluids or high-temperature processes.
Extremely Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This property, often described as "slippery," makes it ideal for dynamic seals where reducing drag and wear is essential.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. The unique properties of PTFE come with distinct mechanical limitations that are critical to understand for successful seal design.
The Challenge of Creep (Cold Flow)
PTFE's most significant mechanical weakness is its tendency to creep, or "cold flow." Under constant compressive pressure, the material can slowly deform permanently.
This can lead to a loss of sealing force over time, particularly in high-pressure applications.
Poor Compression Set (Memory)
Unlike rubber, PTFE has a poor compression set, meaning it does not readily return to its original shape after being compressed. This lack of "memory" can compromise its ability to maintain a long-term, resilient seal.
Enhancing Performance with Fillers
To mitigate these weaknesses, PTFE is often blended with fillers like glass fiber, carbon, or bronze. These fillers significantly improve creep resistance, mechanical strength, and wear stability, though they may slightly alter the material's chemical resistance or temperature range.
Another common solution is an energized seal, where a rubber core is bonded inside the PTFE jacket to provide the resilience and memory that pure PTFE lacks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires aligning its properties with the demands of your specific environment.
- If your primary focus is sealing in extreme chemical or high-temperature environments: Virgin PTFE is an excellent choice due to its unparalleled inertness and thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is a dynamic seal requiring low friction and good wear resistance: A filled grade of PTFE (e.g., carbon- or glass-filled) is likely the superior option.
- If your primary focus is a high-pressure static seal requiring long-term reliability: A standard PTFE O-ring may be prone to creep; consider an energized PTFE seal with a rubber core to ensure consistent sealing force.
Ultimately, understanding PTFE's complete profile—not just its tensile strength—is the key to deploying it successfully.
Summary Table:
| Property | Typical Value Range | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 3,625 - 4,496 psi (25 - 31 MPa) | Moderate strength, sufficient for most O-ring compression loads. |
| Elongation at Break | 300% - 400% | High flexibility for easy installation and surface conformity. |
| Hardness (Shore D) | 60 - 65 | Harder than rubber seals, contributing to durability and abrasion resistance. |
| Service Temperature | -100°F to 400°F (-73°C to 204°C) | Exceptional thermal stability for extreme environments. |
Need a PTFE Seal Solution Tailored to Your Demands?
Understanding the properties is the first step; applying them correctly is what ensures success. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We go beyond standard specs to provide custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your seals deliver unmatched chemical resistance, thermal stability, and reliability.
Let's engineer your perfect seal. Contact our experts today to discuss your application requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Industrial Environments
- How do Teflon FEP and PFA perform against bases? Superior Resistance for Alkaline Environments
- Why is the manufacturing cost of PTFE processing machines high? The Engineering Behind High-Performance Polymer Processing
- What are some alternative names for PTFE O-rings? Teflon®, TFE, and Polytetrafluoroethylene Explained
- How is MoS2 (Moly) typically combined in PTFE applications? Synergistic Fillers for Low Friction
- For what types of bridge structures are PTFE sliding elastomeric bearings suitable? Ideal for Large Horizontal Movement
- In which industries are PTFE tri clamp gaskets commonly used? Essential for Purity & Chemical Resistance
- What are the key advantages of using PTFE/Teflon tri-clamp sanitary gaskets? Maximize Purity & Performance



















