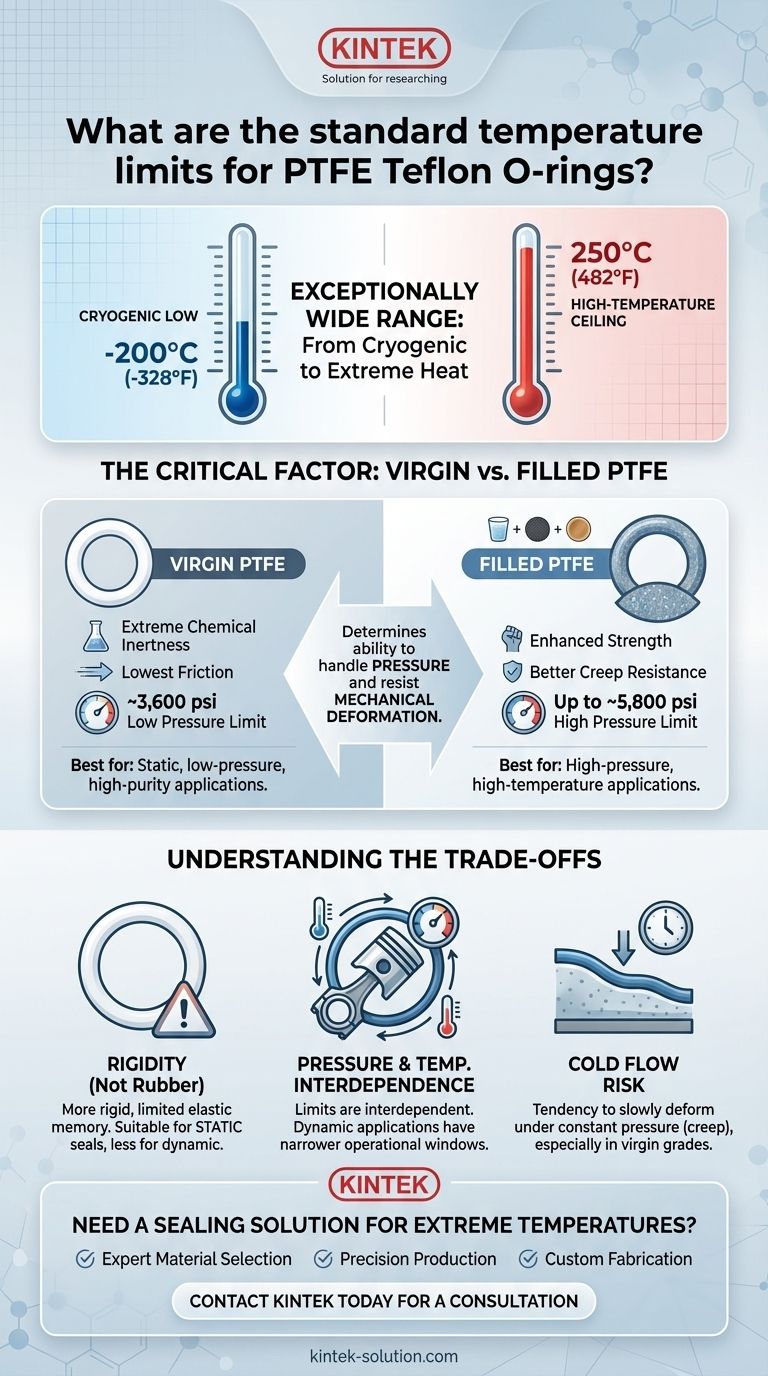
The standard operational temperature range for PTFE (Teflon) O-rings is exceptionally wide, spanning from a cryogenic low of -200°C (-328°F) to a high of 250°C (482°F). This remarkable thermal stability makes it one of the most versatile sealing materials available for extreme temperature environments.
While PTFE's temperature range is its defining feature, the critical decision factor is not just the temperature itself. The choice between "virgin" and "filled" PTFE grades is essential, as this determines the material's ability to handle pressure and resist mechanical deformation within that temperature window.

The Exceptional Temperature Range of PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a fluoropolymer with properties that make it suitable for applications where other elastomers would fail catastrophically.
The Cryogenic Low-Temperature Limit
PTFE maintains its integrity and sealing properties down to -200°C (-328°F). At these temperatures, most rubber compounds become extremely brittle and will crack or shatter under minimal stress. PTFE's ability to withstand such cold makes it a default choice for cryogenic systems.
The High-Temperature Ceiling
The material performs reliably in continuous service up to 250°C (482°F), with some sources citing limits up to 260°C (500°F). This allows it to be used in high-temperature industrial processes, engines, and systems where heat degradation is a primary concern for sealing components.
Beyond Temperature: Why "Virgin" vs. "Filled" Matters
Understanding PTFE requires looking past the single material name. The performance, particularly under pressure, changes dramatically based on whether the PTFE is in its pure form or has been compounded with other materials.
Virgin PTFE: The Pure Performer
Virgin PTFE is the pure, unfilled polymer. Its primary advantages are its extreme chemical inertness and one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid.
However, its mechanical properties are weaker. Virgin PTFE is limited to lower pressure applications, typically around 3,600 psi.
Filled PTFE: Enhancing Mechanical Strength
To overcome the mechanical limitations of virgin PTFE, fillers like glass, carbon, graphite, or bronze are added to the compound.
These "filled" grades offer significantly improved strength and resistance to deformation. This allows them to handle much higher pressures, with some variants rated for up to 5,800 psi.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simply choosing PTFE for its temperature range without considering its other properties can lead to seal failure. It is a unique material with specific limitations.
The Rigidity Problem: It's Not a Rubber
Unlike a traditional rubber O-ring, PTFE is a relatively rigid plastic. It does not have the same elastic memory, meaning it won't spring back to its original shape as effectively after being compressed. This makes it more suitable for static face seals than for dynamic applications that require constant compression and relaxation.
Pressure and Temperature Interdependence
The maximum temperature and pressure limits are not independent variables. In demanding applications like a dynamic piston ring, the operational window can be more constrained. For example, a PTFE piston ring might be rated for a narrower range of –60°C to +200°C when sealing pressures up to 100 bar (1,450 psi).
The Risk of "Cold Flow"
A key weakness of PTFE, especially virgin grades, is its tendency to "cold flow" or creep. This is a phenomenon where the material slowly deforms over time when subjected to a constant pressure. Adding fillers helps to mitigate this but does not eliminate it entirely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct material, you must align the PTFE grade with the specific demands of the operating environment.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature range and chemical purity: Virgin PTFE is the ideal choice for static, low-pressure applications where contamination is a concern.
- If your primary focus is high pressure combined with high temperature: A filled PTFE variant (carbon, glass, or bronze) is necessary to provide the required mechanical strength and resistance to creep.
- If your application is dynamic (like a piston seal): You must evaluate specific grades rated for dynamic service, as their operational temperature and pressure limits will be interdependent and more constrained.
Ultimately, selecting the correct PTFE material requires looking beyond the impressive temperature specifications to match its unique mechanical properties with the precise demands of your system.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | Filled PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Temp. Range | -200°C to 250°C | -200°C to 250°C |
| Key Feature | Extreme chemical inertness, low friction | Enhanced strength, better creep resistance |
| Pressure Limit (Typical) | ~3,600 psi | Up to ~5,800 psi |
| Best For | Static, low-pressure, high-purity applications | High-pressure, high-temperature applications |
Need a Sealing Solution for Extreme Temperatures?
PTFE's exceptional thermal range is just the beginning. The right choice between virgin and filled grades is critical for performance under pressure.
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, O-rings, liners, and custom labware—for the most demanding environments in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide:
- Expert Material Selection: Guidance on virgin vs. filled PTFE to match your exact temperature, pressure, and chemical resistance requirements.
- Precision Production: High-quality components manufactured to your exact specifications.
- Custom Fabrication: From rapid prototypes to high-volume production runs.
Let our experts help you select and fabricate the perfect PTFE seal for your application.
Contact KINTENG today for a consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications



















