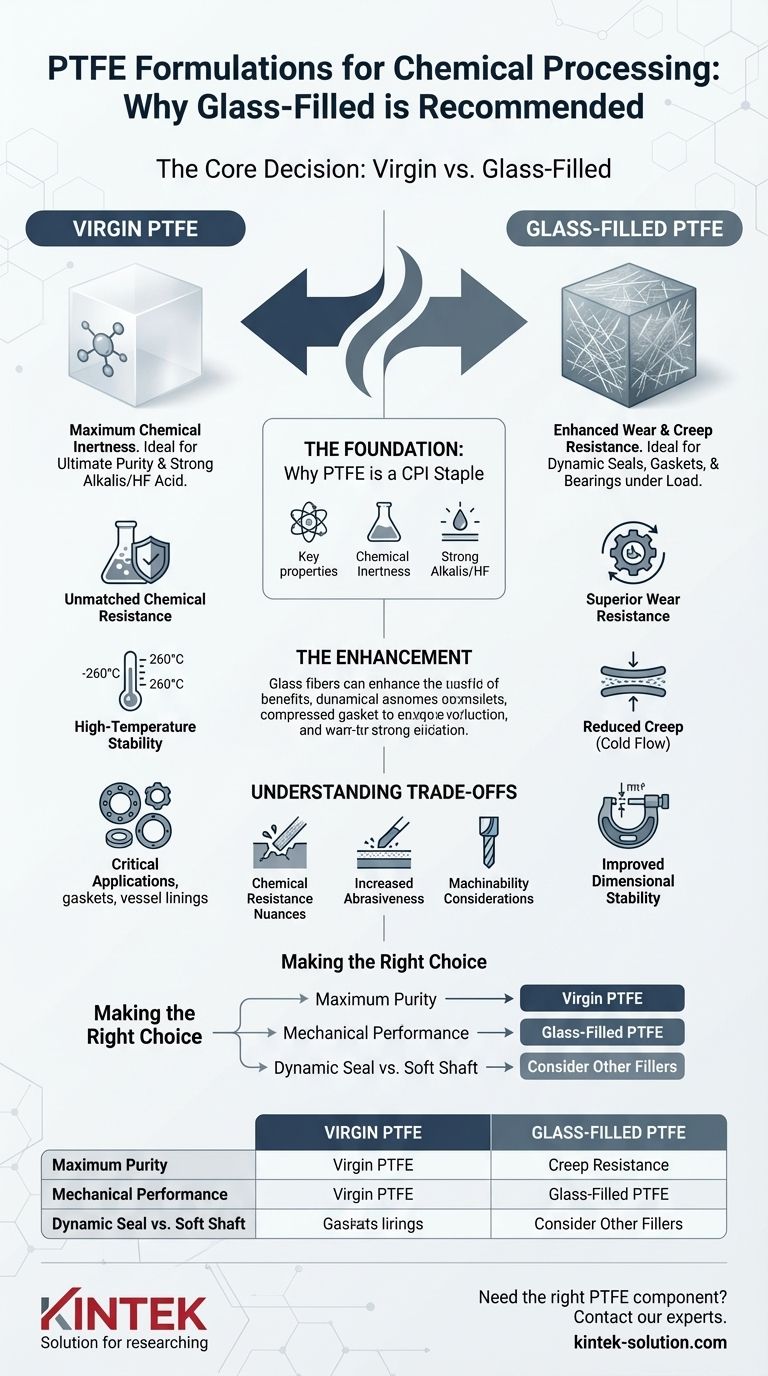
For demanding applications in the chemical processing industry, the most frequently recommended formulation is glass-filled PTFE. While standard, or "virgin," PTFE provides a baseline of exceptional chemical resistance, the addition of glass fibers significantly enhances the mechanical properties required for the industry's most challenging environments.
The core decision hinges on a simple principle: Virgin PTFE provides unparalleled chemical inertness, while glass-filled PTFE adds the crucial mechanical strength—specifically wear and creep resistance—needed for durable seals, gaskets, and components under constant physical stress.

The Foundation: Why PTFE is a CPI Staple
Before examining formulations, it's essential to understand why Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a cornerstone material in chemical processing. Its value stems from a unique combination of inherent properties.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually immune to almost all industrial chemicals and solvents. This exceptional resistance prevents material degradation, ensuring the purity of the processed chemicals and the integrity of the equipment.
High-Temperature Stability
This material maintains its properties across a wide range of operating temperatures common in chemical processing, from cryogenic levels up to 260°C (500°F).
Critical Applications
Because of these properties, PTFE is used to manufacture essential components like gaskets, seals, vessel linings, and expansion joints that are in direct contact with aggressive substances.
The Enhancement: Why Glass-Filled PTFE is Recommended
Adding glass fibers to the PTFE matrix directly addresses the mechanical weaknesses of the virgin material, making it far more robust for industrial use.
Superior Wear Resistance
Glass-filled PTFE exhibits significantly improved resistance to wear and abrasion. This is critical for dynamic components like seals and bearings that experience constant friction.
Reduced Creep (Cold Flow)
One of the primary limitations of virgin PTFE is its tendency to "creep" or deform over time when under a constant load, such as a compressed gasket. The glass fibers provide structural reinforcement, drastically reducing this deformation and ensuring a long-lasting, reliable seal.
Improved Dimensional Stability
The addition of glass makes the material stiffer and more dimensionally stable. This allows for tighter tolerances during machining and better performance under pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While glass-filled PTFE is a superior choice for many applications, it is not a universal solution. An expert decision requires acknowledging its limitations.
Chemical Resistance Nuances
The addition of glass can slightly compromise the material's legendary chemical inertness in very specific, aggressive environments. Strong alkalis and hydrofluoric acid, for instance, can attack the glass filler itself, making virgin PTFE a better choice in those niche cases.
Increased Abrasiveness
The glass fibers make the material more abrasive. This can cause increased wear on softer, opposing surfaces (like certain metal shafts) in dynamic applications.
Machinability Considerations
Machining glass-filled PTFE requires more robust tooling and techniques. Carbide-tipped tools are necessary, and parameters like cutting speed and depth must be carefully controlled to manage heat and prevent delamination, ensuring the final component's integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the optimal material requires a clear understanding of the component's primary function and operating environment.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity or resistance to strong alkalis: Virgin PTFE is the safest and most reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is mechanical performance under load (gaskets, valve seats, bearings): Glass-filled PTFE provides the necessary wear and creep resistance for a long service life.
- If you are designing a dynamic seal against a soft metal shaft: You may need to consider other fillers (like bronze or carbon) to balance wear resistance with the preservation of the mating surface.
Ultimately, choosing the right PTFE formulation is a process of matching the material's specific strengths to the distinct chemical and mechanical stresses of your application.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Formulation | Key Property | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | Maximum Chemical Inertness | Applications requiring ultimate purity, resistance to strong alkalis/HF acid. |
| Glass-Filled PTFE | Enhanced Wear & Creep Resistance | Dynamic seals, gaskets, bearings under constant load and stress. |
Need the right PTFE component for your chemical processing application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components (seals, liners, labware, and more) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production and custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure you get a component perfectly matched to your specific chemical and mechanical demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a solution that delivers lasting reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Conductive Glass Substrate Cleaning Rack
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is expanded PTFE and what are its key properties? A Guide to the Microporous Wonder Material
- What are the basic chemical properties of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Chemical Resistance and Non-Stick Performance
- What are some additional physical properties of PTFE? Beyond Non-Stick: Discover PTFE's Elite Thermal & Chemical Resistance
- What are the common applications of PTFE in aggressive chemical environments? Ensure Reliability and Safety
- Why is PTFE suitable for medical applications? The Key to Biocompatibility and Sterilization
- What precautions should be taken when using Teflon cookware? Essential Safety Tips for Non-Stick Pans
- In which industries is PTFE commonly used? Discover High-Performance Applications
- How is PTFE laminated fabric manufactured? A Guide to High-Performance Material Engineering



















