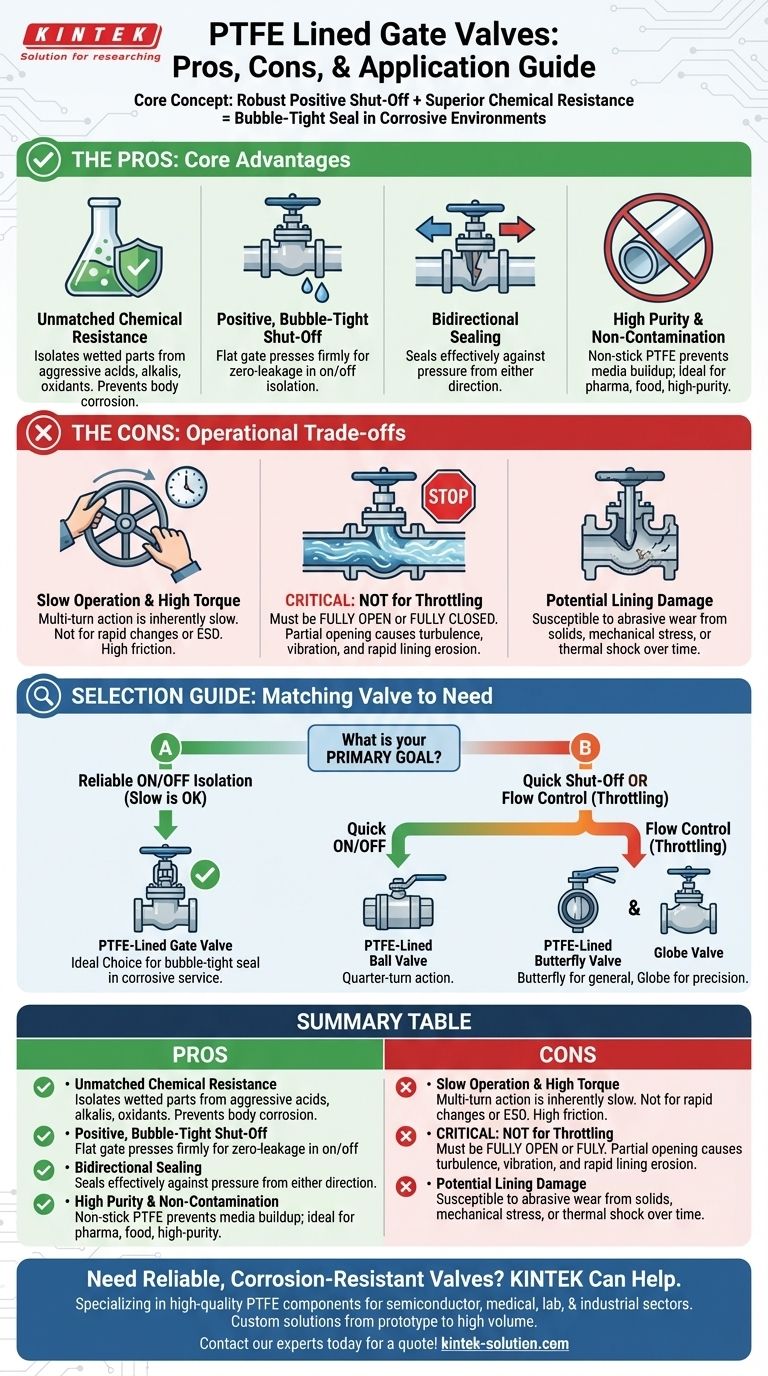
In essence, a PTFE-lined gate valve combines the robust, positive shut-off of a gate valve design with the superior chemical resistance of a PTFE lining. Its primary advantage is providing a bubble-tight seal in highly corrosive environments. However, its significant disadvantages are its slow operation and its unsuitability for any application that requires throttling or flow control.
The decision to use a PTFE-lined gate valve hinges on a single question: Is your primary goal reliable, on/off isolation in a corrosive service where speed is not a factor? If so, it is an excellent choice. If you need flow control or quick action, you must consider a different valve type entirely.

The Core Advantage: Combining Sealing with Chemical Inertness
The value of a PTFE-lined gate valve comes from pairing a time-tested mechanical design with a highly resilient modern polymer. This creates a valve specialized for very specific, demanding conditions.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
The defining feature is the PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) lining. This chemically inert fluoropolymer isolates all wetted parts of the valve from the process media.
This provides exceptional protection against a wide range of aggressive substances, including strong acids, alkalis, and oxidants, preventing corrosion of the base valve body (typically cast or ductile iron).
Positive, Bubble-Tight Shut-Off
Gate valves are designed for one primary purpose: stopping flow completely. They use a flat gate that slides down to press firmly and evenly against the valve seat.
When properly closed, this design provides a "positive shut-off," meaning it is highly effective at preventing leaks, often achieving zero-leakage performance for on/off isolation tasks.
Bidirectional Sealing
The symmetric design of a gate valve allows it to seal effectively against pressure from either the upstream or downstream direction.
This is a key advantage in systems where the direction of pressure or flow might reverse, ensuring reliable isolation regardless of system dynamics.
High Purity and Non-Contamination
PTFE has excellent non-stick properties. This prevents media from adhering to the valve's internal surfaces.
This feature is critical in pharmaceutical, food, or high-purity chemical applications where preventing media buildup, contamination, and bacterial growth is paramount.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
The strengths of the gate valve design are also the source of its significant limitations. These trade-offs make it entirely unsuitable for certain applications.
Slow Operation and High Torque
Gate valves are multi-turn valves. Opening or closing one requires turning a handwheel many times to slowly raise or lower the gate.
This makes them inherently slow to operate and unsuitable for emergency shut-down (ESD) systems or any process that requires rapid changes in flow. The friction of the PTFE-on-PTFE sealing can sometimes increase the torque required for actuation.
Not Suitable for Throttling
A gate valve must only be used in the fully open or fully closed position. Using it in a partially open state for "throttling" or regulating flow is a critical mistake.
When partially open, the high-velocity flow creates turbulence and chatter, which will cause severe vibration and rapidly erode the soft PTFE lining and the gate itself, leading to valve failure.
Potential for Lining Damage
The sliding action of the gate against the seat can, over many cycles, cause wear and abrasion on the PTFE lining. This is especially true if the media contains suspended solids.
Furthermore, the lining can be susceptible to damage from mechanical stress, excessive pressure, or thermal shock, which could compromise its integrity and expose the valve body to the corrosive media.
Gate Valve vs. Other Lined Valves
The most common error is choosing a valve based on the lining material alone. You must match the valve type to the operational need.
For On/Off Isolation (No Throttling)
A PTFE-lined gate valve is ideal for on/off isolation where slow operation is acceptable and a positive, bubble-tight seal is the top priority.
A PTFE-lined ball valve also provides excellent on/off isolation but does so with a quick, quarter-turn action. It is often preferred for smaller line sizes and when faster operation is needed.
For Flow Control (Throttling)
A PTFE-lined butterfly valve is a common choice for both on/off and throttling services. It is quick-acting, lighter, and often more cost-effective than a gate valve, but its sealing capability may not be as robust in high-pressure applications.
A PTFE-lined globe valve is the superior design for precise flow regulation but typically has a lower flow capacity (higher pressure drop) and is more expensive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection must be driven by the operational requirements of your system, not just the chemical compatibility.
- If your primary focus is absolute, bubble-tight isolation in a highly corrosive line: The PTFE-lined gate valve is a strong candidate, provided you do not need fast operation or throttling.
- If your primary focus is quick shut-off or flow control (throttling): You must look at other options like a PTFE-lined butterfly valve (for general control) or a globe valve (for precision control).
- If your primary focus is balancing cost and operational flexibility: A PTFE-lined butterfly valve often presents the best all-around choice for general-purpose corrosive services that may require some throttling.
Ultimately, choosing the right valve means matching the fundamental design of the valve itself to the specific job it needs to do.
Summary Table:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Unmatched chemical resistance (acids, alkalis) | Slow operation, not for quick shut-off |
| Positive, bubble-tight shut-off | Unsuitable for throttling/flow control |
| Bidirectional sealing | Potential for PTFE lining wear/damage |
| High purity, non-contaminating | High torque required for operation |
Need a reliable, corrosion-resistant valve for your application?
PTFE-lined gate valves are ideal for achieving a positive, bubble-tight seal in highly corrosive environments where slow operation is acceptable. If your primary goal is reliable on/off isolation in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors, KINTEK can help.
We specialize in the precision manufacturing of high-quality PTFE components, including custom valve solutions. From prototypes to high-volume orders, we ensure your components meet the exact demands of your application.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a custom solution quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- How do Teflon bellow mechanical seals contribute to environmental protection in pulp and paper mills? Prevent Hazardous Leaks
- How do PTFE envelope gaskets address the limitations of pure PTFE gaskets? Enhance Sealing Performance
- How do PTFE encapsulated O-rings compare to solid PTFE O-rings? Choose the Right Seal for Your Application
- What is the thermal shock resistance of PTFE lined pipes? Engineered for Extreme Temperature Cycling
- Are PTFE diaphragms suitable for all chemical environments? The Critical Limits You Must Know
- Why are PTFE gaskets popular in various industries? Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Reliability
- What factors should be considered when selecting PTFE seals? Ensure Perfect Sealing for Your Critical Applications
- What are the advantages of using PTFE filled compounds? Enhance Wear, Strength & Performance



















