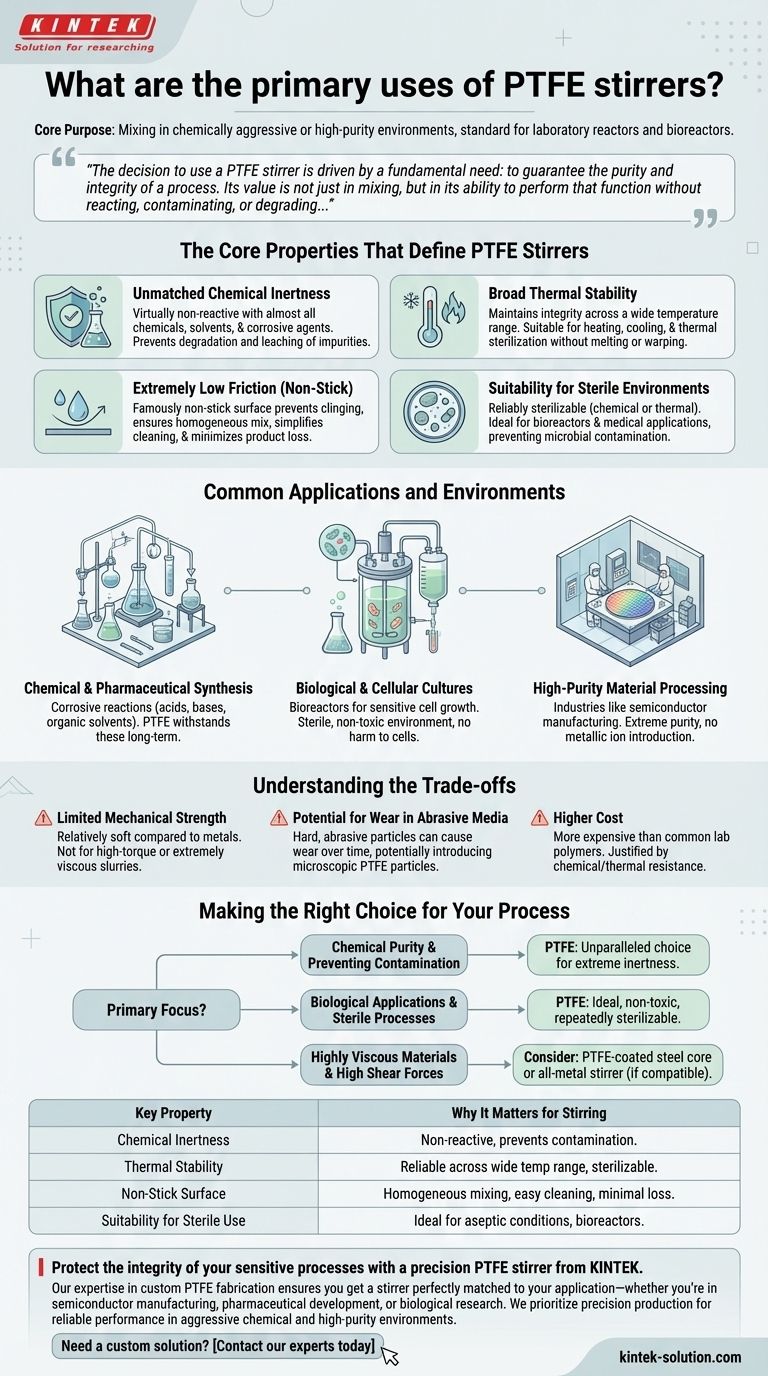
At their core, PTFE stirrers are used for mixing solutions in chemically aggressive or high-purity environments. They are the standard choice for stirring inside glass laboratory reactors and bioreactors because their unique material properties ensure the stirrer itself does not interfere with the chemical or biological process.
The decision to use a PTFE stirrer is driven by a fundamental need: to guarantee the purity and integrity of a process. Its value is not just in mixing, but in its ability to perform that function without reacting, contaminating, or degrading, even under extreme chemical and thermal conditions.
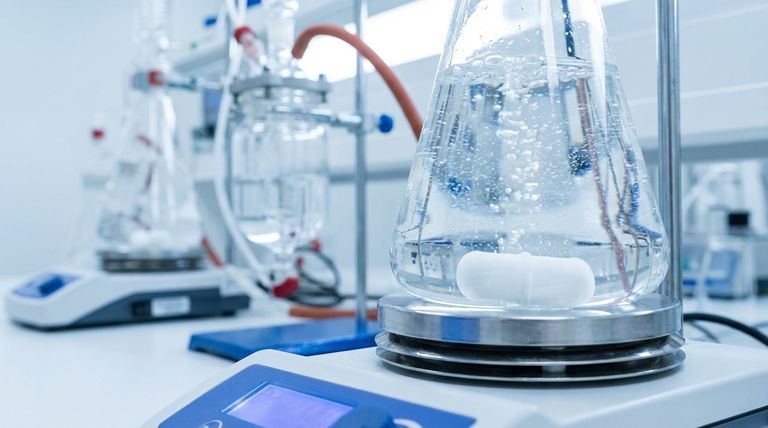

The Core Properties That Define PTFE Stirrers
The effectiveness of a PTFE stirrer is not an accident; it is a direct result of the inherent characteristics of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). These properties make it uniquely suited for sensitive laboratory and industrial work.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually non-reactive with almost all chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This is its most critical feature for stirring applications.
This inertness prevents the stirrer from degrading and leaching impurities into the mixture, which is essential for ensuring the validity of an experiment or the purity of a final product.
Broad Thermal Stability
PTFE maintains its integrity across a very wide range of temperatures.
This allows it to be used reliably in reactions that require significant heating or cooling, without risk of the material melting, warping, or breaking down. It also means it can be thermally sterilized.
Extremely Low Friction (Non-Stick Surface)
The surface of PTFE is famously non-stick, exhibiting one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid.
In stirring, this prevents the material being mixed from clinging to the stirrer shaft or blades. This ensures a more homogeneous mix, simplifies cleaning, and minimizes product loss.
Suitability for Sterile Environments
PTFE can be reliably sterilized through either chemical or thermal methods without compromising its structure.
Combined with its non-reactive nature, this makes it an ideal material for use in bioreactors and medical applications where preventing microbial contamination is paramount.
Common Applications and Environments
While the function is always "mixing," the context in which PTFE stirrers are used highlights their importance.
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Synthesis
In research labs and industrial chemical plants, reactions often involve highly corrosive acids, bases, or organic solvents. PTFE is one of the few materials that can withstand these environments long-term.
Biological and Cellular Cultures
Bioreactors used for growing sensitive cell cultures demand a sterile, non-toxic environment. PTFE stirrers ensure that the mixing mechanism does not harm the cells or introduce contaminants into the growth medium.
High-Purity Material Processing
Industries like semiconductor manufacturing require extreme purity. PTFE is used for handling and mixing aggressive chemicals used in wafer fabrication because it won't introduce the metallic ions or other contaminants that a metal stirrer could.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While exceptionally useful, PTFE is not the solution for every mixing challenge. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Limited Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material compared to metals like stainless steel. It is not suitable for high-torque applications or mixing extremely viscous, thick slurries that would cause the stirrer to bend or deform.
Potential for Wear in Abrasive Media
If the mixture contains hard, abrasive particles, the softness of PTFE can lead to wear over time. This could potentially introduce microscopic PTFE particles into the solution.
Higher Cost
PTFE is generally more expensive than other common lab polymers like polypropylene or polyethylene. Its use is justified when its specific properties—primarily chemical and thermal resistance—are non-negotiable requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct stirrer material is a critical decision that directly impacts the outcome of your work.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity and preventing reaction contamination: PTFE is the unparalleled choice due to its extreme inertness with nearly all chemicals.
- If your primary focus is biological applications or sterile processes: PTFE is ideal because it is non-toxic and can be repeatedly sterilized without degradation.
- If you are mixing highly viscous materials or require high shear forces: Consider a PTFE-coated steel core stirrer for added strength, or an all-metal stirrer if chemical compatibility allows.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE stirrer is a strategic decision to eliminate a potential variable and protect the integrity of your work.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters for Stirring |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Non-reactive with virtually all chemicals, prevents contamination. |
| Thermal Stability | Performs reliably across a wide temperature range and can be sterilized. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Ensures homogeneous mixing, easy cleaning, and minimal product loss. |
| Suitability for Sterile Use | Ideal for bioreactors and medical applications requiring aseptic conditions. |
Protect the integrity of your sensitive processes with a precision PTFE stirrer from KINTEK.
Our expertise in custom PTFE fabrication ensures you get a stirrer perfectly matched to your application—whether you're in semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceutical development, or biological research. We prioritize precision production for reliable performance in aggressive chemical and high-purity environments.
Need a custom solution? Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Magnetic Stirring Bar
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PTFE stirrers? Ensure Chemical Purity and Protect Your Labware
- In which industries is PTFE commonly used? Key Applications for Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the temperature range and mechanical properties of PTFE? The Ultimate Guide to Performance
- How is PTFE used in laboratory stirrer bars? Ensuring Chemical Inertness and Purity in Mixing
- What are the primary applications of Teflon? Leverage Its Unique Properties for Your Industry



















