At their core, PTFE/silicone septa are high-performance seals used to cap sample vials in analytical chemistry. Their primary use is in gas and liquid chromatography (GC/LC), where they form a clean, impenetrable, yet pierceable barrier. This dual-layer design ensures that a sample remains pure and contained until the moment of analysis.
The central challenge in chromatography is maintaining absolute sample integrity. PTFE/silicone septa solve this by combining the chemical inertness of PTFE with the resealable elasticity of silicone, creating a barrier that protects the sample without contaminating it.

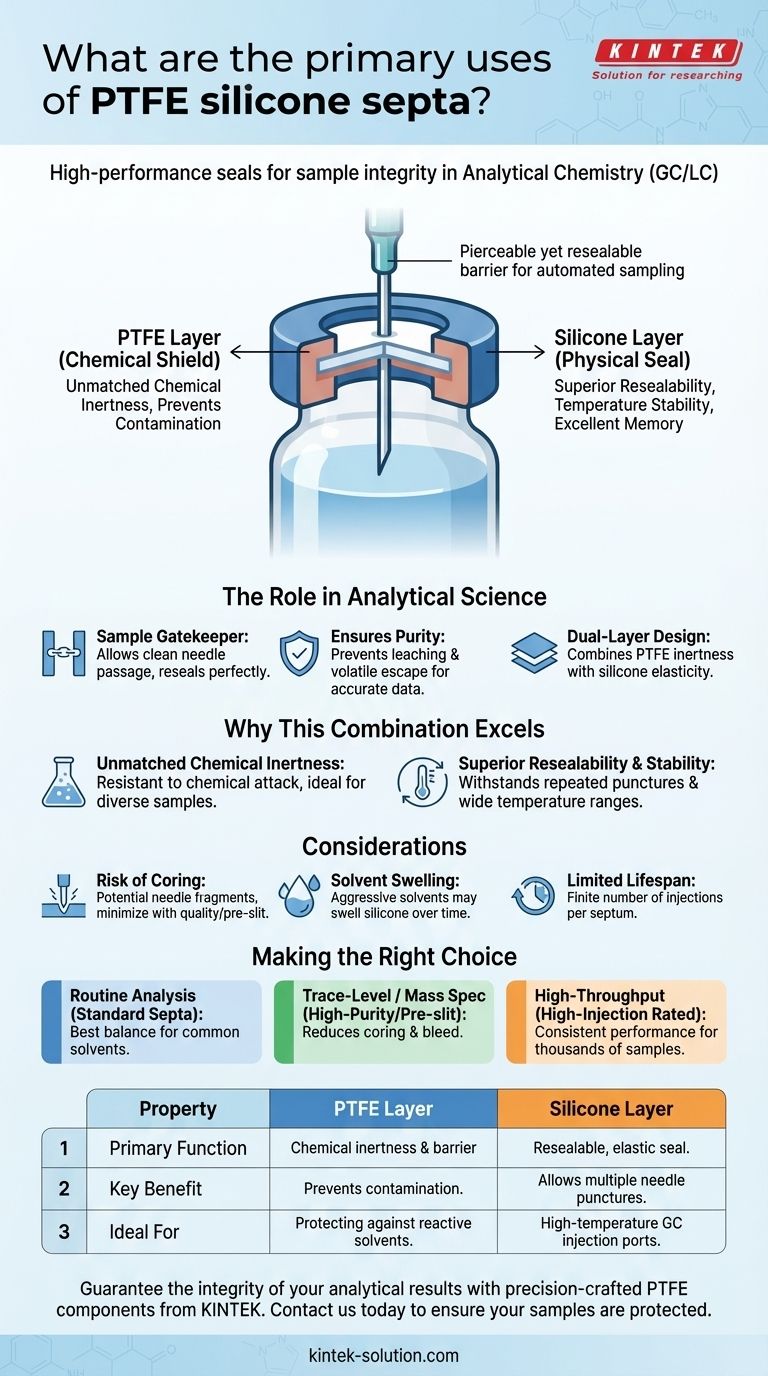
The Role of a Septum in Analytical Science
A septum acts as a gatekeeper for the sample vial. It must allow an autosampler needle to pass through cleanly and then reseal perfectly upon withdrawal. Failure on either front compromises the entire analysis.
The Two-Layer System: A Perfect Partnership
The genius of these septa lies in their composite structure. Each material is chosen to perform a distinct and critical function.
The PTFE Layer (The Chemical Shield): This ultra-thin layer faces inward, in direct contact with the sample. PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is used because it is one of the most chemically non-reactive substances known. Its job is to prevent any interaction between the sample and the much more reactive silicone layer.
The Silicone Layer (The Physical Seal): This much thicker layer provides the mechanical properties. Silicone is a flexible elastomer that is easy to pierce with a needle. Crucially, it has excellent "memory," allowing it to reseal tightly after the needle is removed, preventing sample evaporation and contamination from the outside air.
Ensuring Purity in Chromatography
In both GC and LC, an automated needle pierces the septum to draw a precise volume of the sample for injection into the instrument.
The septum ensures that nothing leaches into the sample before analysis and that no part of the volatile sample escapes. This guarantees that the data generated by the instrument is a true and accurate representation of the original sample.
Why This Specific Combination Excels
The widespread adoption of PTFE/silicone septa is a direct result of the unique properties each material brings to the table.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
As noted in its use for lining chemical tanks and handling corrosive materials, PTFE is exceptionally resistant to chemical attack. This makes it ideal for protecting a wide array of analytical samples, from environmental pollutants to pharmaceutical compounds, ensuring the septum itself does not become a source of contamination.
Superior Resealability and Temperature Stability
Silicone's ability to withstand repeated punctures is vital for labs running many samples or performing multiple injections from the same vial. Furthermore, it remains stable and flexible across a wide temperature range, a critical requirement for the high-temperature injection ports used in gas chromatography.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, no component is perfect. Awareness of potential failure modes is key to preventing analytical errors.
The Risk of Coring
"Coring" occurs when the needle punches out a microscopic piece of the septum instead of parting the material. This small fragment of PTFE and silicone can clog the syringe needle or be injected along with the sample, creating spurious peaks in the analytical results. High-quality or pre-slit septa are designed to minimize this risk.
Solvent Swelling
Although the PTFE layer provides excellent protection, aggressive organic solvents can, over time, migrate into the silicone layer. This can cause the silicone to swell, compromising the integrity of the seal and potentially leading to leaks.
Limited Lifespan After Puncture
While septa are designed to reseal, each puncture creates a small, permanent pathway. For analyses requiring absolute airtightness over long periods (such as headspace analysis), a punctured septum is a point of potential failure. Most are designed for a limited number of injections.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct septum is a critical decision that directly impacts data quality. Your choice should be guided by the specific demands of your analysis.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis with common solvents: Standard PTFE/silicone septa offer the best balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is trace-level analysis or mass spectrometry: Opt for higher-purity, bonded, or pre-slit septa to drastically reduce the risk of coring and chemical bleed.
- If your primary focus is automation and high-throughput screening: Choose septa specifically rated for the maximum number of injections to ensure consistent performance across thousands of samples.
By understanding the distinct roles of each material layer, you can confidently select the septum that guarantees the integrity of your analytical work.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Layer | Silicone Layer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Chemical inertness & barrier | Resealable, elastic seal |
| Key Benefit | Prevents sample contamination | Allows multiple needle punctures |
| Ideal For | Protecting against reactive solvents | High-temperature GC injection ports |
Guarantee the integrity of your analytical results with precision-crafted PTFE components from KINTEK.
Our PTFE/silicone septa are engineered for superior performance in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. We prioritize precision manufacturing and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact specifications.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and ensure your samples are protected with the highest quality seals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PTFE shovels over metal shovels? Precision Handling for Sensitive Materials
- What are the benefits of PTFE shovels being antistatic? Prevent Fires & Protect Sensitive Electronics
- Why should PTFE plugs not be used for long-term storage of liquids that attack glass? Avoid Dangerous Seal Failure
- What are the key benefits of PTFE silicone septa in pharmaceutical research? Ensure Sample Integrity & Data Accuracy
- What are the benefits of colored PTFE caps? Boost Lab Safety and Efficiency with Visual Coding
- What are the characteristics of wide mouth PTFE laboratory bottles? Engineered for Extreme Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the key features of PTFE-lined bottle caps? Ensure Chemical Integrity and Purity for Your Samples
- In what ways are PTFE silicone septas versatile for pharmaceutical applications? Ensuring Sample Integrity from Discovery to QC



















