From deep space to commercial kitchens, the use of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is remarkably widespread. The primary industrial sectors that utilize PTFE materials are chemical processing, electronics, aerospace, automotive, and food and beverage processing, each leveraging the material's unique combination of properties to solve critical engineering challenges.
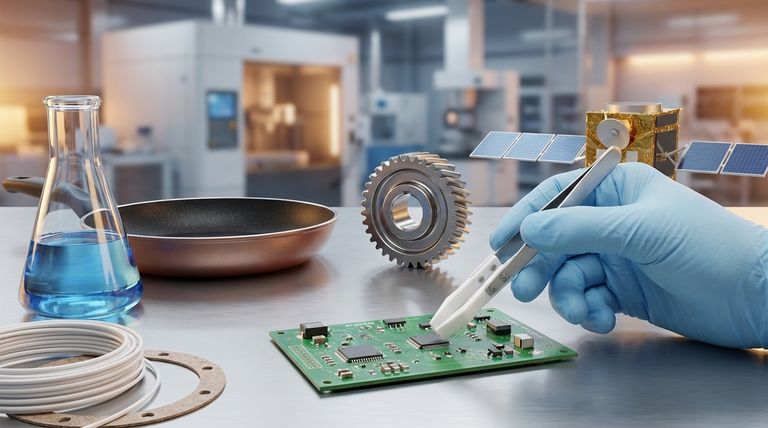
The core reason for PTFE's broad adoption is not a single feature, but its rare combination of four distinct characteristics: extreme chemical inertness, a very low friction coefficient, high-temperature stability, and excellent electrical insulation. Industries don't just use "PTFE"; they leverage a specific one of these properties to solve a problem that few other materials can address.
The Four Pillars of PTFE's Industrial Value
To understand why PTFE is so ubiquitous, we must look beyond a simple list of industries and examine the fundamental properties that make it so valuable. Different sectors prioritize different characteristics.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most non-reactive materials known, resisting virtually all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it an indispensable material for handling corrosive substances.
This property is the primary reason for its heavy use in the chemical processing, oil and gas, and pharmaceutical industries for applications like gaskets, seals, and tank linings.
Extreme Low Friction & Non-Stick Properties
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This inherent slipperiness is perfect for applications where smooth movement is critical.
The automotive sector uses it for friction-reducing components like bearings and seals. The food and beverage industry relies on its non-stick quality for hygienic, easy-to-clean processing surfaces.
High-Temperature Stability
PTFE can operate continuously at high temperatures (up to 260°C or 500°F) without degrading, a trait that sets it apart from most other plastics.
This stability is crucial for the aerospace industry, where it is used for seals and components that must withstand extreme thermal cycling. It's also vital in demanding automotive and industrial applications.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with a very high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand high voltages without breaking down. Its performance is also stable across a wide range of frequencies.
This makes it the material of choice in the electronics industry for high-performance applications like wire and cable insulation, connectors, and printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Tailoring PTFE for Specific Demands
Not all PTFE is the same. The base polymer is often modified to enhance specific properties, expanding its use into even more demanding applications.
Standard (Virgin) PTFE
This is the pure, unmodified form of the polymer. It offers the best performance in terms of chemical resistance and electrical insulation, making it ideal for the electronics and chemical processing industries.
Filled PTFE
To improve mechanical properties like wear resistance, compressive strength, and creep resistance, fillers such as glass, carbon, or bronze are added to the PTFE base. This makes it suitable for demanding mechanical parts like bearings and seals in the automotive and industrial machinery sectors.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
This form of PTFE is stretched to create a microporous structure of fibers. The resulting material is strong yet pliable, making it an excellent gasketing material for sealing uneven surfaces in chemical plants and industrial equipment. It is also the basis for waterproof, breathable fabrics used in the textile industry.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its remarkable capabilities, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to engineering plastics like nylon or PEEK, standard PTFE is relatively soft and has poor wear resistance. It can deform under a constant load, a phenomenon known as "creep." This is precisely why filled grades were developed.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion. This means its dimensions can change significantly with temperature, a factor that must be accounted for when designing components with tight tolerances.
Higher Cost
PTFE is a specialty polymer, and its manufacturing process makes it more expensive than common plastics like polypropylene or polyethylene. Its use is justified only when its unique performance characteristics are a necessity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct type of PTFE depends entirely on the primary engineering challenge you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance: Standard or expanded PTFE is the ideal choice for gaskets, seals, and linings in harsh chemical environments.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: High-purity, virgin PTFE is essential for high-frequency wiring, connectors, and circuit boards.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: A filled PTFE grade, often with carbon or bronze additives, provides the durability needed for bearings and dynamic seals.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sealing: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) offers superior conformity and stability for critical gasketing in aerospace and industrial plants.
Ultimately, PTFE's value lies not in being a single solution, but in serving as a versatile platform material that can be adapted to the world's most demanding industrial environments.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Industrial Sectors | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Chemical Processing, Oil & Gas, Pharmaceutical | Gaskets, Seals, Tank Linings |
| Low Friction / Non-Stick | Automotive, Food & Beverage | Bearings, Seals, Processing Surfaces |
| High-Temperature Stability | Aerospace, Automotive | Seals, Components for Thermal Cycling |
| Electrical Insulation | Electronics | Wire/Cable Insulation, Connectors, PCBs |
Need a high-performance PTFE component tailored to your specific challenge?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and custom parts—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require the ultimate chemical resistance of virgin PTFE, the enhanced durability of filled PTFE, or the superior sealing capabilities of ePTFE, we provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise in PTFE can solve your most demanding application requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















