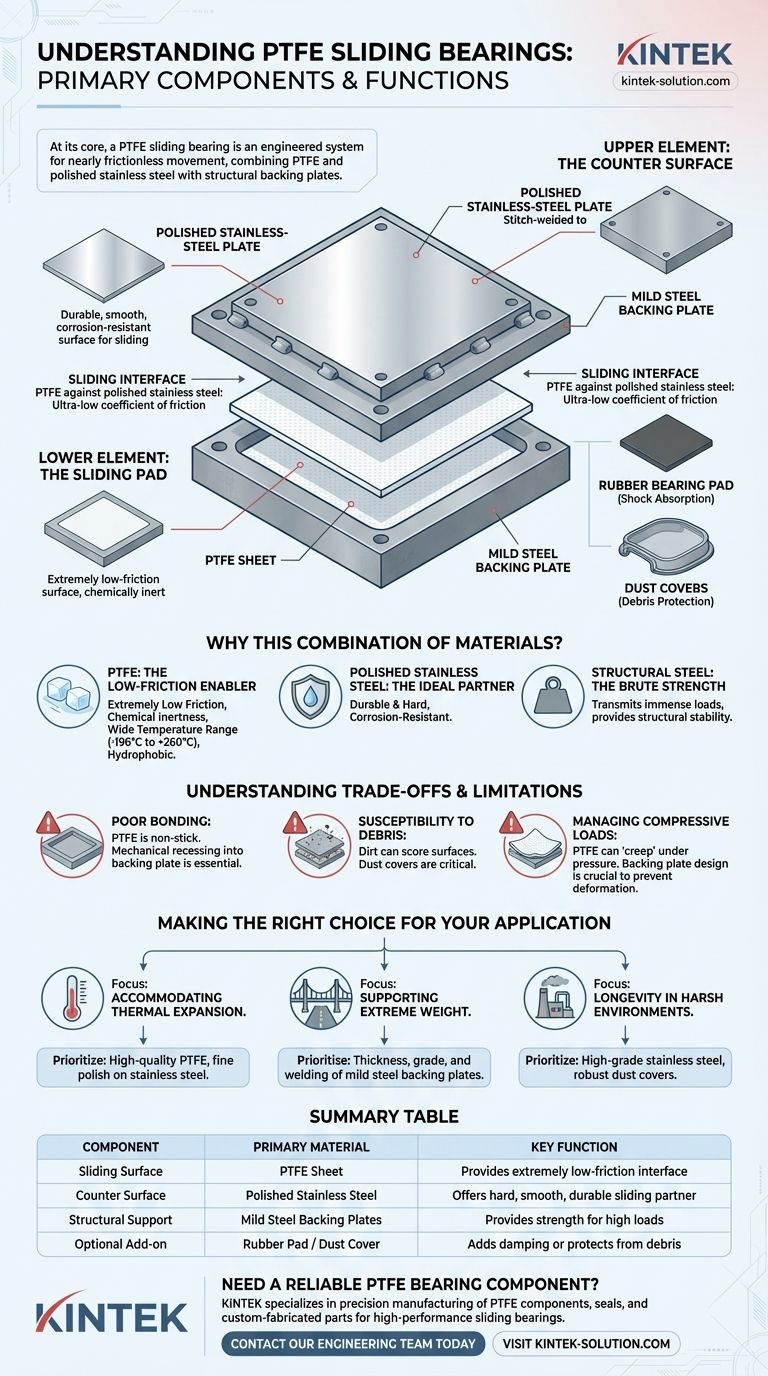
At its core, a PTFE sliding bearing is an engineered system composed of two primary sliding surfaces: a PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) plate and a highly polished stainless-steel plate. These are paired with structural backing plates that provide the necessary strength and stability to handle significant loads, creating an assembly that allows for nearly frictionless movement.
The critical insight is that a PTFE bearing is not just a piece of plastic; it is a multi-component assembly where the PTFE provides the low-friction surface, the stainless steel offers a durable counter-surface, and steel backing plates deliver the structural integrity required for high-load applications.

Deconstructing the Bearing Assembly
To understand how these bearings function, we must examine each component's specific role. The assembly is typically divided into an upper and lower element that move relative to each other.
The Sliding Interface: PTFE & Stainless Steel
This is the heart of the bearing. The combination of PTFE sliding against polished stainless steel produces one of the lowest coefficients of friction between any two solid materials. This allows massive structures to move or expand with minimal resistance.
The Lower Element: The PTFE Pad
The lower element consists of the PTFE sheet itself. Because PTFE is a relatively soft material, it requires a rigid support base. It is typically bonded into a recessed pocket within a thicker mild steel backing plate, which prevents it from deforming or moving under extreme pressure.
The Upper Element: The Stainless Steel Plate
The upper element features the polished stainless-steel plate. This thin sheet of stainless steel provides the hard, smooth, and corrosion-resistant surface for the PTFE to slide against. It is typically stitch-welded to its own mild steel backing plate for long-term stability and structural support.
Ancillary Components for Performance
More complex assemblies may include additional parts. A rubber bearing pad can be incorporated for shock absorption and vibration damping. Dust covers are often used to protect the sliding surfaces from debris, which could otherwise compromise performance and cause damage.
Why This Specific Combination of Materials?
The selection of these materials is a deliberate engineering choice driven by their unique and complementary properties. Each material solves a specific part of the overall problem.
The Unmatched Properties of PTFE
PTFE is the key enabler of the bearing's function. It possesses an extraordinary combination of characteristics:
- Extremely Low Friction: Often compared to wet ice on wet ice, it allows for effortless sliding.
- Chemical Inertness: It is highly resistant to virtually all industrial chemicals, acids, and solvents.
- Wide Temperature Range: It remains effective in temperatures from -196°C to +260°C (-321°F to +500°F).
- Hydrophobic: It does not absorb water, ensuring consistent performance in any weather.
The Role of Polished Stainless Steel
While PTFE is the star, it needs a suitable partner. Polished stainless steel is the ideal counter-surface because it is:
- Durable and Hard: It resists scratching and scoring, maintaining a smooth surface for the PTFE.
- Corrosion-Resistant: It will not rust or degrade when exposed to moisture and the elements.
The Necessity of Structural Steel
The mild steel backing plates provide the brute strength. They are responsible for transmitting the immense loads from the structure (like a bridge or building) through the bearing assembly and into the foundation, all while allowing the low-friction interface to do its job.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, this design is not without its challenges. Understanding them is key to successful implementation.
Poor Bonding Characteristics
One of PTFE's most significant challenges is that it is notoriously difficult to bond to other materials—its non-stick quality works against it here. This is why mechanical solutions, such as recessing the PTFE into a precisely machined pocket in the backing plate, are essential for a reliable connection.
Susceptibility to Debris
The extremely low friction between the plates can be compromised if dirt, sand, or other abrasive particles get between them. This can score the surfaces and impede movement. For this reason, protecting the bearing with dust covers or seals is critical in many applications.
Managing Compressive Loads
PTFE is not a structural material and can deform (a process known as "creep") under sustained, high pressure. The design of the steel backing plates is crucial for containing the PTFE and distributing the load evenly to prevent this.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting and designing a PTFE bearing assembly depends entirely on the project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is accommodating thermal expansion: The quality of the PTFE and the fine polish on the stainless-steel plate are paramount to ensure smooth, repeatable movement.
- If your primary focus is supporting extreme weight: The thickness, grade, and welding of the mild steel backing plates are the most critical factors for ensuring structural integrity.
- If your primary focus is longevity in a harsh environment: Prioritize high-grade stainless steel for corrosion resistance and include robust dust covers to protect the sliding surfaces.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of a PTFE bearing lies in how its individual components work together as a unified system to solve a specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Material | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Sliding Surface | PTFE Sheet | Provides an extremely low-friction interface |
| Counter Surface | Polished Stainless Steel | Offers a hard, smooth, and durable sliding partner |
| Structural Support | Mild Steel Backing Plates | Provides strength and stability to handle high loads |
| Optional Add-on | Rubber Pad / Dust Cover | Adds vibration damping or protects from debris |
Need a reliable PTFE bearing component for your project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including the critical seals, liners, and custom-fabricated parts that form the core of high-performance sliding bearings. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors, our expertise ensures your components meet the exacting standards for low friction, chemical resistance, and structural integrity.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE used for thermal and electrical insulation? Unmatched Stability in Extreme Conditions
- Why is machined PTFE popular in the medical field? Unmatched Biocompatibility & Precision
- What does it mean for Teflon coatings to be non-wetting? Unlock Superior Non-Stick & Chemical Resistance
- Can you provide an example of a large-scale PTFE application? The Metrodome's 20-Acre PTFE Roof
- What can happen if excess pressure is applied during PTFE machining? Avoid Costly Part Failure and Deformation
- What makes machined PTFE suitable for industrial applications? Unmatched Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the key properties of PTFE guide strips? Ensure Low-Friction, High-Temp Performance
- What chemical resistance properties does PTFE bellow seal possess? Unmatched Protection Against Corrosive Media



















