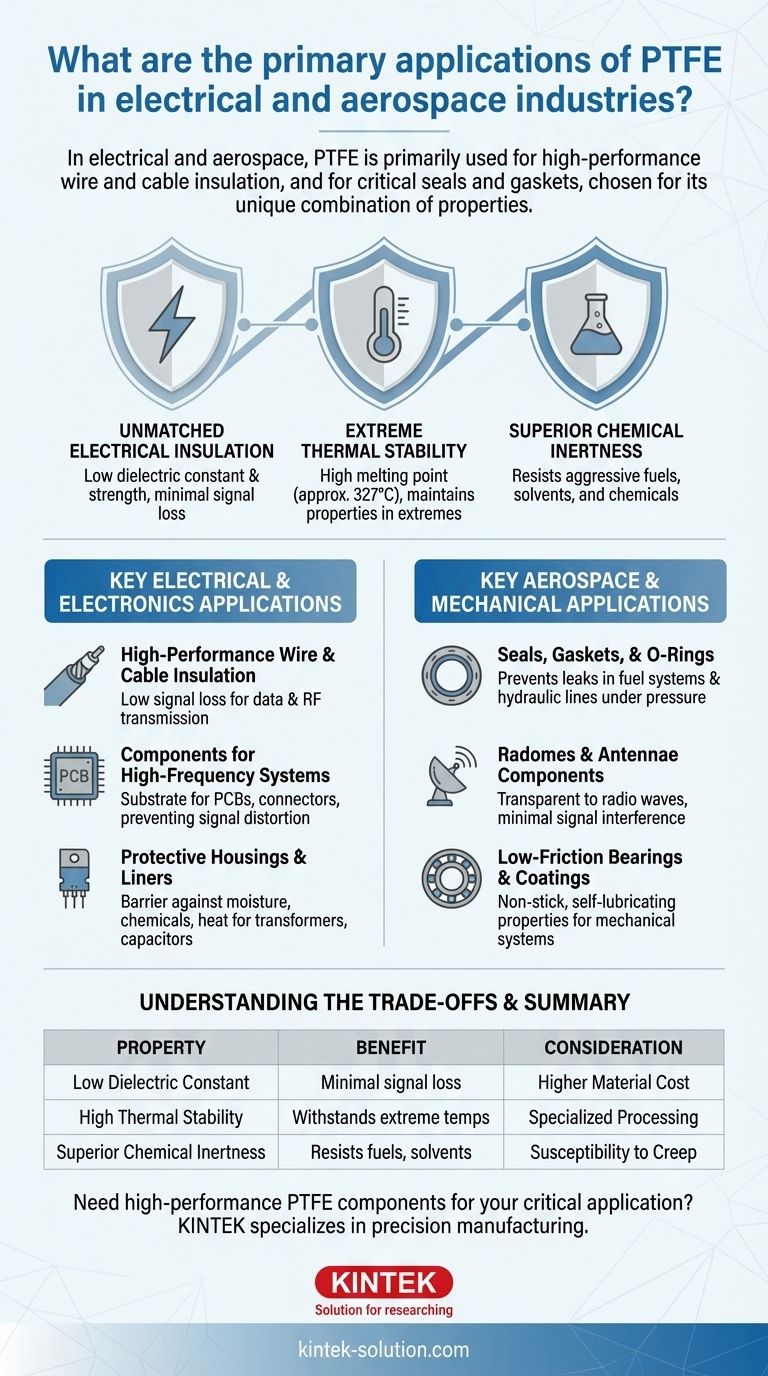
In the electrical and aerospace industries, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is primarily used for high-performance wire and cable insulation, especially in coaxial cables, and for critical seals and gaskets. Its selection is driven by its exceptional dielectric properties for handling high-frequency signals and its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive chemicals, making it a substitute for materials like polyethylene in demanding environments.
PTFE is not chosen for a single benefit, but for its unique combination of properties. Its value lies in its ability to simultaneously provide elite electrical insulation, thermal stability, and chemical inertness in applications where failure is not an option.

The Foundation: Why PTFE Is a Benchmark Material
PTFE’s dominance in critical systems stems from a trio of core properties that make it exceptionally reliable in harsh operating conditions.
Unmatched Electrical Insulation
PTFE has an extremely low dielectric constant and low dissipation factor. This means it allows electromagnetic fields to pass through with minimal energy loss, which is critical for maintaining signal integrity in high-frequency communications.
Its high dielectric strength also allows it to insulate high voltages without breaking down, preventing short circuits and ensuring system safety.
Extreme Thermal Stability
PTFE has a very high melting point (around 327°C or 621°F) and maintains its properties across a wide range of operating temperatures.
This thermal resilience is essential in aerospace applications, where components can be exposed to everything from the cold of high altitudes to the intense heat of engine compartments.
Superior Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most chemically resistant polymers known. It is virtually immune to degradation from fuels, hydraulic fluids, solvents, and other aggressive chemicals found in aerospace and industrial environments.
This inertness ensures the longevity and reliability of components like seals and wire jackets that are in constant contact with corrosive substances.
Key Electrical and Electronics Applications
Nearly 50% of all PTFE is used for wiring in aerospace and computer systems, underscoring its importance in this sector.
High-Performance Wire and Cable Insulation
PTFE is the material of choice for the insulation and jacketing of hook-up wires and coaxial cables. Its low signal loss is vital for transmitting data and radio frequency (RF) signals clearly and efficiently over long distances.
Components for High-Frequency Systems
In printed circuit boards (PCBs), connectors, and insulators designed for microwave and RF frequencies, PTFE is used as the substrate material. Its stable dielectric properties prevent signal distortion and crosstalk between circuits.
Protective Housings and Liners
PTFE is used to insulate and protect a variety of electronic components, including transformers, capacitors, and motors. It acts as a barrier against moisture, chemicals, and heat, extending the operational life of the device.
Key Aerospace and Mechanical Applications
Beyond pure electronics, PTFE's mechanical and chemical properties make it indispensable for the physical integrity of aerospace systems.
Seals, Gaskets, and O-Rings
Due to its chemical inertness and wide temperature range, PTFE is a primary material for seals and gaskets in fuel systems, hydraulic lines, and valve bodies. It prevents leaks under extreme pressure and temperature fluctuations.
Radomes and Antennae Components
A radome is a structural, weatherproof enclosure that protects a radar antenna. PTFE is an ideal material because it is transparent to radio waves, allowing signals to pass through with minimal interference or loss.
Low-Friction Bearings and Coatings
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction, giving it "non-stick" and self-lubricating properties. It is used for bearings and coatings in mechanical systems where traditional liquid lubricants would fail, burn off, or contaminate the environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, PTFE is a premium material with specific considerations that must be balanced against its performance benefits.
Higher Material Cost
PTFE is significantly more expensive than commodity plastics like polyethylene. Its use is typically justified only in applications where its unique performance characteristics are a strict requirement.
Specialized Processing
Fabricating parts from PTFE can be more complex and require specialized molding and machining techniques compared to more common polymers. This can add to the overall cost and complexity of manufacturing.
Susceptibility to Creep (Cold Flow)
Under a sustained mechanical load, PTFE can slowly deform over time, a phenomenon known as creep or cold flow. This must be accounted for in the design of structural components, particularly in seals and bearings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires aligning its properties with your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is signal integrity at high frequencies: PTFE is the benchmark for coaxial cables, connectors, and PCBs due to its exceptionally low dielectric constant.
- If your primary focus is reliability in extreme temperatures: PTFE's high melting point and thermal stability make it essential for wiring and seals in engines and other high-heat aerospace systems.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: PTFE is the definitive choice for seals, gaskets, and liners exposed to aggressive fuels, oils, and hydraulic fluids.
Ultimately, PTFE is the material of choice for critical applications where performance and reliability justify the investment.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit in Electrical & Aerospace Applications |
|---|---|
| Low Dielectric Constant | Minimal signal loss in high-frequency cables and PCBs |
| High Thermal Stability | Withstands extreme temperatures from -200°C to 260°C+ |
| Superior Chemical Inertness | Resists fuels, solvents, and hydraulic fluids |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Self-lubricating for bearings and coatings |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your critical application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the stringent demands of electrical and aerospace systems, and our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure you get the reliability and performance your project requires.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and how our PTFE solutions can enhance your product's performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications



















