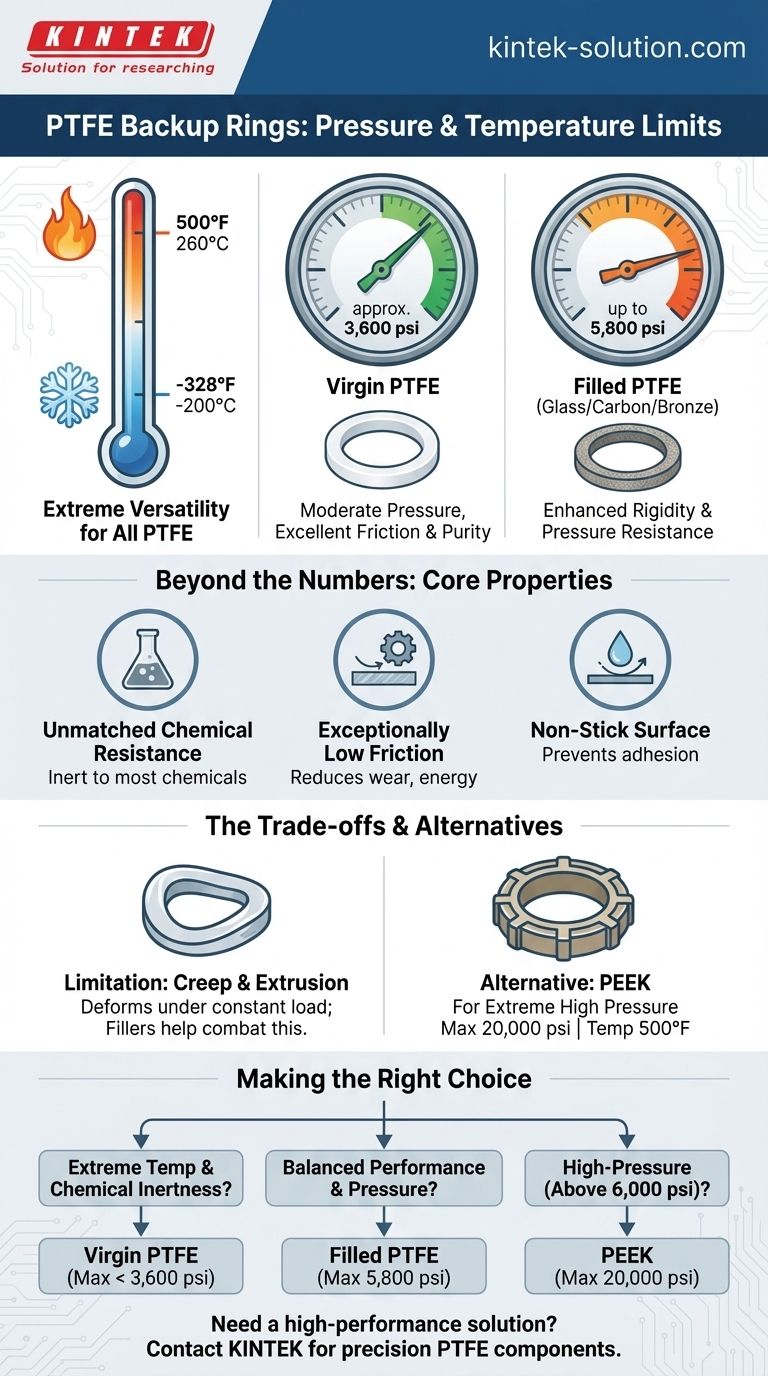
For PTFE backup rings, the key limits depend on the specific grade. Filled PTFE (with glass, carbon, or bronze) can handle pressures up to 5,800 psi, while virgin PTFE is limited to approximately 3,600 psi. The material excels across a vast temperature range, typically from -328°F to 500°F (-200°C to 260°C).
The central takeaway is that PTFE is an elite choice for applications requiring a wide temperature range and chemical inertness, but its pressure capacity is moderate. The choice between virgin and filled PTFE is a direct trade-off between cost and the need for higher pressure resistance.

Deconstructing the Operating Limits of PTFE
To correctly specify a PTFE backup ring, you must understand how its properties align with your application's demands. The limits are not just numbers; they tell the story of the material's strengths and weaknesses.
Temperature Range: Extreme Versatility
PTFE is renowned for its exceptional thermal stability. It functions reliably in cryogenic conditions as low as -328°F (-200°C) without becoming brittle.
At the other extreme, it maintains its integrity in high-heat environments up to 500°F (260°C), making it suitable for a wider range of applications than many common elastomers.
Pressure Capacity: The Critical Distinction
A backup ring's primary job is to prevent the main O-ring from extruding under pressure. Here, the type of PTFE is the single most important factor.
Virgin PTFE, while chemically pure and excellent for friction, is a relatively soft material. Its pressure limit is around 3,600 psi.
Filled PTFE contains additives like glass, carbon, or bronze. These fillers significantly increase the material's rigidity and resistance to deformation, raising the pressure limit to 5,800 psi.
Beyond the Numbers: Core Properties of PTFE
The temperature and pressure ratings are only part of the equation. PTFE's unique combination of other properties often makes it the only viable choice for demanding environments.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is nearly inert, resisting almost all industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This makes it essential for seals in aggressive chemical processing or aerospace applications.
Exceptionally Low Friction
With one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, PTFE is ideal for dynamic applications. It reduces wear, prevents stick-slip motion, and lowers the energy needed to actuate components.
Non-Stick Surface
PTFE's non-stick nature prevents substances from adhering to its surface. In sealing applications, this reduces contamination and ensures consistent performance over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
No material is perfect. Acknowledging PTFE's limitations is key to preventing seal failure and ensuring system reliability.
The Primary Limitation: Creep and Extrusion
The inherent weakness of PTFE is creep, or its tendency to slowly deform under a constant load. This is why its pressure ratings are moderate compared to other high-performance polymers.
Fillers are added specifically to combat this tendency, which is why filled grades offer superior pressure performance.
When to Consider an Alternative: The Case for PEEK
For applications that demand performance beyond PTFE's capabilities, other materials must be considered.
PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) is a common alternative for extreme environments. It can handle pressures up to 20,000 psi while operating at a similar maximum temperature of 500°F, making it the clear choice for high-pressure, high-temperature systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct backup ring material is a critical design decision based on your primary operating conditions.
- If your primary focus is an extreme temperature range and chemical inertness: Virgin PTFE is an excellent choice, provided system pressures remain below 3,600 psi.
- If your primary focus is balancing performance and higher pressure: Filled PTFE provides a significant boost in pressure handling (up to 5,800 psi) while retaining PTFE's core benefits.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure performance (above 6,000 psi): You must look beyond PTFE to a more rigid material like PEEK to prevent seal extrusion and failure.
Understanding these material properties empowers you to design a more robust and reliable sealing system.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | Filled PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Max Pressure | 3,600 psi | 5,800 psi |
| Temperature Range | -328°F to 500°F (-200°C to 260°C) | -328°F to 500°F (-200°C to 260°C) |
| Key Characteristic | Chemical Purity, Low Friction | Enhanced Rigidity, Wear Resistance |
Need a high-performance PTFE backup ring for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals and backup rings, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require the chemical inertness of virgin PTFE or the enhanced pressure resistance of a filled grade, our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure you get a solution that meets your exact operational demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE heat press sheets? Ensure Flawless, Non-Stick Heat Transfers
- Does carbon fiber-filled PTFE damage shafts? Ensure Longevity with Proper Material Pairing
- In which industries are PTFE control valves commonly used? Essential for Corrosive & High-Purity Fluids
- How are PTFE bushes manufactured to ensure quality? A Guide to Precision and Reliability
- What makes Teflon bushings suitable for harsh environments? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the mechanical properties of PTFE O-rings? A Guide to Low Friction, Chemical Resistance, and Trade-offs
- What materials are used in the construction of PTFE-lined bearings? A Guide to Their 4-Layer Composite Design
- What are the advantages of using Teflon coatings over liquid lubricants in food processing? Boost Safety & Efficiency



















