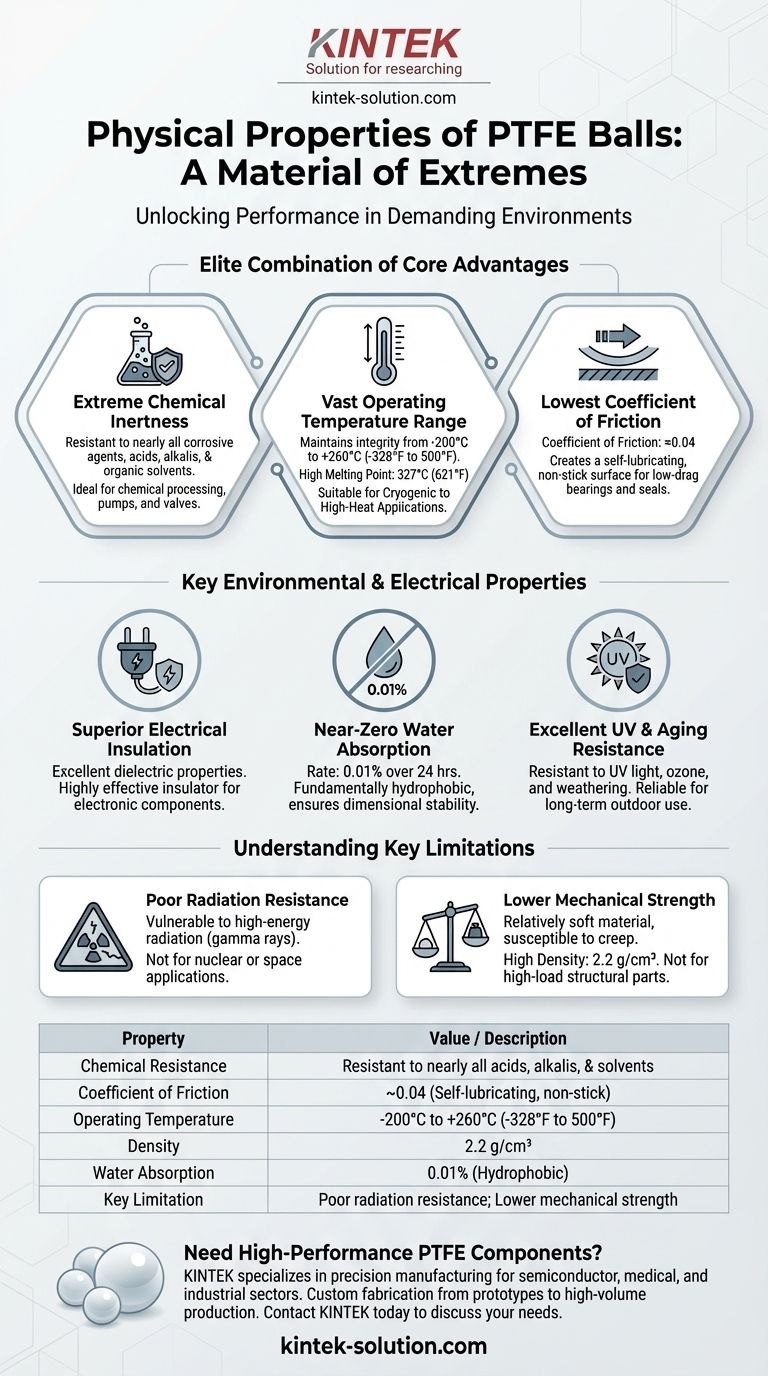
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a material of extremes. The physical properties of PTFE balls include a very high density of 2.2 g/cm³, an extremely low coefficient of friction, exceptional chemical resistance, and a wide operating temperature range. They also exhibit a V0 flammability rating, a limiting oxygen index of 95%, near-zero water absorption (0.01%), and excellent resistance to UV radiation.
While many plastics excel in one area, PTFE's true value lies in its unique combination of three elite properties: near-universal chemical inertness, a massive thermal operating range, and one of the lowest friction coefficients of any solid material. Understanding this combination is key to using it effectively.

Unpacking the Core Advantages
The most sought-after properties of PTFE stem from its unique molecular structure. These characteristics make it a default choice for demanding engineering applications where other materials would quickly fail.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
PTFE offers outstanding resistance to nearly all corrosive agents. This includes strong acids, alkalis, oxidizing agents, and most organic solvents.
This near-total chemical immunity makes PTFE balls ideal for use in pumps, valves, and mixing equipment within chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and laboratory environments.
The only common exceptions to this resistance are molten alkali metals and certain fluorinated media.
A Vast Operating Temperature Range
PTFE maintains its structural integrity and performance across an exceptionally broad temperature spectrum, typically cited from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
Its high melting point of 327°C (621°F) is significantly higher than most conventional plastics, preventing failure in high-temperature applications.
This makes it suitable for everything from cryogenic components to high-temperature seals and bearings.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has an incredibly low coefficient of friction, approximately 0.04. This is one of the lowest values of any known solid material.
This property creates a self-lubricating, non-stick surface. It is the reason PTFE is used for everything from non-stick cookware to low-friction bearings and seals where minimizing drag and wear is critical.
Key Environmental and Electrical Properties
Beyond the primary benefits, several other physical properties broaden the applications for PTFE balls, particularly in electrical and outdoor systems.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE possesses excellent dielectric properties, meaning it is a highly effective electrical insulator.
It resists the flow of electric current, making it a valuable material for components in electronics and electrical equipment where insulation is paramount.
Near-Zero Water Absorption
With a water absorption rate of just 0.01% over 24 hours, PTFE is fundamentally hydrophobic. It repels water and does not swell or degrade in moist environments.
This ensures dimensional stability and consistent performance in fluid handling systems, marine applications, and high-humidity conditions.
Excellent UV and Aging Resistance
PTFE is highly resistant to degradation from ultraviolet (UV) light, ozone, and general weathering.
Unlike many other plastics that become brittle when exposed to sunlight, PTFE maintains its integrity, making it a reliable choice for long-term outdoor applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. To use PTFE effectively, it's critical to understand its limitations, as these define where it is not a suitable choice.
Poor Radiation Resistance
PTFE has poor resistance to high-energy radiation, such as gamma rays or electron beams.
Radiation can break down the polymer chains, causing the material to lose its mechanical properties and become brittle. This makes it unsuitable for most nuclear or space radiation applications.
High Density
At 2.2 g/cm³, PTFE is significantly denser than many other polymers like Polypropylene (≈0.9 g/cm³) or Nylon (≈1.14 g/cm³).
This higher weight can be a disadvantage in applications where minimizing mass is a primary design goal.
Lower Mechanical Strength
While exceptionally stable, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It has lower tensile strength and is more susceptible to "creep" (slow deformation under constant load) compared to high-strength engineering plastics.
This means it is not typically used for high-load structural components, but rather for seals, liners, and bearings where its other properties are the main priority.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if PTFE balls are the right solution, match their elite properties to your primary engineering challenge.
- If your primary focus is chemical compatibility: PTFE is an ideal choice for components in aggressive chemical pumps, valves, and mixers.
- If your primary focus is low-friction movement: PTFE excels in self-lubricating bearings, check valves, and any application requiring a smooth, non-stick surface.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature stability: Its performance from cryogenic lows to high heat makes it perfect for seals and components in demanding thermal environments.
- If your primary focus is outdoor use or electrical insulation: PTFE's resistance to UV, weathering, and electricity makes it a durable choice for exposed or electronic components.
Ultimately, PTFE is the material you choose when performance in extreme chemical and thermal environments is a non-negotiable requirement.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to nearly all acids, alkalis, and solvents |
| Coefficient of Friction | ~0.04 (extremely low, self-lubricating) |
| Operating Temperature | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) |
| Density | 2.2 g/cm³ |
| Water Absorption | 0.01% (near-zero, hydrophobic) |
| Key Limitation | Poor radiation resistance; lower mechanical strength vs. other plastics |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
PTFE balls are ideal for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors where extreme chemical resistance, low friction, and thermal stability are critical.
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware. We offer custom fabrication services, from initial prototypes to high-volume production runs, ensuring your components meet the exact specifications required for your most challenging environments.
Let us help you solve your toughest engineering problems. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your PTFE component needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What size range do PTFE balls come in? A Guide from 3mm to 100mm
- What are the tolerances for PTFE balls based on size? Precision vs. Standard Grade Explained
- What are the key features of Teflon balls? Unlock Superior Performance in Demanding Environments
- What are the common applications of PTFE balls? Leverage Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Low Friction
- What temperature range can PTFE balls withstand? Unlock Extreme Thermal Stability from -200°C to 260°C



















