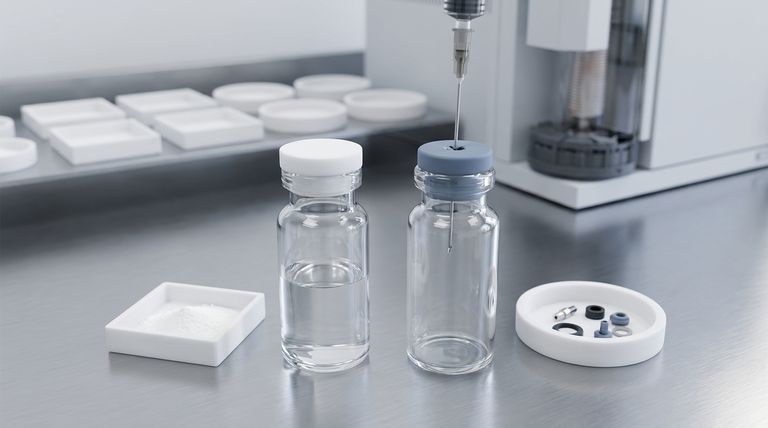
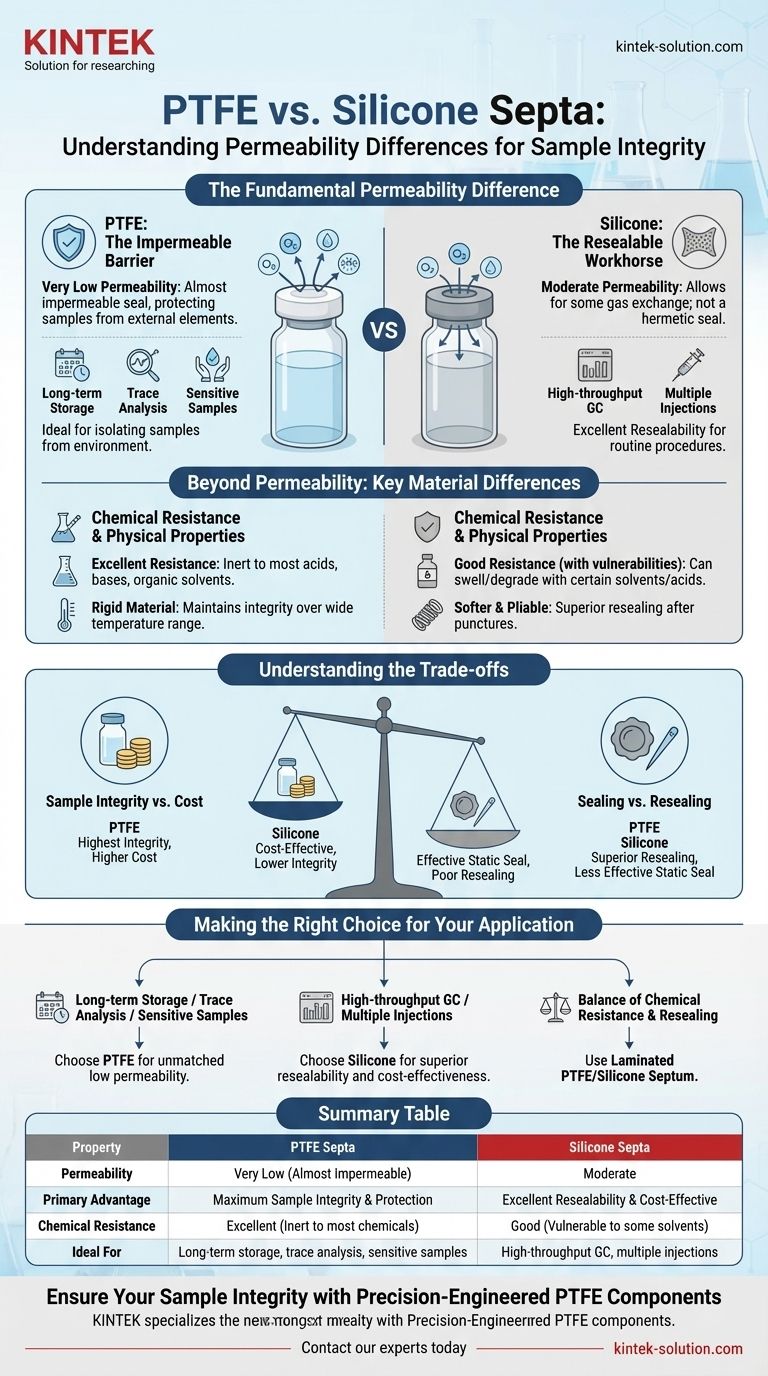
The fundamental permeability difference is that PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) septa have very low permeability, creating an almost impermeable seal, while silicone septa have moderate permeability, allowing for some gas exchange. This makes PTFE the superior choice for protecting samples from external air, moisture, and contaminants.
Choosing between PTFE and silicone septa is a critical decision based on a core trade-off. PTFE offers maximum sample integrity due to its low permeability and chemical inertness, while silicone provides a cost-effective, resealable option for applications where an absolute seal is not the primary requirement.

The Role of Permeability in Sample Protection
The permeability of a septum directly impacts the stability and purity of the sample contained within a vial. It dictates how well the seal can prevent analytes from escaping and contaminants from entering.
PTFE: The Impermeable Barrier
PTFE's molecular structure creates an exceptionally dense material with very low permeability. This makes it an effective barrier against the passage of gases.
This property is critical for applications involving long-term storage, trace analysis, or samples that are sensitive to oxygen or moisture. The goal is to isolate the sample from the external environment completely.
Silicone: The Resealable Workhorse
Silicone is a softer, more flexible polymer, which results in moderate permeability. It does not provide the same hermetic seal as PTFE.
However, its primary advantage is excellent resealability after being punctured by a needle. This makes it ideal for applications like gas chromatography (GC) where multiple injections from the same vial are common. Some gas exchange is often tolerable in these routine procedures.
Beyond Permeability: Key Material Differences
While permeability is a critical factor, the choice is also heavily influenced by chemical resistance and cost.
Chemical Resistance
PTFE is almost universally inert. It shows exceptional resistance to nearly all acids, bases, and organic solvents, ensuring it will not react with or contaminate the sample.
Silicone is generally inert but has known vulnerabilities. It can swell, soften, or degrade when exposed to certain organic solvents or strong acids, which can lead to sample contamination and seal failure.
Physical Properties and Temperature
PTFE is a more rigid material and maintains its integrity over a wide temperature range, making it suitable for both high and low-temperature applications.
Silicone is softer and more pliable, which contributes to its superior resealing capabilities after puncture.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right septum requires balancing the need for sample integrity against practical laboratory considerations like cost and workflow.
Sample Integrity vs. Cost
PTFE provides the highest level of sample protection due to its combination of low permeability and chemical inertness. This performance comes at a higher price point.
Silicone septa are significantly more cost-effective. They are a practical and economical choice for high-volume, routine procedures where solvent compatibility is not an issue and absolute sample isolation is unnecessary.
Sealing vs. Resealing
The low permeability of PTFE creates the most effective static seal. However, its rigidity means it is less effective at resealing after being punctured multiple times.
The flexibility of silicone makes it far superior for applications requiring repeated needle punctures, as it re-forms a functional seal around the puncture site more effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your analytical goal should dictate your choice of septum material.
- If your primary focus is long-term storage, trace analysis, or working with oxygen-sensitive samples: Choose PTFE for its unmatched low permeability and chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput gas chromatography with multiple injections: Choose silicone for its superior resealability and cost-effectiveness, ensuring your solvents are compatible.
- If you need a balance of chemical resistance and resealability: Use a laminated PTFE/Silicone septum, which combines a chemically inert PTFE facing with the resealing capability of a silicone backing.
By matching the septum's properties to your application's demands, you ensure the integrity of your sample and the accuracy of your results.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Septa | Silicone Septa |
|---|---|---|
| Permeability | Very Low (Almost Impermeable) | Moderate |
| Primary Advantage | Maximum Sample Integrity & Protection | Excellent Resealability & Cost-Effective |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Inert to most chemicals) | Good (Vulnerable to some solvents) |
| Ideal For | Long-term storage, trace analysis, sensitive samples | High-throughput GC, multiple injections |
Ensure Your Sample Integrity with Precision-Engineered PTFE Components
Choosing the right septum is critical for accurate results. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-purity PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We understand that your application demands a perfect balance of chemical inertness, low permeability, and reliable performance. Whether you need a custom PTFE septum for sensitive analysis or a high-volume order for routine procedures, our expertise in precision production ensures you get a component that protects your sample and your data.
Let us help you achieve uncompromising sample integrity. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements for custom PTFE fabrication, from prototypes to production runs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the recommended storage method for PTFE stopcock plugs when not in use? Prevent Seizing and Leaks
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for chromatography septums? Ensure Sample Integrity and Reliable Results
- How does the transparency feature of PTFE vials aid in laboratory work? Enhance Visibility and Efficiency
- What role does thermal stability play in the use of Teflon membranes? Ensuring Reliable Performance in High-Heat Lab Applications
- How is PTFE used in laboratory settings? Essential for Chemical Resistance and Sample Purity
- What can happen if PTFE plugs are rotated with solid particles lodged between the plug and barrel? Avoid Permanent Seal Failure
- Why is a non-stick surface beneficial for chromatography vials? Ensure Maximum Sample Recovery & Data Integrity



















