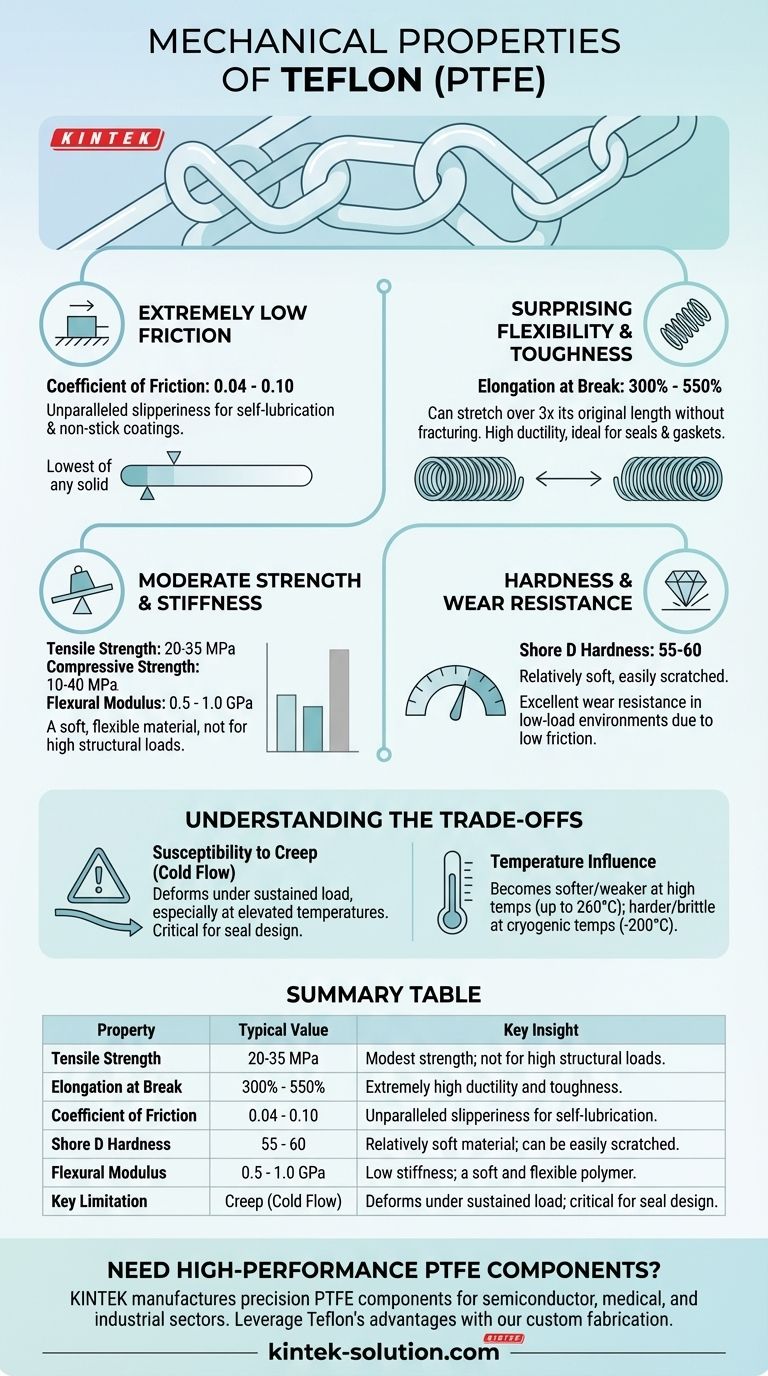
To put it directly, Teflon (PTFE) is a polymer defined by its exceptionally low friction, high flexibility, and moderate strength. Its key mechanical properties include a tensile strength of 20-35 MPa, a very high elongation at break of over 300%, a Shore D hardness of 55-60, and an extremely low coefficient of friction, often cited as low as 0.04.
Teflon is not selected for its raw strength, which is modest compared to other engineering plastics. Instead, it is chosen for its unique combination of extreme chemical inertness, thermal stability, and an unparalleled low-friction surface, making it a specialized problem-solver for specific engineering challenges.

A Deep Dive into Teflon's Key Mechanical Traits
To understand if Teflon is the right material for your application, you must look beyond the raw numbers and understand what they mean in a practical context.
The Defining Trait: Extremely Low Friction
The most famous property of Teflon is its "slipperiness." This is quantified by its coefficient of friction, which is one of the lowest of any solid material, ranging from 0.04 to 0.10.
This trait makes it an exceptional material for self-lubricating bearings, non-stick coatings, and any application where reducing surface drag is the primary goal.
Surprising Flexibility and Toughness
Teflon exhibits an elongation at break between 300% and 550%. This means it can stretch to over three times its original length before fracturing.
This high ductility, combined with a respectable impact strength, makes Teflon a very tough and resilient material. It can deform and conform to surfaces without cracking, which is ideal for seals and gaskets.
Moderate Strength and Stiffness
Teflon's strength metrics are modest for a polymer. Its tensile strength is typically in the 20-35 MPa range, with a compressive strength of 10-40 MPa.
Its stiffness, measured by its flexural modulus (0.5-1.0 GPa), is also relatively low. This confirms Teflon is a soft, flexible material, not a rigid one designed for high structural loads.
Hardness and Wear Resistance
With a Shore D hardness of 55-60, Teflon is a relatively soft material. You can easily scratch it with a sharp metal object.
However, in the right application, its low friction contributes to excellent wear resistance. Because surfaces slide past it so easily, abrasive wear is minimized in low-load environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. Teflon's unique strengths come with critical limitations that you must consider for any successful design.
Low Strength Compared to Other Polymers
While sufficient for many applications, Teflon's tensile and compressive strength are significantly lower than other common engineering plastics like Nylon or PEEK. It should not be considered for high-load structural components.
Susceptibility to Creep (Cold Flow)
Perhaps its most significant mechanical weakness is creep. Under sustained compressive load, especially at elevated temperatures, Teflon will slowly deform over time.
This tendency, also known as "cold flow," is a critical design consideration for applications like seals and gaskets, where maintaining constant pressure is essential.
Temperature's Influence on Properties
Teflon is famous for its wide operating temperature range (from -200°C to 260°C). However, its mechanical properties are not static across this range.
The material becomes significantly softer and weaker as it approaches its upper temperature limit. Conversely, it becomes harder and more brittle at cryogenic temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting Teflon requires aligning its unique profile with the demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is low-friction and self-lubrication: Teflon is an unparalleled choice for non-stick surfaces, slide bearings, or bushings where external lubrication is undesirable.
- If your primary focus is sealing in harsh environments: Its combination of extreme chemical inertness and material flexibility makes it a premier choice for gaskets and seals.
- If your primary focus is high structural load or rigidity: You must consider other engineering plastics, as Teflon's moderate strength and tendency to creep make it unsuitable for these roles.
Ultimately, understanding Teflon's unique balance of properties is the key to leveraging its exceptional performance in the right context.
Summary Table:
| Property | Typical Value | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 20-35 MPa | Modest strength; not for high structural loads. |
| Elongation at Break | 300% - 550% | Extremely high ductility and toughness. |
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.04 - 0.10 | Unparalleled slipperiness for self-lubrication. |
| Shore D Hardness | 55 - 60 | Relatively soft material; can be easily scratched. |
| Flexural Modulus | 0.5 - 1.0 GPa | Low stiffness; a soft and flexible polymer. |
| Key Limitation | Creep (Cold Flow) | Deforms under sustained load; critical for seal design. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Understanding Teflon's properties is the first step. KINTEK manufactures precision PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to complex labware—that are engineered to excel in your specific application.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, offering custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Let us help you leverage Teflon's unique advantages while designing around its limitations for a superior product.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation on your PTFE solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are PTFE's electrical insulation properties? Discover the Ultimate Insulator for Demanding Electronics
- In what types of chemical applications is PTFE commonly used? For Sealing, Transport & Component Manufacturing
- Why is PTFE used in medical equipment? Ensuring Safety and Performance in Critical Devices
- What are the two main methods of producing PTFE? A Guide to Granular and Dispersion PTFE
- What are the culinary applications of Teflon? Leverage Non-Stick Performance for Cooking & Processing
- How is Teflon (PTFE) produced chemically? Unlocking the Secrets of High-Performance Polymer Manufacturing
- What are the general properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)? Master Its Strengths and Limitations
- What are common uses of PTFE in laboratory and industrial settings? Unlock Chemical and Thermal Resistance



















