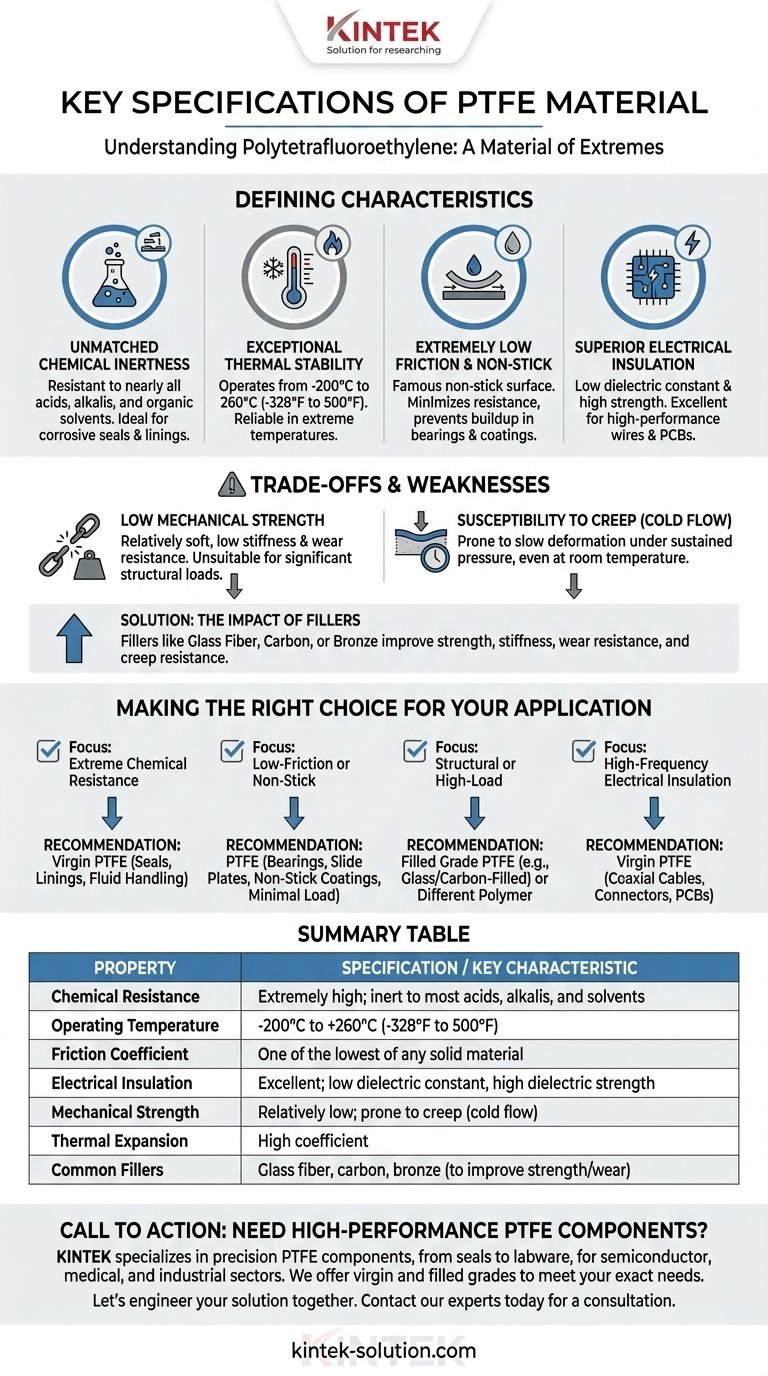
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a material of extremes, defined by a unique combination of properties. It is renowned for its exceptional chemical inertness, an extremely wide operating temperature range, a remarkably low coefficient of friction, and superior performance as an electrical insulator.
PTFE's value lies in its unparalleled resistance to heat and chemicals and its non-stick surface. However, these elite properties come with a significant trade-off: relatively low mechanical strength, which is the critical factor to consider for any structural application.

The Defining Characteristics of PTFE
To properly evaluate PTFE, you must understand its primary specifications. These properties are what make it a unique solution for a specific set of engineering challenges.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE exhibits extremely high resistance to nearly all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, alkalis, and organic solvents.
This chemical inertness makes it an ideal choice for seals, gaskets, and linings in corrosive environments where other materials would quickly degrade.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
One of PTFE's most cited features is its vast operating temperature range.
It remains functional and stable from cryogenic conditions at -200°C up to a continuous 260°C (-328°F to 500°F). This allows it to perform reliably in applications involving extreme heat or cold.
Extremely Low Friction and Non-Stick Surface
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, giving it a uniquely smooth and "lubricious" quality.
This property is responsible for its famous non-stick surface. It is crucial for applications like low-friction bearings, valve components, and non-stick coatings where minimizing resistance and preventing material buildup is essential.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator with a low dielectric constant and high dielectric strength.
Its insulating properties remain stable across a wide range of temperatures and frequencies, making it a first-choice material for high-performance wires, cables, and circuit board substrates.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Weaknesses
No material is perfect. While PTFE's strengths are significant, its limitations are just as important to understand for successful implementation. Ignoring these weaknesses is a common cause of component failure.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
The primary drawback of PTFE is its low mechanical strength, stiffness, and wear resistance compared to other engineering plastics. It is a relatively soft material.
This makes pure, or "virgin," PTFE unsuitable for components that must bear significant structural loads.
Susceptibility to Creep (Cold Flow)
Related to its low strength, PTFE is prone to creep, or "cold flow." Under sustained pressure, the material will slowly deform over time, even at room temperature.
Designers must account for this by ensuring mechanical loads are minimal or by using filled grades of the material.
The Impact of Fillers
To counteract its mechanical weaknesses, PTFE is often blended with fillers like glass fiber, carbon, or bronze.
These additives can dramatically improve strength, stiffness, wear resistance, and resistance to creep. However, they may slightly alter other properties, such as chemical resistance or the coefficient of friction.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a high coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts more significantly with temperature changes than metals or other polymers.
This must be factored into the design of assemblies to avoid stress or failure when parts undergo temperature cycling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material grade is critical. Your decision should be guided by the primary demand of your specific project.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance: Virgin PTFE is an ideal choice for seals, linings, and fluid handling in aggressive environments.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction or non-stick surface: PTFE is a top-tier material for bearings, slide plates, and non-stick coatings where load is minimal.
- If your primary focus is a structural or high-load component: Pure PTFE is the wrong choice; you must specify a filled grade (e.g., glass- or carbon-filled PTFE) or select a different polymer.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: Virgin PTFE is one of the best materials available for coaxial cables, connectors, and printed circuit boards.
By understanding both its unique advantages and its critical limitations, you can leverage PTFE to solve problems that few other materials can.
Summary Table:
| Property | Specification / Key Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Extremely high; inert to most acids, alkalis, and solvents |
| Operating Temperature | -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to 500°F) |
| Friction Coefficient | One of the lowest of any solid material |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent; low dielectric constant, high dielectric strength |
| Mechanical Strength | Relatively low; prone to creep (cold flow) |
| Thermal Expansion | High coefficient |
| Common Fillers | Glass fiber, carbon, bronze (to improve strength/wear) |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Understanding PTFE's specifications is the first step. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We help you navigate the trade-offs by offering both virgin and filled PTFE grades, ensuring your parts deliver the exact chemical resistance, thermal stability, or mechanical performance your application demands. From prototypes to high-volume orders, our custom fabrication prioritizes precision and reliability.
Let's engineer your solution together. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE perform as an electrical insulator? Unmatched Signal Integrity & High-Voltage Reliability
- What are the advantages of FEP compared to PTFE and PFA? Achieve Cost-Effective Performance for Your Application
- What is the dielectric constant of PTFE and why is it important? Unlock Superior Signal Integrity
- What should consumers be cautious about regarding PTFE? The Hidden Risks of 'Forever Chemicals'
- What fillers are used to enhance PTFE properties? Tailor PTFE for Superior Wear and Strength
- How does PTFE behave in terms of chemical inertness? Unmatched Resistance for Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE contribute to sustainable and eco-friendly design practices? Enhance Durability and Efficiency
- What is reprocessed PTFE? A Cost-Effective Alternative for Non-Critical Applications



















