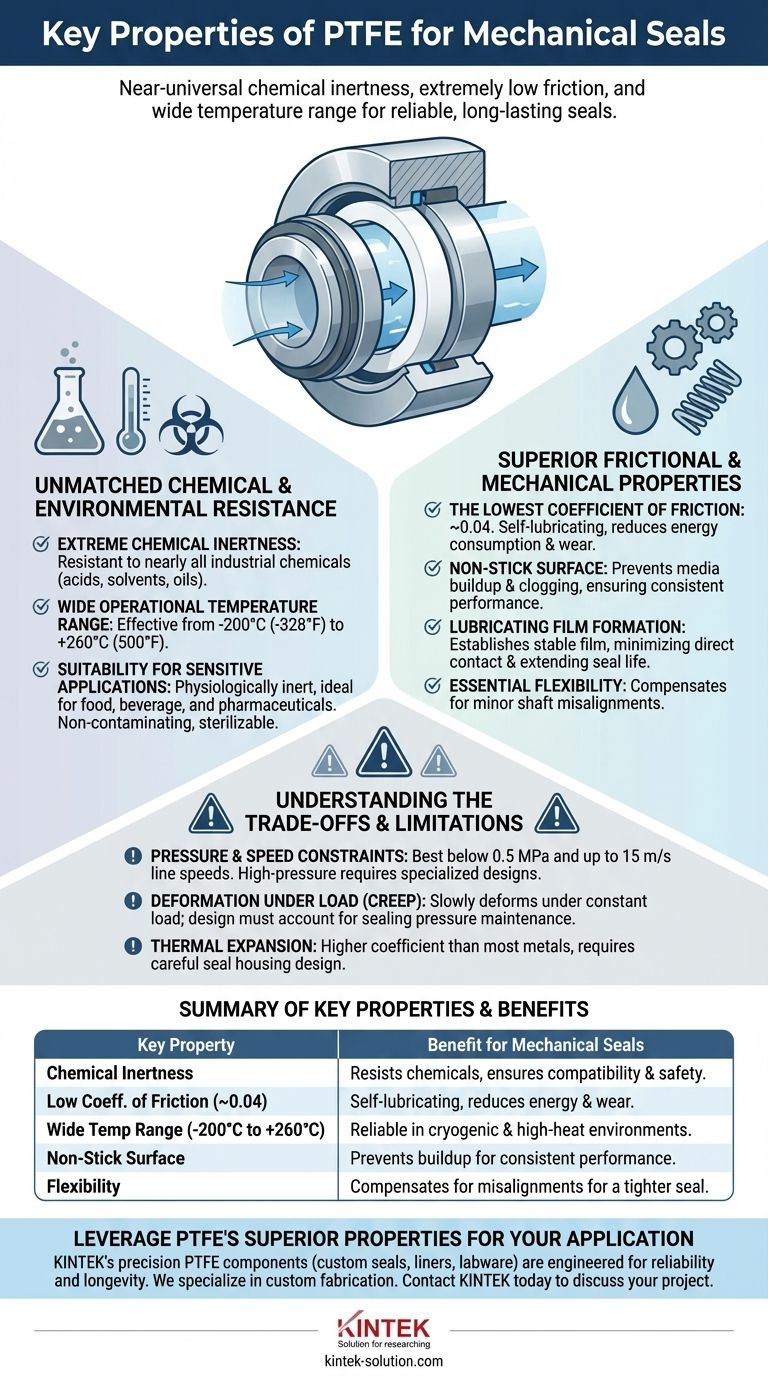
The defining properties of PTFE that make it exceptional for mechanical seals are its near-universal chemical inertness, an extremely low coefficient of friction, and its ability to perform across a vast temperature range. These characteristics allow it to create a reliable, long-lasting seal in demanding chemical, thermal, and mechanical environments where other materials would quickly fail.
PTFE is not just a passive barrier; it's an active participant in creating a superior seal. Its unique combination of chemical resistance and self-lubricating properties solves the dual challenges of preventing leaks while simultaneously minimizing wear and energy consumption.

Unmatched Chemical and Environmental Resistance
A seal's primary function is to withstand its operating environment. PTFE excels here by being one of the most chemically resistant materials known, making it a default choice for aggressive applications.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
Often called the "king of plastic," PTFE is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, solvents, oils, and aggressive oxidizing agents. This allows a single seal material to be specified for a wide variety of services, simplifying inventory and reducing the risk of material incompatibility.
Wide Operational Temperature Range
PTFE maintains its integrity and sealing properties across an exceptionally broad thermal spectrum. It is effective in cryogenic applications as low as -200°C (-328°F) and can handle high temperatures up to +260°C (500°F), a range that few other polymers can tolerate.
Suitability for Sensitive Applications
Because it is physiologically inert, PTFE is suitable for applications in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries. It does not contaminate the process medium, and it can be effectively sterilized, ensuring product purity.
Superior Frictional and Mechanical Properties
Beyond mere resistance, a mechanical seal must manage the dynamic friction between rotating and stationary faces. PTFE's properties in this area are what truly set it apart, directly contributing to seal efficiency and longevity.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest friction coefficients of any solid material, approximately 0.04. This inherent slipperiness means it is self-lubricating, drastically reducing the energy needed to turn the shaft and minimizing heat generation at the seal faces.
Non-Stick Surface
Its non-adhesive surface prevents process media from sticking or building up on the seal components. This is critical for preventing clogging, maintaining seal face contact, and ensuring consistent performance over time.
Lubricating Film Formation
The low-friction nature of PTFE helps establish a stable lubricating film between the seal faces. This film is essential for extending the operational life of the seal by minimizing direct contact and wear.
Essential Flexibility
PTFE seals exhibit good flexibility and deformation resistance. This allows them to compensate for minor shaft misalignments or imperfections on the sealing surfaces, ensuring a tighter and more reliable seal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While PTFE is a superior material, its properties create specific design considerations that must be respected for successful implementation. No material is without its limitations.
Pressure and Speed Constraints
Standard PTFE bellow seal designs often have specific operational limits. They perform best under moderate pressures (typically below 0.5 MPa) and line speeds (up to 15 m/s). High-pressure applications may require specialized designs or different materials.
Deformation Under Load (Creep)
A key characteristic of PTFE is its tendency to "creep" or slowly deform under a constant load, especially at elevated temperatures. Seal design must account for this behavior to maintain the correct sealing pressure over the life of the component.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than most metals. This means it expands and contracts more significantly with temperature changes. This must be factored into the design of the seal housing and components to avoid excessive stress or loss of sealing force.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a seal material requires matching its properties to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE's near-universal chemical inertness makes it the safest and most reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is minimizing energy loss and wear: Its extremely low coefficient of friction directly reduces drag and extends the life of rotating components.
- If your primary focus is product purity: PTFE's physiologically inert and non-stick nature ensures it will not contaminate sensitive media in food or pharmaceutical processes.
Ultimately, understanding these core properties empowers you to leverage PTFE's unique advantages for creating highly reliable and efficient sealing systems.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Mechanical Seals |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all industrial chemicals, ensuring compatibility and safety. |
| Low Coefficient of Friction (~0.04) | Self-lubricating, reduces energy consumption and wear. |
| Wide Temperature Range (-200°C to +260°C) | Performs reliably in cryogenic and high-heat environments. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Prevents media buildup and clogging for consistent performance. |
| Flexibility | Compensates for minor misalignments for a tighter seal. |
Leverage PTFE's Superior Properties for Your Application
PTFE's unique combination of chemical resistance, self-lubrication, and thermal stability solves the toughest sealing challenges. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, KINTEK's precision PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to labware—are engineered for reliability and longevity.
We specialize in custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring a perfect fit for your specific requirements.
Ready to enhance your sealing system's performance and efficiency? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when specifying PTFE Lip Seals? Ensure Long-Term Reliability for Your Application
- Why can PTFE ball valves be used in corrosive media? Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Safe Fluid Control
- What overall value do PTFE-free bushings provide? A Strategic Choice for Environmental & Mechanical Performance
- What is the temperature range for welded PTFE bellow seals? Unlock Extreme Thermal Performance
- What post-machining steps improve PTFE surface finish? Achieve a Smooth, High-Performance Surface
- Why is understanding the PTFE operating temperature range crucial for design integration? Ensure Component Reliability
- What nominal sizes are available for PTFE gaskets? From DN15 to DN2000 and Beyond
- Are PTFE O-rings safe for use in food processing equipment? Ensure Compliance and Safety



















