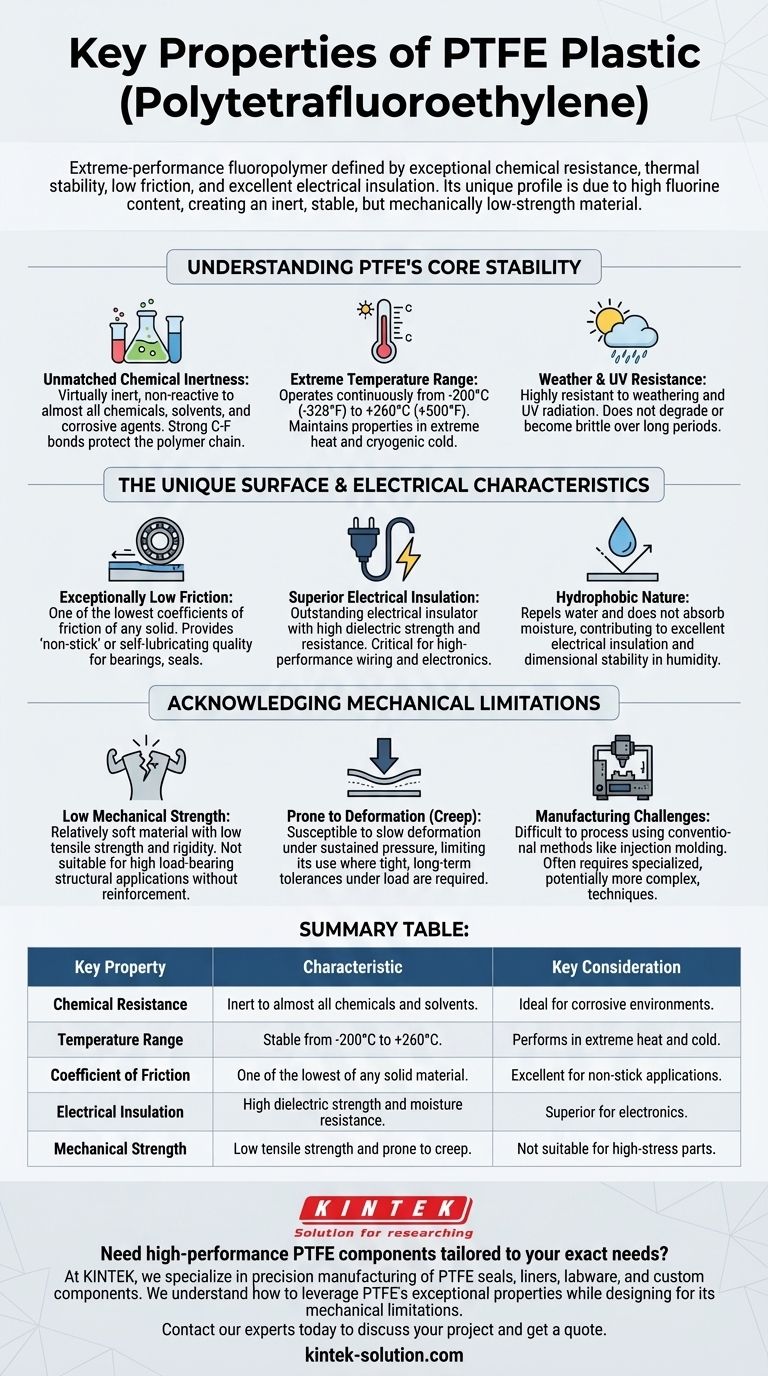
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is an extreme-performance fluoropolymer defined by its remarkable combination of properties. Its most notable characteristics are exceptional chemical resistance, stability across a vast temperature range, an extremely low coefficient of friction creating a non-stick surface, and excellent electrical insulation.
The core reason for PTFE's unique profile is its high fluorine content, which creates a chemically inert and thermally stable material. However, this same molecular structure results in low mechanical strength, a critical trade-off that must be considered for any structural application.

Understanding PTFE's Core Stability
The primary value of PTFE lies in its ability to remain stable and functional in environments where most other plastics would fail. This resilience stems from its unique chemical makeup and molecular structure.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert, meaning it is non-reactive to almost all chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This resistance is a direct result of the strong carbon-fluorine bonds that protect the polymer chain from chemical attack.
Extreme Temperature Range
The material demonstrates unparalleled thermal stability. It can operate continuously at temperatures as high as 260°C (500°F) and maintains its properties even at cryogenic temperatures as low as -200°C (-328°F).
Weather and UV Resistance
PTFE is highly resistant to weathering and UV radiation. Unlike many other plastics, it does not degrade or become brittle when exposed to the elements over long periods, making it ideal for outdoor applications.
The Unique Surface and Electrical Characteristics
Beyond its stability, PTFE is known for a distinct set of properties related to its surface and its interaction with electricity.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material. This gives it its famous non-stick or self-lubricating quality, which is essential for applications like low-friction bearings, seals, and non-stick cookware.
Superior Electrical Insulation
The material is an outstanding electrical insulator with high dielectric strength and very high electrical resistance. This prevents the flow of electricity, making it a critical component in high-performance wiring, cables, and electronic components.
Hydrophobic Nature
PTFE is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and does not absorb moisture. This property contributes to its excellent electrical insulation and ensures dimensional stability in humid environments.
Acknowledging the Mechanical Limitations
To use PTFE effectively, it is critical to understand its significant trade-offs. Its chemical and thermal strengths come at the cost of mechanical performance.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material with low tensile strength and rigidity. It is not suitable for applications that require high load-bearing capacity without reinforcement.
Prone to Deformation (Creep)
Under sustained pressure, PTFE is susceptible to "creep," or slow deformation over time. This limits its use in applications requiring tight, long-term dimensional tolerances under load.
Manufacturing Challenges
The same properties that make PTFE so resilient also make it difficult to process using conventional methods like injection molding. Specialized techniques are often required, which can impact manufacturing complexity and cost.
Is PTFE the Right Choice for Your Application?
Choosing PTFE depends entirely on prioritizing its unique strengths while respecting its limitations.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical or temperature resistance: PTFE is an ideal candidate, capable of withstanding environments that would destroy most other materials.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction or non-stick surface: PTFE is one of the best materials available for applications requiring slick, self-lubricating properties.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electrical insulation: PTFE's high dielectric strength and resistance to moisture make it a superior choice for demanding electronics and wiring.
- If your primary focus is high structural strength or load-bearing: You must account for PTFE's low mechanical strength; consider using it as a coating or liner, or choose a reinforced grade or a different polymer entirely.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE successfully means designing applications around its elite chemical, thermal, and surface properties, not its mechanical strength.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Characteristic | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to almost all chemicals and solvents. | Ideal for corrosive environments. |
| Temperature Range | Stable from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). | Performs in extreme heat and cold. |
| Coefficient of Friction | One of the lowest of any solid material. | Excellent for non-stick and self-lubricating applications. |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength and moisture resistance. | Superior for high-performance electronics. |
| Mechanical Strength | Low tensile strength and prone to creep under load. | Not suitable for high-stress structural parts without design consideration. |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored to your exact needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components. We understand how to leverage PTFE's exceptional properties while designing for its mechanical limitations. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors, our expertise ensures a perfect fit for your application's demanding environment.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems



















