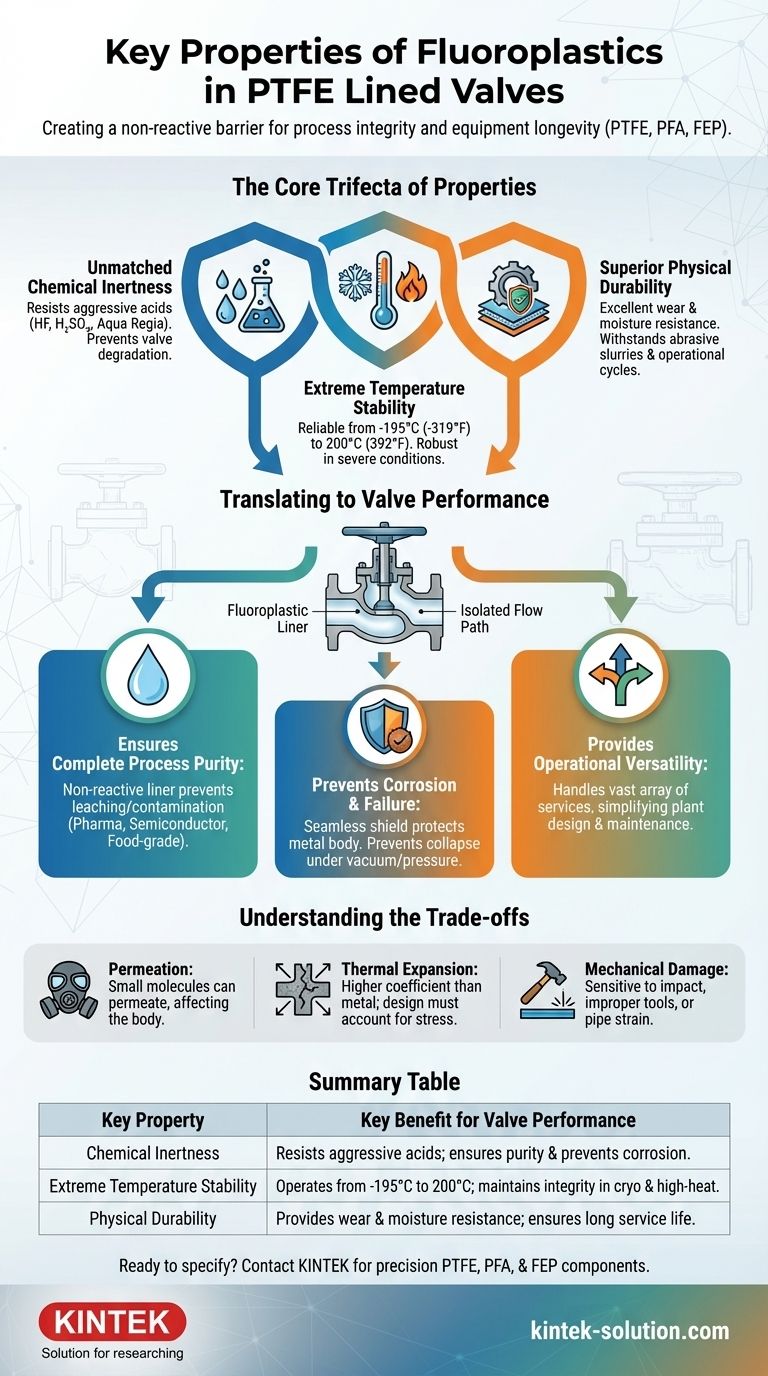
At their core, fluoroplastics used in valve linings are defined by three critical properties: exceptional chemical inertness, a vast operating temperature range, and high physical durability. These materials, most notably PTFE, PFA, and FEP, create a non-reactive barrier that protects both the valve's structural components and the purity of the media passing through it.
The fundamental purpose of a fluoroplastic liner is not merely to coat the valve, but to create a completely isolated, chemically inert flow path that ensures process integrity and equipment longevity in the most hostile industrial environments.
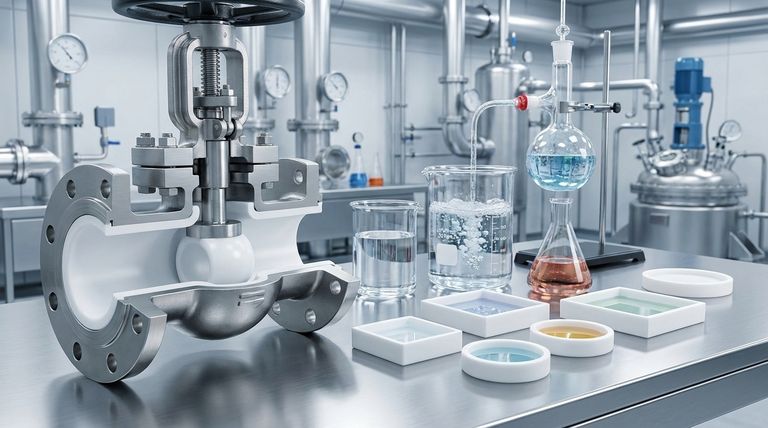

The Core Trifecta of Fluoroplastic Properties
To understand why these materials are indispensable in demanding applications, we must look at their three primary characteristics. These properties work in concert to deliver reliable and safe performance.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
The defining feature of fluoroplastics is their near-total resistance to chemical attack. They are virtually unaffected by even the most aggressive substances.
This includes chemicals notorious for corroding metals, such as hydrofluoric acid, concentrated sulfuric acid, and aqua regia. This inertness prevents the valve body from degrading and ensures the process fluid remains uncontaminated.
Extreme Temperature Stability
Fluoroplastic liners offer remarkable performance across a very wide thermal spectrum, ensuring mechanical integrity in severe conditions.
They can operate reliably at continuous high temperatures up to 200°C (392°F) and remain robust and functional at cryogenic lows down to -195°C (-319°F).
Superior Physical Durability
Beyond chemical and thermal resistance, these materials possess key physical traits that contribute to a long service life.
They exhibit excellent wear resistance against abrasive slurries, high moisture resistance, and are not degraded by oils or solvents. This ensures the liner maintains its integrity over countless operational cycles.
How These Properties Translate to Valve Performance
Understanding the material science is only half the story. The true value is revealed in how these properties directly enhance the function and reliability of the valve itself.
Ensuring Complete Process Purity
Because the liner is non-reactive, it does not leach or corrode. This means the wetted parts of the valve will not introduce impurities into the process media, a critical requirement in pharmaceutical, semiconductor, and food-grade applications.
Preventing Corrosion and Structural Failure
The liner acts as a seamless, protective shield for the valve's metal body (typically cast iron or stainless steel). Materials like FEP and PFA are applied with uniform thickness throughout the body and face area.
This method of application is crucial, as it prevents the liner from collapsing under vacuum or blowing out under high pressure, which would expose the metal body to the corrosive media.
Providing Operational Versatility
The combination of broad chemical compatibility and a wide temperature range means a single, well-specified lined valve can handle a vast array of different services. This versatility can simplify plant design, reduce inventory, and streamline maintenance protocols.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, fluoroplastics are not without their limitations. An objective assessment requires acknowledging their engineering trade-offs.
Susceptibility to Permeation
While highly resistant, fluoroplastic liners are not completely impermeable. Certain small-molecule gases or chemicals can, over time, permeate through the liner and potentially affect the valve body. This is a critical consideration for specific high-purity or highly toxic gas services.
Thermal Expansion
Fluoroplastics have a much higher coefficient of thermal expansion than the metal bodies they line. Valve designs must carefully account for this difference to prevent stress, deformation, or delamination during significant temperature swings.
Sensitivity to Mechanical Damage
The liner, while durable against chemical attack, can be damaged by mechanical impact, improper tool use during installation, or excessive pipe strain. A scratched or gouged liner compromises the entire protective barrier.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct lined valve depends entirely on the primary challenge you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive media: The valve's seamless, uniform fluoroplastic lining provides the most reliable and complete barrier against chemical attack.
- If your primary focus is operating in extreme temperatures: The material's exceptional thermal stability ensures consistent mechanical performance and sealing from cryogenic lows to high-heat processes.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute process purity: The inert, non-leaching nature of the liner is the critical feature that prevents contamination of your final product.
By understanding these core material properties, you can confidently specify valves that deliver safety, purity, and reliability in your most demanding processes.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Key Benefit for Valve Performance |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists aggressive acids (e.g., HF, H₂SO₄); ensures process purity and prevents corrosion. |
| Extreme Temperature Stability | Operates from -195°C to 200°C; maintains integrity in cryogenic and high-heat processes. |
| Physical Durability | Provides wear and moisture resistance; ensures long service life against abrasive slurries. |
Ready to specify the right PTFE-lined valve for your demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE, PFA, and FEP components. Our expertise ensures your valves deliver unmatched chemical resistance, thermal stability, and operational reliability in semiconductor, pharmaceutical, laboratory, and industrial processes.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact specifications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and ensure process integrity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE ring gaskets still preferred despite their disadvantages? For Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the medical uses of Teflon? Essential for Safe, Non-Reactive Medical Devices
- What are the potential issues of not using a Teflon sheet with a heat press? Protect Your Equipment & Projects
- Why are PTFE extruded rods suitable for sealing applications? The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance Seals
- Are expanded PTFE gaskets as durable as standard PTFE gaskets? Discover the Best Choice for Your Seal.
- What are PTFE lined valves and what is their primary purpose? Achieve Superior Corrosion Resistance
- How do PTFE-lined valves compare to traditional metallic valves? Maximize Performance in Corrosive Applications
- How does the low friction property of PTFE rotary shaft seals benefit machinery? Boost Efficiency & Reliability



















