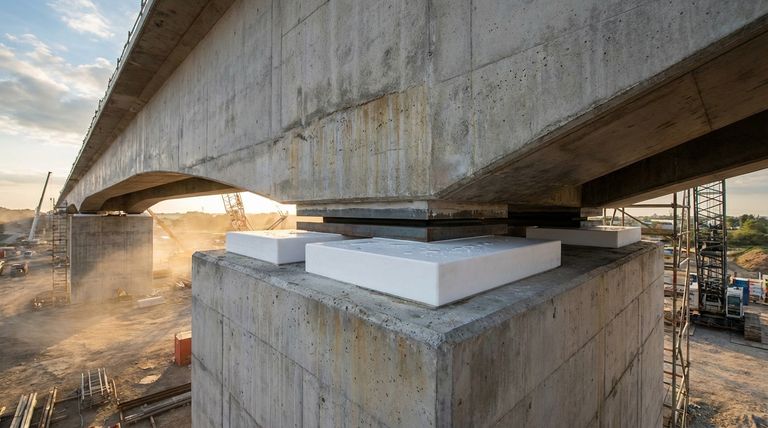
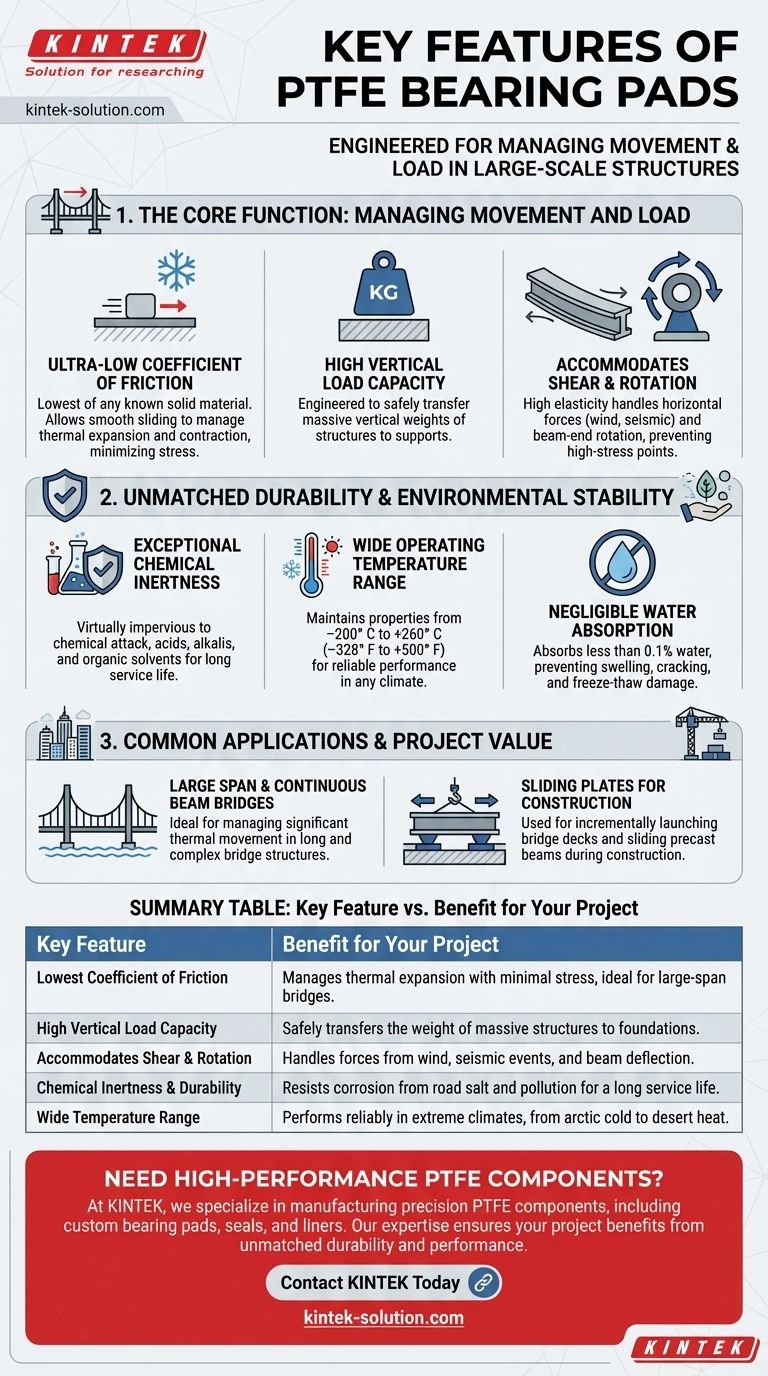
At their core, PTFE bearing pads are engineered components designed to solve one of the biggest challenges in large-scale construction: managing movement. Their key features are an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, high load-bearing capacity, and remarkable durability, which allow them to support massive structures while accommodating forces from thermal expansion, rotation, and shear.
The true value of a PTFE bearing pad isn't just in supporting weight, but in its ability to create a controlled, low-friction sliding surface. This isolates the superstructure from the substructure, preventing the buildup of destructive stress caused by natural movements.

The Core Function: Managing Movement and Load
A bearing pad in a bridge or large building must do more than just sit there. It must actively manage a complex interplay of forces to ensure the structure's integrity and longevity.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE, often known by the brand name Teflon, has the lowest coefficient of friction of any known solid material—even lower than wet ice on wet ice.
This ultra-low friction surface is the pad's most critical feature. It allows the heavy superstructure to slide smoothly and with minimal resistance during thermal expansion and contraction.
Without this feature, temperature changes would induce immense stress in the support columns and abutments, leading to potential structural failure.
High Vertical Load Capacity
Despite being a sliding surface, PTFE bearing pads are engineered to withstand enormous vertical loads.
They safely transfer the entire weight of the bridge deck or building floor down to the supporting piers or foundation.
Accommodating Shear and Rotation
PTFE pads have a high degree of elasticity. This allows them to deform to accommodate shear forces, which are the horizontal loads caused by wind, braking vehicles, or seismic events.
This same elasticity allows the pad to handle beam-end rotation. As a beam deflects or bends slightly under load, the pad flexes with it, preventing the creation of a high-stress pivot point.
Unmatched Durability and Environmental Stability
Structural components are expected to last for decades with minimal maintenance, often in harsh and exposed environments. PTFE's material properties are exceptionally well-suited for this demand.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually impervious to chemical attack. It is highly resistant to acids, alkalis, organic solvents, and other corrosive agents.
This ensures the pad will not degrade from exposure to road salt, pollution, or other environmental chemicals, guaranteeing a long service life.
Wide Operating Temperature Range
These pads maintain their key properties across an incredibly wide temperature range, from –200° C to +260° C (–328° F to +500° F).
This stability ensures reliable and consistent performance in any climate, from arctic cold to desert heat.
Negligible Water Absorption
PTFE absorbs almost no water (less than 0.1%). This prevents the material from swelling, cracking, or losing its structural integrity due to moisture, freezing, and thawing cycles.
Common Applications and Use Cases
The unique combination of these features makes PTFE bearing pads ideal for specific, demanding engineering scenarios.
Large Span and Continuous Beam Bridges
These bearings are the standard choice for large-span bridges and multi-span continuous beams. The longer the structure, the greater the thermal movement it will experience. PTFE's low friction is essential to manage this displacement.
Sliding Plates for Construction
Their low-friction properties are also leveraged during the construction process. PTFE pads are often used as sliding plates for incrementally launching a bridge deck across piers or for sliding heavy precast beams into their final position.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing the right bearing is about matching its primary features to your project's most critical demand.
- If your primary focus is managing thermal expansion in large structures: PTFE's ultra-low friction coefficient is its most critical feature, allowing movement with minimal stress transfer.
- If your primary focus is long-term durability in a harsh environment: Its chemical inertness and wide temperature range ensure a long, maintenance-free service life.
- If your primary focus is accommodating complex, multi-directional forces: The combined ability to handle vertical loads, shear deformation, and beam rotation makes it a versatile solution for modern structural designs.
Ultimately, PTFE bearing pads provide a robust, multi-functional solution for controlling the immense forces and movements inherent in large-scale structural engineering.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit for Your Project |
|---|---|
| Lowest Coefficient of Friction | Manages thermal expansion with minimal stress, ideal for large-span bridges. |
| High Vertical Load Capacity | Safely transfers the weight of massive structures to foundations. |
| Accommodates Shear & Rotation | Handles forces from wind, seismic events, and beam deflection. |
| Chemical Inertness & Durability | Resists corrosion from road salt and pollution for a long service life. |
| Wide Temperature Range | Performs reliably in extreme climates, from arctic cold to desert heat. |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your critical project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom bearing pads, seals, and liners. Our expertise ensures your structural, semiconductor, medical, or industrial project benefits from unmatched durability and performance.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, guaranteeing a perfect fit for your specific requirements.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project needs and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency



















