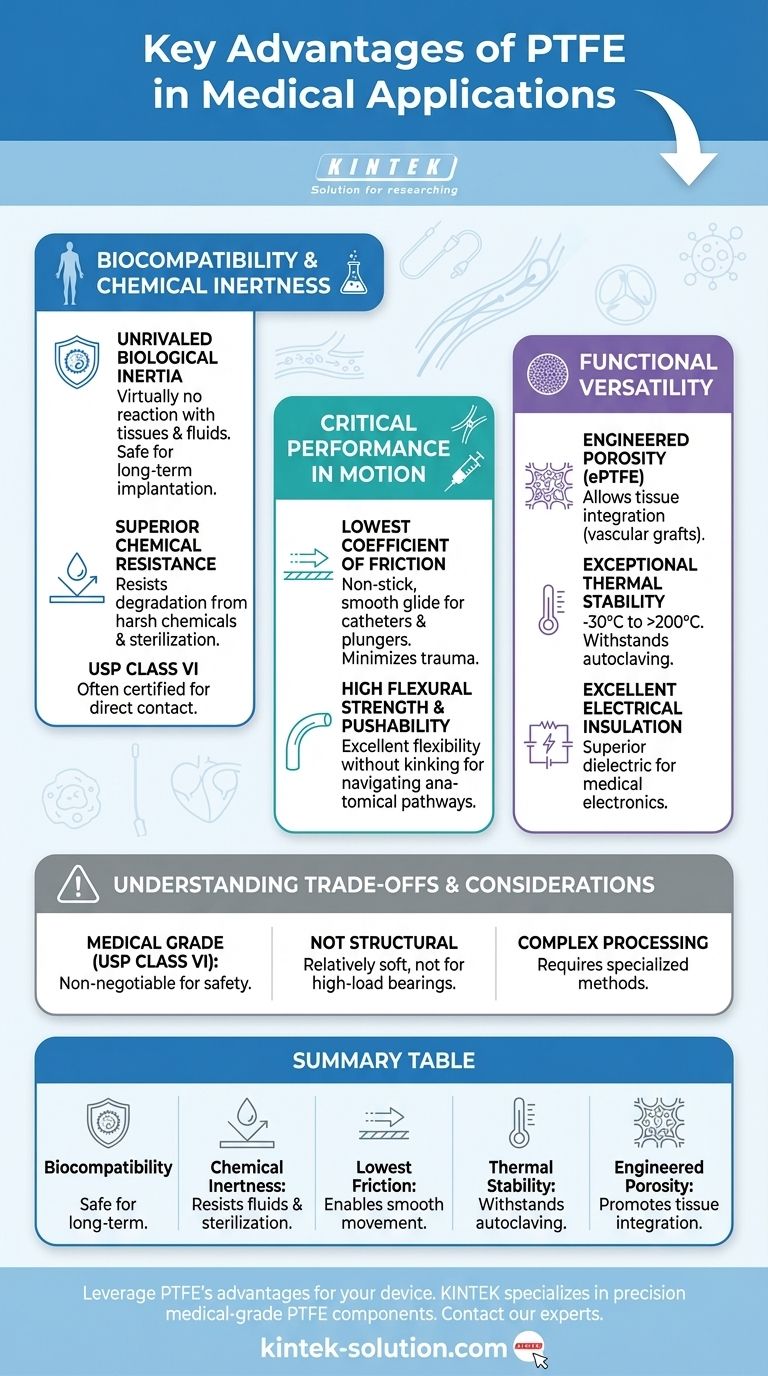
The primary advantages of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) in medical applications stem from its unique combination of biological inertness, extreme chemical resistance, and an exceptionally low coefficient of friction. These core properties make it a trusted material for a wide range of uses, from internal implants like vascular grafts to external devices like high-performance catheters and hygienic syringe plungers. Its reliability is rooted in the powerful carbon-fluorine bonds that define its molecular structure.
While its list of properties is long, the core value of PTFE in medicine comes from a unique duality: it is simultaneously one of the most chemically non-reactive and lowest-friction solid materials known. This combination ensures it can safely exist within the human body while minimizing physical irritation and unwanted interactions.

The Foundation: Biocompatibility and Chemical Inertness
The most critical requirement for any material used in the body is that it does not cause harm. PTFE excels in this area due to its fundamental molecular stability.
Unrivaled Biological Inertia
PTFE exhibits virtually no reaction when exposed to bodily tissues and fluids. This biocompatibility prevents adverse immune responses, making it safe for long-term implantation.
Materials like PTFE are often classified under standards like USP Class VI, confirming their suitability for direct contact with the human body.
Superior Chemical Resistance
The material is highly resistant to degradation from aggressive chemicals. This ensures the integrity of a medical device is maintained, even when exposed to harsh sterilization processes or complex biological environments.
Critical Performance in Motion: Mechanical Properties
For devices that must move, slide, or be inserted into the body, PTFE's mechanical characteristics are indispensable.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest friction coefficients of any known solid material. This non-stick, non-adhesive surface is crucial for applications like catheters, where it must glide smoothly through blood vessels with minimal trauma.
It also ensures hygienic and effortless movement in components like syringe plungers and pump seals, preventing sticking and ensuring accurate operation.
High Flexural Strength and Pushability
In applications like medical catheters, PTFE liners provide excellent flexibility and pushability. This allows the device to navigate complex anatomical pathways without kinking or deforming.
The material's high yield strength ensures it can resist externally applied forces during a procedure, improving both performance and patient safety.
Functional Versatility: Key Material Characteristics
Beyond its core benefits, PTFE offers a range of properties that allow it to be adapted for highly specific medical needs.
Engineered Porosity for Tissue Integration
In a modified form known as expanded PTFE (ePTFE), the material can be manufactured with a porous structure. This is vital for applications like vascular grafts, as it allows for the patient's own cells to grow into the material, promoting better integration with the body.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
PTFE can withstand a very wide operating temperature range, from approximately -30°C to over 200°C. This makes it compatible with common sterilization methods, such as autoclaving, which is a critical requirement for reusable medical tools.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
As a superior dielectric material, PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator. This property is valuable in the construction of sophisticated medical electronics and diagnostic equipment where signals must be isolated.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly advantageous, PTFE is not a universal solution. A clear understanding of its limitations is essential for proper application.
Medical Grade Is Non-Negotiable
Not all PTFE is created equal. Only materials that meet strict regulatory standards, such as USP Class VI, are suitable for medical use. The specific application dictates the required grade and documentation.
Not a High-Strength Structural Material
PTFE is a relatively soft polymer. It is not intended for high-load-bearing applications, such as the primary structural components of orthopedic implants. Its strengths lie in lining, coating, and low-friction movement.
Processing Can Be Complex
Due to its high melting point and viscosity, PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt-processing techniques like injection molding. Specialized methods are required, which can influence design and manufacturing considerations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To leverage PTFE effectively, align its primary advantages with the most critical need of your medical device.
- If your primary focus is internal implants or long-term fluid contact: Its proven biocompatibility and chemical inertness provide the highest degree of safety and stability.
- If your primary focus is interventional devices requiring smooth movement: Its unmatched low coefficient of friction and pushability are the most critical factors for performance.
- If your primary focus is reusable equipment requiring frequent cleaning: Its thermal stability and resistance to sterilization chemicals ensure durability and a long service life.
Ultimately, PTFE's reliability stems from its fundamental molecular stability, making it a predictable and safe choice for the most demanding medical environments.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Why It Matters in Medicine |
|---|---|
| Biocompatibility (USP Class VI) | Safe for long-term implantation; prevents adverse immune reactions. |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists degradation from bodily fluids and harsh sterilization processes. |
| Lowest Coefficient of Friction | Enables smooth insertion and movement of catheters and other devices. |
| Thermal Stability | Withstands autoclaving and other high-temperature sterilization methods. |
| Engineered Porosity (ePTFE) | Allows for tissue integration in applications like vascular grafts. |
Leverage PTFE's critical advantages for your medical device. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of medical-grade PTFE components—from seals and liners to complex custom labware. We ensure your devices meet the highest standards of safety and performance, supporting applications from catheters to diagnostic equipment. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the standard bearing assembly configurations for PTFE slide bearings? Choose the Right PTFE Bearing for Your Project
- What are key considerations for tool selection when machining Teflon? Maximize Precision and Prevent Deformation
- What factors affect PTFE seal performance? Optimize Your System for Reliability & Longevity
- What does the material compatibility chart indicate about PTFE? A Guide to Its Broad Chemical Resistance
- What temperature range can PTFE-lined butterfly valves withstand? Ensuring Safe & Reliable Operation
- What is the preferred composition for PTFE wear resistant material and why? Achieve Superior Performance with Bronze-Filled PTFE
- What are the challenges in manufacturing PTFE impellers? Overcoming the Complexities of Machining
- How does PCTFE compare to PTFE for cryogenic applications? Choose the Right Material for Extreme Cold



















