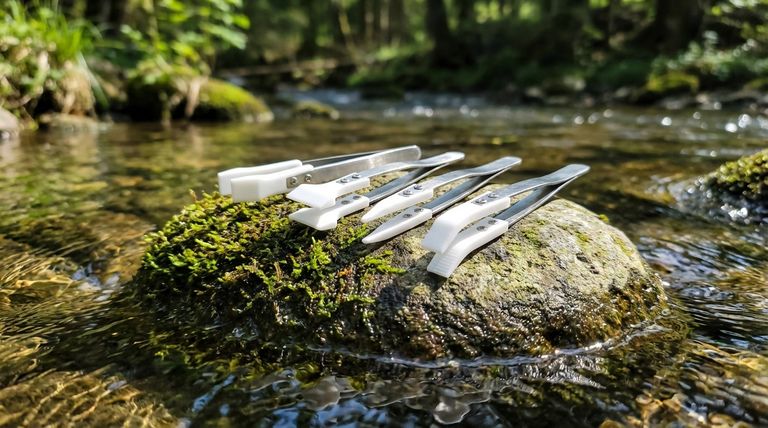
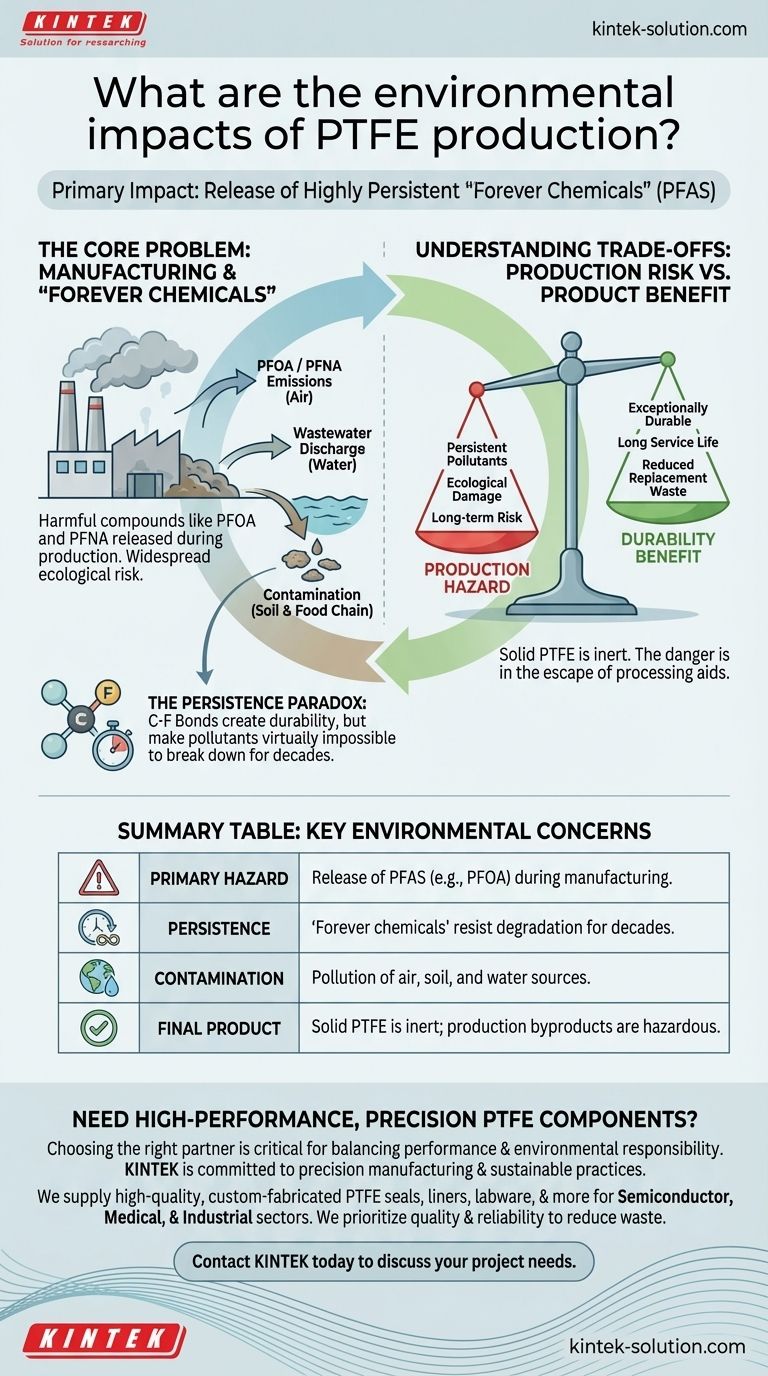
The primary environmental impact of PTFE production is the potential release of highly persistent and harmful chemicals, known as PFAS, into the surrounding environment. Substances like PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid) used in the manufacturing process can contaminate air, soil, and water, posing significant long-term ecological risks.
The core issue with PTFE is a paradox: the same chemical stability that makes the final product incredibly durable also makes its manufacturing byproducts, if released, almost impossible for the environment to break down.

The Core Problem: "Forever Chemicals" in Manufacturing
The most significant environmental concerns are not with the final, solid PTFE product itself, but with the auxiliary chemicals required to produce it. These substances are often referred to as "forever chemicals" for their extreme persistence.
PFOA and Related Emissions
During production, harmful compounds like PFOA and PFNA (perfluorononanoic acid) can be emitted. These chemicals are part of the larger PFAS family (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances).
These emissions can spread widely. For instance, one manufacturing facility in the Netherlands was linked to PFOA contamination in vegetation found kilometers away from the plant.
Widespread Environmental Contamination
The release of these substances is not limited to air. Wastewater discharged from fluoropolymer manufacturing plants has been identified as a major source of pollution.
Once in the environment, these chemicals can accumulate in water sources, soil, and even the food chain, leading to widespread and long-lasting damage.
The Persistence Paradox
PTFE's value comes from its incredibly strong carbon-fluorine bonds, which make it virtually immune to chemical attack.
Unfortunately, this same chemical stability is what makes the associated manufacturing pollutants so problematic. Once they enter the ecosystem, these "forever chemicals" resist natural degradation processes for decades or even centuries.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Durability vs. Production Hazard
While the production process carries clear environmental risks, the final PTFE material possesses properties that can offer environmental benefits in certain applications.
The Benefit of Longevity
PTFE is exceptionally durable and resistant to UV radiation, harsh weather, and corrosive chemicals.
Components made from PTFE have an extremely long service life. This reduces the need for frequent replacements, thereby minimizing the waste and manufacturing impacts associated with less durable materials.
The Inert Nature of Final PTFE
It is critical to distinguish between the manufacturing process and the final product. Solid, finished PTFE is chemically inert and stable. The primary environmental danger lies with the escape of processing aids like PFOA during its creation.
The Lifecycle Consideration
The decision to use PTFE involves a complex lifecycle assessment. One must weigh the significant, localized environmental hazard of its production against the potential long-term benefit of a product that will not need to be replaced for many years.
Evaluating PTFE for Your Application
Choosing whether to use PTFE requires a clear understanding of your project's priorities and the potential downstream consequences.
- If your primary focus is avoiding persistent pollutants: You should investigate PTFE alternatives, as the risk of contamination within the global supply chain remains a significant concern.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability in a harsh environment: PTFE may be a justifiable choice, as its long service life can prevent the greater cumulative waste from manufacturing and replacing less resilient materials.
Ultimately, the responsible use of PTFE hinges on weighing its exceptional in-service performance against the significant environmental hazards of its production.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Impact | Key Concern |
|---|---|
| Primary Hazard | Release of PFAS (e.g., PFOA) during manufacturing |
| Persistence | 'Forever chemicals' resist degradation for decades |
| Contamination | Pollution of air, soil, and water sources |
| Final Product | Solid PTFE is inert, but production byproducts are hazardous |
Need High-Performance, Precision PTFE Components?
Choosing the right materials partner is critical for balancing performance with environmental responsibility. At KINTEK, we are committed to precision manufacturing and sustainable practices.
We supply high-quality, custom-fabricated PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. From prototypes to high-volume orders, we prioritize quality and reliability to ensure your components last longer, reducing waste and replacement cycles.
Let us help you meet your technical requirements with integrity. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are PTFE and Teflon, and why are they important? Unlock the Power of High-Performance Polymers
- Why is PTFE's chemical resistance important for industrial use? Ensure Operational Safety and Reliability
- What unique characteristic of PTFE prevents geckos from sticking to it? Its Extremely Low Surface Energy
- How do molybdenum disulfide fillers improve PTFE? Enhance Wear Resistance and Lubricity
- Is there any difference between PTFE and Teflon? Understanding the Brand vs. Material Distinction
- How does PTFE compare to other materials in terms of chemical resistance? The Unmatched Leader in Chemical Inertness
- How does PTFE compare to Polyethylene (PE) in terms of chemical and temperature resistance? Choose the Right Polymer for Extreme Conditions
- What forms does Teflon come in? A Guide to PTFE States, Formulations, and Applications



















