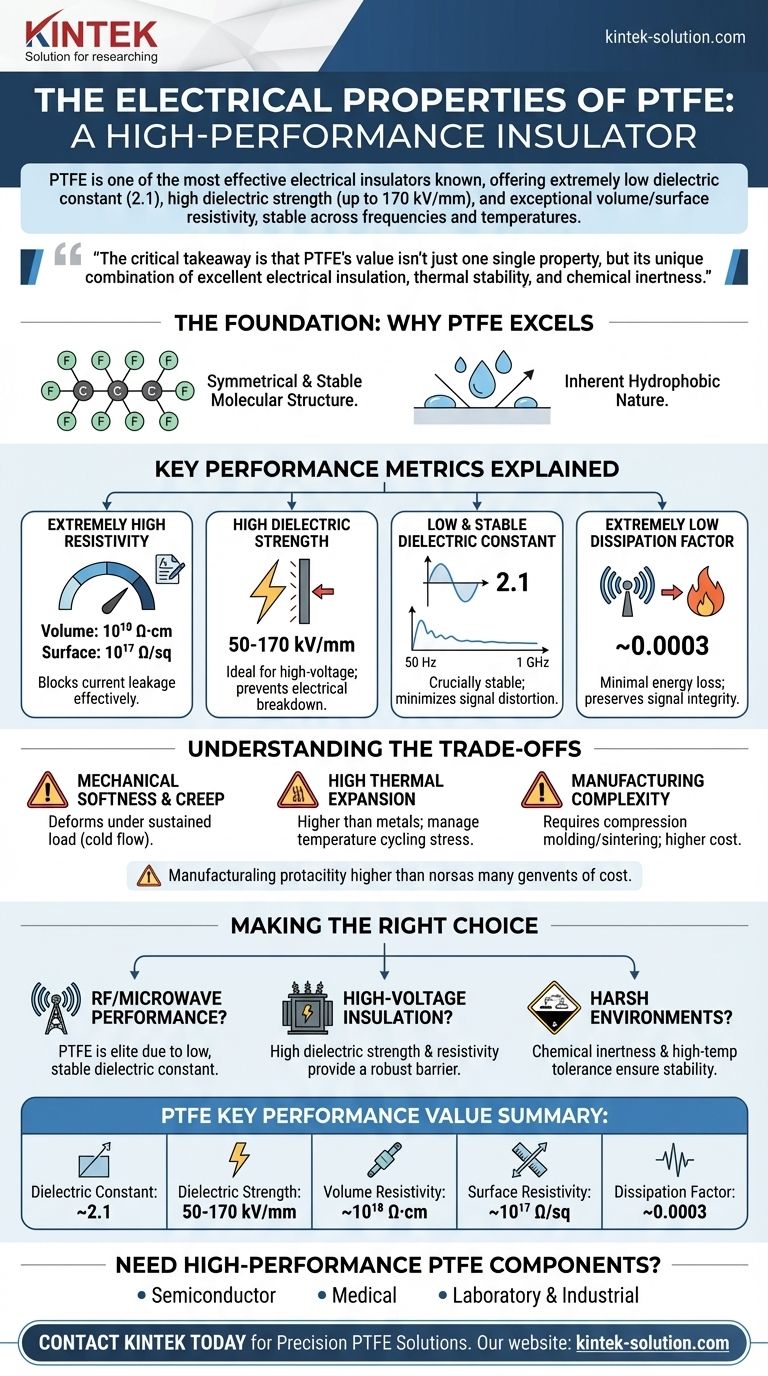
In summary, PTFE is one of the most effective electrical insulators known. Its performance stems from a combination of an extremely low dielectric constant (2.1), high dielectric strength (up to 170 kV/mm), and exceptionally high volume and surface resistivity. These properties remain stable across a wide range of frequencies and temperatures, making it a benchmark material for demanding electrical and electronic applications.
The critical takeaway is that PTFE's value isn't just one single property, but its unique combination of excellent electrical insulation, thermal stability, and chemical inertness. This synergy makes it a highly reliable choice where performance cannot be compromised.

The Foundation: Why PTFE Excels as an Insulator
The exceptional electrical properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are not accidental; they are a direct result of its unique molecular architecture.
A Symmetrical and Stable Molecular Structure
At its core, PTFE consists of a long chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by fluorine atoms. The high electronegativity of fluorine creates an incredibly stable and non-polar molecular sheath.
This structure prevents electron displacement when an electric field is applied, which is the fundamental reason for its superb insulating capabilities.
Inherent Hydrophobic Nature
PTFE is highly hydrophobic, meaning it actively repels water. In electrical applications, moisture can create conductive paths on an insulator's surface, leading to shorts or signal degradation.
Because PTFE resists water and is chemically inert, its surface integrity and insulating properties are maintained even in humid or corrosive environments.
Key Electrical Performance Metrics Explained
To properly evaluate PTFE, it is essential to understand the specific metrics that define its performance as a world-class insulator.
Extremely High Resistivity
Resistivity measures a material's opposition to the flow of electric current. PTFE excels in both volume and surface resistivity, with typical values of 10¹⁸ Ω·cm and 10¹⁷ Ω/sq, respectively.
These astronomically high numbers signify that it is incredibly effective at blocking current leakage, both through its bulk and across its surface.
High Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength is the maximum electric field a material can withstand without "breaking down" and becoming conductive. PTFE has a very high dielectric strength, typically in the range of 50-170 kV/mm.
This makes it an ideal insulator for high-voltage applications, from wiring to high-power capacitors, as it can prevent electrical arcing and failure under significant electrical stress.
Low and Stable Dielectric Constant
The dielectric constant indicates a material's ability to store electrical energy in an electric field. PTFE's dielectric constant is very low, around 2.1.
Crucially, this value remains remarkably stable across a vast frequency spectrum, from 50 Hz up to 1 GHz (10⁹ Hz). A low, stable constant is vital for high-frequency applications like coaxial cables and microwave circuits, as it minimizes signal distortion and capacitance issues.
Extremely Low Dissipation Factor
The dissipation factor, or loss tangent, measures how much of a signal's energy is absorbed and lost as heat within the insulator. PTFE has a very low dissipation factor of approximately 0.0003.
This minimal energy loss is critical for preserving signal integrity in high-frequency and RF applications, ensuring that power is transmitted efficiently without being wasted as heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While its electrical properties are outstanding, PTFE is not the ideal choice for every situation. A true technical evaluation requires acknowledging its limitations.
Mechanical Softness and Creep
PTFE is a relatively soft material with poor creep resistance, often referred to as "cold flow." Under sustained mechanical load, especially at elevated temperatures, the material can deform permanently. This must be accounted for in structural designs.
High Thermal Expansion
The coefficient of thermal expansion for PTFE is significantly higher than that of metals. In assemblies that experience temperature cycling, this mismatch must be carefully managed to avoid stress and component failure.
Manufacturing Complexity
PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt-processing techniques like injection molding. Instead, it requires specialized methods like compression molding and sintering, which can increase manufacturing complexity and cost compared to more common thermoplastics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final material decision should be guided by the primary demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency performance (RF/Microwave): PTFE is an elite choice due to its low, stable dielectric constant and minimal dissipation factor, which preserve signal integrity.
- If your primary focus is high-voltage insulation: PTFE's high dielectric strength and phenomenal resistivity provide a robust and reliable barrier against electrical breakdown.
- If your primary focus is reliability in harsh environments: PTFE's chemical inertness and high-temperature tolerance ensure its electrical properties will not degrade when exposed to corrosive substances or heat.
Ultimately, PTFE's electrical performance makes it a premier material for applications where failure is not an option.
Summary Table:
| Key Electrical Property | PTFE Performance Value |
|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant | ~2.1 (stable from 50 Hz to 1 GHz) |
| Dielectric Strength | 50-170 kV/mm |
| Volume Resistivity | ~10¹⁸ Ω·cm |
| Surface Resistivity | ~10¹⁷ Ω/sq |
| Dissipation Factor | ~0.0003 |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Critical Application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—that leverage these exceptional electrical properties. Our expertise is critical for industries where performance cannot be compromised, such as:
- Semiconductor: For high-purity, high-frequency applications.
- Medical: Where reliability and biocompatibility are paramount.
- Laboratory & Industrial: For harsh chemical and high-temperature environments.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components meet exact specifications for dielectric strength, signal integrity, and long-term reliability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our precision PTFE solutions can enhance your product's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE considered important in RF PCB applications? Ensure Superior Signal Integrity
- What are some challenges in CNC machining Teflon? Mastering Material Instability for Precision Parts
- How does PTFE perform in chemical resistance applications? Unmatched Inertness for Harsh Environments
- Why are PTFE bushes suitable for high-temperature environments? Unlock Superior Heat & Chemical Resistance
- How are PTFE gaskets utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing? Ensuring Purity and Compliance
- What are the characteristics of Modified PTFE with Premium Organic Fill? Superior Wear Resistance Without Abrasion
- What are the advantages of using PTFE rotary seals over rubber elastomer seals? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the advantages of using PTFE lip seals over traditional radial shaft seals? Maximize Performance in Harsh Conditions



















