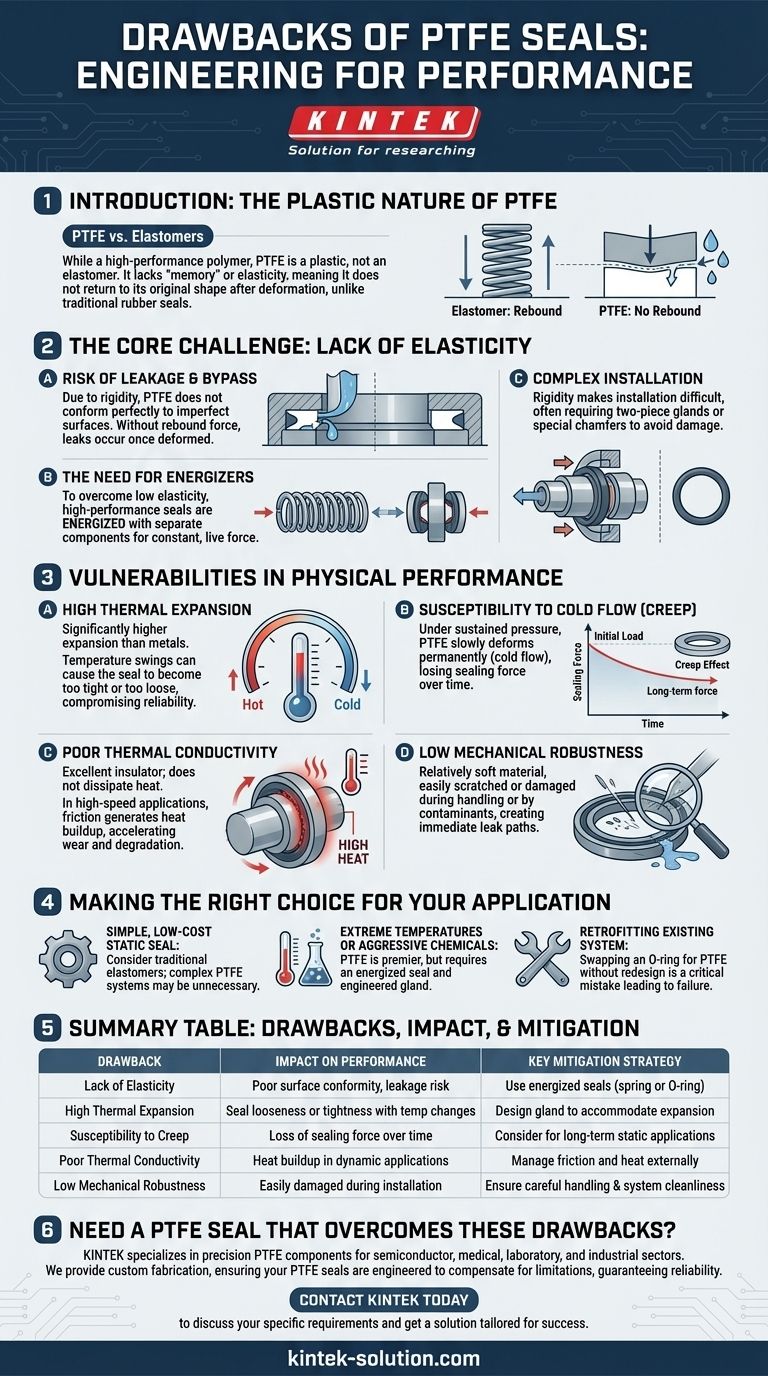
While PTFE is a high-performance polymer, its primary drawbacks stem from its inherent nature as a plastic, not an elastomer. This lack of "memory" or elasticity means it does not readily return to its original shape, leading to potential leakage if not paired with an energizer. Furthermore, its physical properties, such as high thermal expansion and susceptibility to creep, require careful engineering consideration to prevent seal failure.
The core issue is that PTFE is not a universal, drop-in replacement for rubber seals. Its successful application depends entirely on a system design that actively compensates for its inherent rigidity, thermal sensitivity, and mechanical limitations.
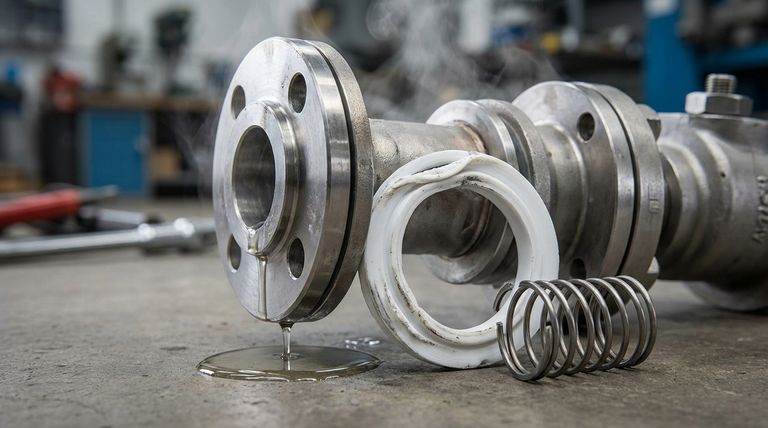

The Core Challenge: Lack of Elasticity
The fundamental difference between PTFE and traditional elastomeric seals (like rubber) is its plastic nature. This creates several engineering challenges that must be addressed in the design phase.
Risk of Leakage and Bypass
Because PTFE is rigid, it does not conform perfectly to sealing surfaces on its own. Microscopic imperfections in hardware can create leak paths that a more compliant rubber seal would easily fill.
This lack of "rebound" means that once compressed or deformed, PTFE has very little internal force pushing back to maintain a tight seal.
The Need for Energizers
To overcome its low elasticity, most high-performance PTFE seals are energized. This involves incorporating a separate component, such as a metal spring or an elastomeric O-ring, into the seal design.
This energizer provides the constant, live force needed to press the PTFE lips against the sealing surfaces, maintaining contact and preventing leaks even under fluctuating pressures or temperatures.
Complex Installation Requirements
The rigidity of PTFE makes installation more difficult than with flexible rubber seals. It cannot be easily stretched or squeezed into tight grooves.
This often necessitates more complex hardware designs, such as two-piece glands, retaining flanges, or specially designed chamfers to allow the seal to be properly seated without damage.
Vulnerabilities in Physical Performance
Beyond its lack of elasticity, PTFE has several other physical characteristics that can be liabilities if not properly managed in the application design.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a significantly higher coefficient of thermal expansion compared to most metals. This means it expands and contracts much more with temperature changes.
In applications with wide temperature swings, this can cause the seal to become too tight (increasing friction and wear) or too loose (causing leakage), compromising its reliability.
Susceptibility to Cold Flow (Creep)
Under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE is prone to cold flow, also known as creep. This is a slow, permanent deformation of the material.
Over time, creep can cause the seal to lose its initial pre-load and sealing force, leading to eventual failure. This is a critical consideration in long-term static sealing applications.
Poor Thermal Conductivity
PTFE is an excellent thermal insulator, which means it does not dissipate heat well. In high-speed dynamic applications, friction can generate significant heat.
Because the seal cannot effectively shed this heat, temperatures can build up at the sealing interface, potentially accelerating wear, causing material degradation, and exacerbating thermal expansion issues.
Low Mechanical Robustness
While durable in a chemical sense, PTFE is a relatively soft material. The sealing surfaces can be easily scratched or damaged during installation or by contaminants in the system.
Any damage to the critical sealing lip can immediately create a leak path, making careful handling and system cleanliness essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these drawbacks is not a reason to avoid PTFE, but a guide to using it correctly. Its performance is unmatched in certain contexts, but only when the complete system is designed to support it.
- If your primary focus is a simple, low-cost static seal: Consider traditional elastomers, as the complexity and cost of a properly designed PTFE sealing system may be unnecessary.
- If your primary focus is sealing in extreme temperatures or with aggressive chemicals: PTFE is a premier choice, but you must engineer the gland and select an energized seal to compensate for its lack of elasticity and thermal expansion.
- If your primary focus is retrofitting an existing system: Be aware that simply swapping an O-ring for a PTFE seal without redesigning the groove is a common and critical mistake that almost always leads to failure.
By understanding and designing for these limitations, you can successfully leverage PTFE's unparalleled performance in the applications where it truly excels.
Summary Table:
| Drawback | Impact on Performance | Key Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Lack of Elasticity | Poor surface conformity, risk of leakage | Use energized seals (spring or O-ring) |
| High Thermal Expansion | Seal looseness or tightness with temperature changes | Design gland to accommodate expansion |
| Susceptibility to Creep | Loss of sealing force over time | Consider for long-term static applications |
| Poor Thermal Conductivity | Heat buildup in dynamic applications | Manage friction and heat externally |
| Low Mechanical Robustness | Easily damaged during installation | Ensure careful handling and system cleanliness |
Need a PTFE Seal That Overcomes These Drawbacks?
PTFE's performance is unmatched for extreme temperatures and aggressive chemicals, but only when the seal is correctly designed and manufactured. KINTEK specializes in precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We provide custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensuring your PTFE seals are engineered to compensate for their inherent limitations, guaranteeing reliability and longevity in your most demanding applications.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and get a solution tailored for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why are pressure conditions important when choosing PTFE packing? Ensure a Reliable Seal for Your System
- What are the key properties of PTFE Teflon O-rings? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the main benefits of PTFE envelope gaskets? Achieve Superior Chemical Resistance and Sealing Integrity
- What are the maintenance requirements for PTFE slide bearings? Ensure Long-Term, Maintenance-Free Performance
- What are common applications of low-friction PTFE? Solve Friction & Corrosion Challenges
- Why are PTFE gaskets important in systems with varying temperatures? Ensure Leak-Proof Sealing from Cryogenic to High Heat
- How does surface finish impact PTFE sheet performance? A Guide to Optimizing for Your Application
- What are the advantages of using Teflon-coated bolts? Achieve Reliable Performance in Harsh Environments



















