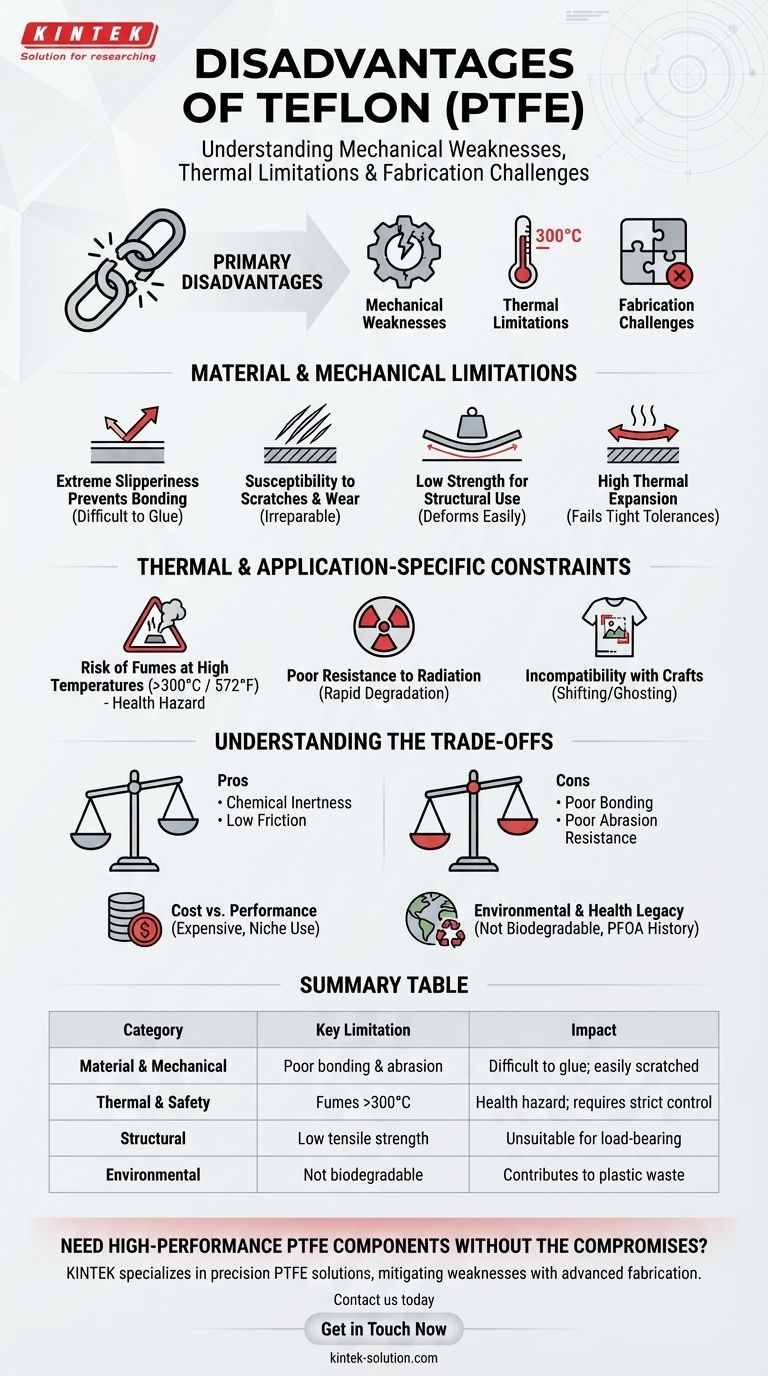
The primary disadvantages of Teflon (PTFE) are its mechanical weaknesses, thermal limitations, and fabrication challenges. While prized for being non-stick, this very property makes it difficult to bond with adhesives, and it is susceptible to scratches, has poor strength for structural use, and can release toxic fumes if heated above 300°C (572°F).
Teflon's greatest strengths are also the source of its most significant weaknesses. Its chemical inertness and extreme slipperiness make it uniquely valuable for certain applications, but these same properties create considerable limitations in wear resistance, structural integrity, and bonding capability.

Material and Mechanical Limitations
Teflon’s core chemical structure results in physical properties that make it unsuitable for many common engineering and manufacturing scenarios.
### Extreme Slipperiness Prevents Bonding
The famous non-stick quality of Teflon is a significant disadvantage when you need to glue or bond it to other surfaces. Its low surface energy repels almost all adhesives.
Achieving a strong bond requires expensive and complex surface treatments, such as chemical etching, which are often not practical.
### Susceptibility to Scratches and Wear
Teflon is a relatively soft material with poor abrasion resistance. Coatings can be easily scratched by metal utensils or abrasive materials, compromising the non-stick surface.
Once a Teflon coating is worn down or damaged, it is irreparable, requiring the entire part to be replaced or recoated.
### Low Strength for Structural Use
Teflon has low tensile strength and stiffness, meaning it deforms easily under load. This makes it a poor choice for any load-bearing or structural applications.
### High Thermal Expansion
Compared to metals and even most other plastics, Teflon exhibits a very high coefficient of thermal expansion.
This means it expands and contracts significantly with temperature changes, which can cause components to fail in applications that require tight tolerances.
Thermal and Application-Specific Constraints
While known for heat resistance, Teflon has a clear operational ceiling and specific weaknesses that can cause failure.
### Risk of Fumes at High Temperatures
This is Teflon's most critical safety limitation. When heated above 300°C (572°F), it begins to decompose and release toxic fluorocarbon gases.
These fumes can cause polymer fume fever, a temporary flu-like illness, and pose a significant health risk, especially in unventilated areas.
### Poor Resistance to Radiation
Teflon has very poor resistance to high-energy radiation, such as gamma rays. Exposure causes the material's molecular structure to break down, leading to rapid degradation and loss of its mechanical properties.
### Incompatibility with Certain Crafts
In heat press applications for apparel or crafts, Teflon sheets can cause issues. They may absorb too much heat, affecting transfer quality.
Their slippery surface can also cause graphics to shift during pressing, leading to misaligned or "ghosted" images, particularly with dye-sublimation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing to use Teflon requires a clear understanding of its compromises, particularly regarding its core properties, cost, and environmental impact.
### The Double-Edged Sword of Inertness
Teflon's defining feature is its chemical inertness. This makes it incredibly resistant to chemicals but also contributes to its difficulty in bonding and its environmental persistence.
Similarly, its low coefficient of friction makes it an excellent bearing surface but also contributes to its poor abrasion resistance.
### Cost vs. Performance
Teflon is generally more expensive than many other polymers. Its price is only justified in applications where its unique combination of non-stick, chemical resistance, and low-friction properties is absolutely essential.
### Environmental and Health Legacy
Historically, the manufacturing of Teflon involved PFOA, a persistent environmental pollutant. While PFOA has been phased out of production by major manufacturers, the material's legacy raises environmental concerns.
Furthermore, Teflon is not biodegradable, contributing to plastic waste if not properly recycled, which can be a complex and energy-intensive process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if Teflon is appropriate, you must weigh its distinct advantages against its significant limitations.
- If your primary focus is a non-stick or low-friction surface: Teflon is an excellent choice, but you must account for its low scratch resistance and operate well below its 300°C (572°F) temperature limit.
- If your primary focus is a structural or load-bearing component: You should choose a different material, as Teflon lacks the required strength and stiffness.
- If your primary focus is an application requiring adhesives: Avoid Teflon unless you are prepared to implement specialized and costly surface preparation techniques.
- If your primary focus is a high-radiation or high-temperature (above 300°C) environment: Teflon is fundamentally unsuitable and potentially hazardous.
Ultimately, selecting the right material depends on a clear-eyed assessment of its inherent weaknesses, not just its advertised strengths.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Limitation | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Material & Mechanical | Poor bonding & abrasion resistance | Difficult to glue; easily scratched |
| Thermal & Safety | Fumes above 300°C (572°F) | Health hazard; requires strict temperature control |
| Structural | Low tensile strength & stiffness | Unsuitable for load-bearing applications |
| Environmental | Not biodegradable; complex recycling | Contributes to plastic waste if not handled properly |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components Without the Compromises?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware, and more) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the limitations of Teflon and use advanced fabrication techniques to deliver solutions that maximize its benefits while mitigating its weaknesses.
Our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure you get the right part for your specific application, with a focus on durability, safety, and performance.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and let our expertise guide you to the optimal material solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What impact has PTFE industrial coating had on daily life? Unlocking Modern Convenience & Performance
- How do molybdenum disulfide fillers improve PTFE? Enhance Wear Resistance and Lubricity
- How is Expanded PTFE (EPTFE) material constructed? A Deep Dive into the Microporous Transformation
- How is RPTFE different from standard PTFE in composition? A Guide to Enhanced Material Performance
- How have material producers attempted to mitigate creep in PTFE? Discover the Best Strategies for Your Application
- How does the electronegativity of fluorine affect PTFE's structure? The Key to Its Unmatched Chemical Resistance
- What makes PTFE plastic uniquely versatile across industries? The 4 Key Properties Explained
- How does PTFE perform as an electrical insulator? Unmatched Signal Integrity & High-Voltage Reliability



















