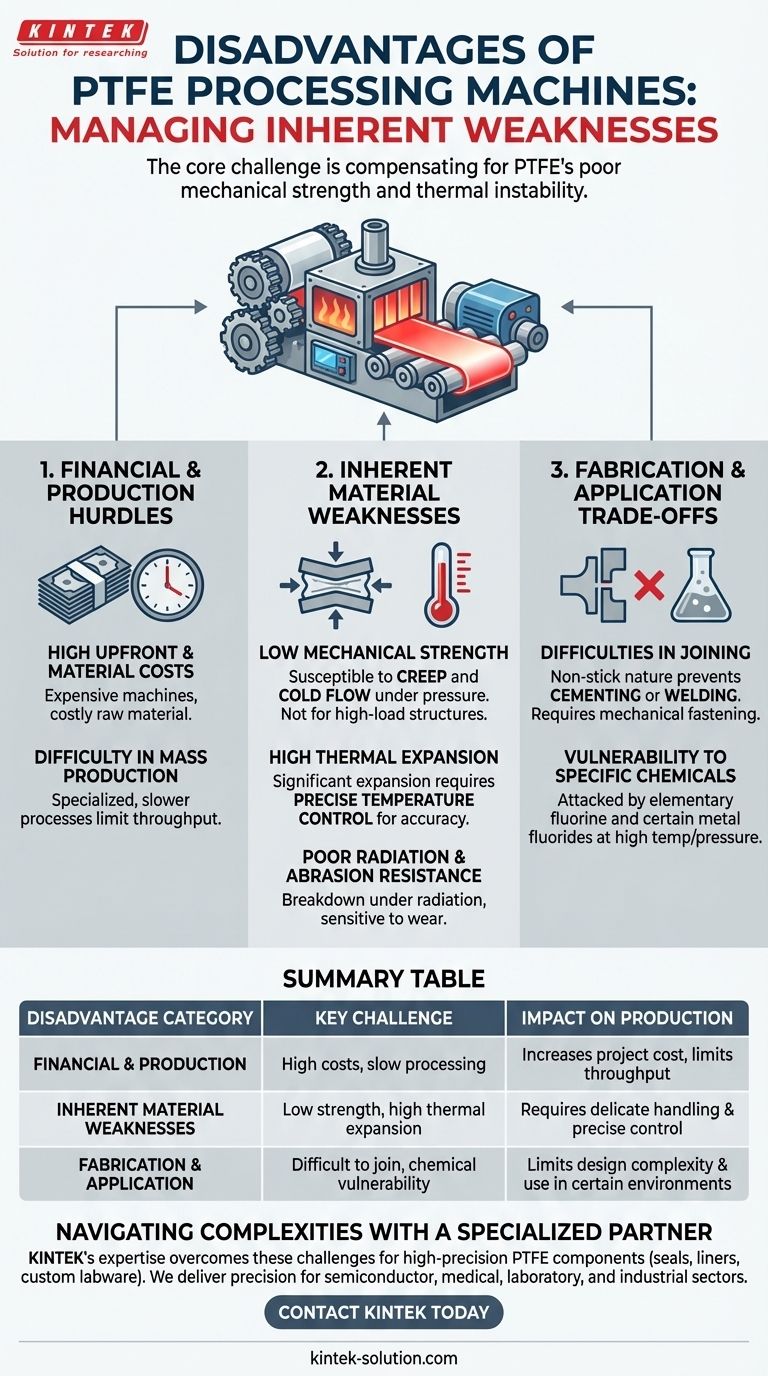
The primary disadvantages of PTFE processing machines are directly tied to the inherent and challenging properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) itself. These include high operational and manufacturing costs, the need to compensate for the material's low mechanical strength, and the requirement for sophisticated controls to manage its high thermal expansion.
The core challenge is that PTFE processing machines are not just shaping a material; they are managing a material with inherent weaknesses. Their primary disadvantages—cost, complexity, and precision requirements—are all necessary compensations for PTFE's poor mechanical strength and thermal instability.

The Financial and Production Hurdles
Processing PTFE is a resource-intensive endeavor, which introduces significant financial and logistical challenges compared to working with more common polymers.
High Upfront and Material Costs
The machines themselves are expensive to produce due to the complex systems required to handle PTFE properly. Furthermore, the raw PTFE material is more costly than many other polymers, adding to the overall expense of any project.
Difficulty in Mass Production
PTFE's unique properties make it ill-suited for traditional, high-speed mass production methods. The specialized processes, such as compression and sintering, are often slower and more complex, limiting production throughput.
Inherent Material Weaknesses to Overcome
The most significant disadvantages stem from the physical and chemical properties of PTFE. The processing equipment must be engineered specifically to work around these limitations.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a soft material that is highly susceptible to creep and cold flow, meaning it will deform over time when under pressure. This lack of sturdiness makes it unsuitable for high-load structural applications.
Processing machines must handle the material delicately to avoid causing damage or deformation during the manufacturing cycle.
High Thermal Expansion Coefficient
PTFE expands and contracts significantly with changes in temperature. This requires extremely precise temperature control during processing to maintain dimensional accuracy and tight tolerances in the final part.
Failure to manage this can result in inconsistent or out-of-spec products, especially in environments with fluctuating temperatures.
Poor Radiation and Abrasion Resistance
The material does not stand up well to high-energy radiation, which can cause its molecular structure to break down. It is also sensitive to abrasion and wear, which must be considered in both the part design and the handling process.
Understanding the Fabrication and Application Trade-offs
While known for its chemical inertness and low friction, PTFE presents clear limitations that affect its use in certain applications.
Difficulties in Joining and Assembly
PTFE is famously non-stick, which means it cannot be cemented or welded using conventional methods. This severely limits fabrication options for creating complex assemblies, often requiring mechanical fastening as an alternative.
Vulnerability to Specific Chemicals
While resistant to most chemicals, PTFE is not invincible. It can be attacked by highly reactive agents like elementary fluorine and certain metal fluorides, particularly at high temperatures and pressures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Navigating these disadvantages requires aligning your project's goals with the material's inherent properties.
- If your primary focus is high-load structural components: PTFE is a poor choice due to its low mechanical strength and tendency to creep under pressure.
- If your primary focus is achieving tight tolerances: You must invest in processing equipment with precise thermal controls to manage PTFE's high expansion coefficient.
- If your primary focus is rapid, low-cost mass production: The high material cost and complex, slower processing of PTFE make other polymers more suitable.
Ultimately, successfully processing PTFE depends on acknowledging its limitations and employing specialized machinery designed to overcome them.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenge | Impact on Production |
|---|---|---|
| Financial & Production | High upfront machine & material costs, slow processing | Increases project cost, limits mass production throughput |
| Inherent Material Weaknesses | Low mechanical strength (creep/cold flow), high thermal expansion | Requires delicate handling, demands precise temperature control for accuracy |
| Fabrication & Application | Difficult to join/weld, vulnerable to specific chemicals | Limits design complexity, restricts use in certain chemical environments |
Navigating the complexities of PTFE processing requires a specialized partner. At KINTEK, we understand these challenges intimately. Our expertise in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—is built on overcoming these very disadvantages. We utilize advanced fabrication techniques and precise controls to ensure your parts meet the highest standards for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, let KINTEK deliver the precision and reliability your application demands.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your PTFE component needs and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















