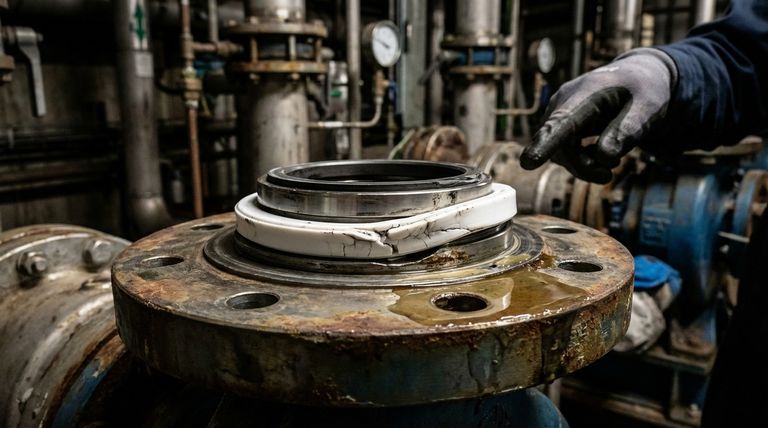
While highly valued for their chemical resistance, mechanical seals with PTFE rings possess critical disadvantages that can lead to failure if not properly understood. The primary drawbacks stem from its physical properties, including low mechanical strength, a high coefficient of thermal expansion, and installation difficulties, which often make it unsuitable for high-load or thermally dynamic applications.
The core challenge with PTFE seals is the conflict between their exceptional chemical resilience and their inherent physical weaknesses. Success depends on designing the application around the material's poor mechanical strength and thermal instability, not in spite of them.

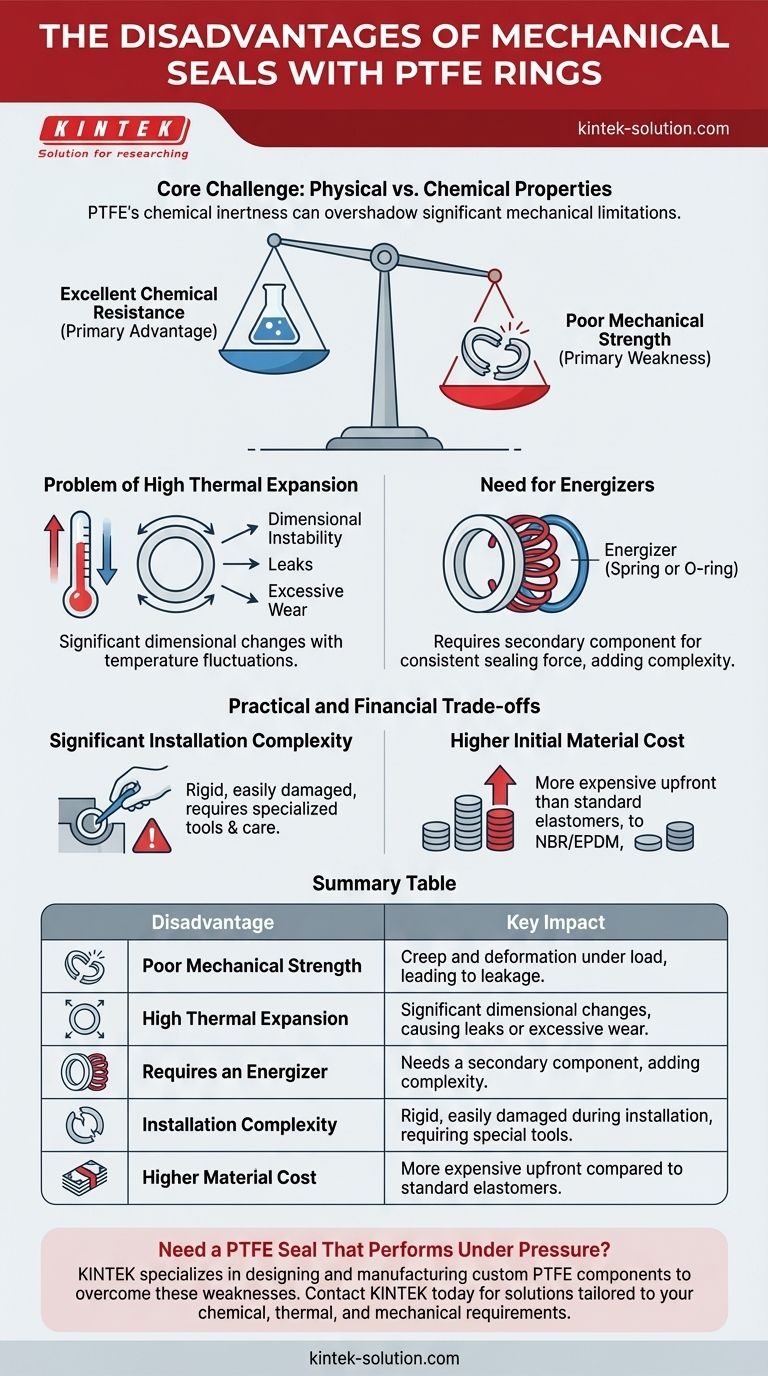
The Core Challenge: Physical vs. Chemical Properties
PTFE's reputation is built on its near-universal chemical inertness, but this single benefit can overshadow its significant mechanical limitations.
Excellent Chemical Resistance (The Primary Advantage)
PTFE is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. This, combined with its extremely low coefficient of friction, makes it a go-to material for sealing in corrosive environments where elastomers would quickly degrade.
Poor Mechanical Strength (The Primary Weakness)
The main drawback of PTFE is its nature as a "plastic" rather than an elastomer. It is susceptible to creep and deformation, especially under high pressure or load. This can cause the seal to lose its shape and sealing force over time, resulting in leakage.
This low strength also makes pure PTFE seals unsuitable for high dynamic load applications, where pressure spikes or frequent movement can cause the material to deform permanently.
How Environmental Factors Expose PTFE's Weaknesses
The operational environment, particularly temperature, plays a critical role in the performance of a PTFE seal and can quickly expose its core weaknesses.
The Problem of High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a very high coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts significantly with temperature changes. A seal that fits perfectly at room temperature may become too loose (causing leaks) or too tight (causing excessive friction and wear) as the system heats up or cools down.
This dimensional instability is a major liability in applications with wide or rapid temperature fluctuations.
The Need for Energizers to Compensate
Because PTFE is rigid and does not have the "memory" of rubber, it often cannot maintain consistent contact with a sealing surface on its own. To overcome this, many PTFE seals require an energizer, such as a rubber O-ring or a metal spring, placed behind the ring.
The energizer provides the constant force needed to keep the PTFE lip pressed against the hardware. However, this adds complexity and introduces another material that must be compatible with the system's chemistry and temperature.
Practical and Financial Trade-offs
Beyond the material's physical properties, there are practical considerations that can make PTFE a challenging and costly choice.
Significant Installation Complexity
PTFE's rigidity can make installation exceptionally difficult. Unlike a flexible rubber O-ring that can be easily stretched into a groove, a solid PTFE ring can be easily scratched, gouged, or permanently deformed if not installed with extreme care and specialized tools.
This often necessitates more complex hardware designs, such as multi-part glands or retainer plates, to allow the seal to be installed correctly without damage.
Higher Initial Material Cost
Compared to many common elastomers like NBR, EPDM, or even FKM (Viton™), PTFE is a more expensive material. While its long life in a chemically aggressive environment can justify the cost, the initial investment is a clear disadvantage for applications where a less expensive material would suffice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Carefully weighing these disadvantages against PTFE's benefits is crucial for selecting the right seal and avoiding premature failure.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals at stable temperatures: PTFE is an excellent candidate, provided the mechanical loads are well within its limits.
- If your application involves high pressures or dynamic loads: You should strongly consider more robust materials like PEEK, other engineered plastics, or metal seals, as PTFE will likely deform and fail.
- If your system experiences significant temperature swings: A standard PTFE seal is a high-risk choice; you must engineer the hardware to accommodate its thermal expansion or select a more dimensionally stable material.
- If your main constraints are budget and simple assembly: Standard elastomers are almost always a more practical and cost-effective solution for less demanding chemical environments.
Understanding these physical and practical limitations is the key to successfully leveraging PTFE's unmatched chemical resistance.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Poor Mechanical Strength | Susceptible to creep and deformation under load, leading to leakage. |
| High Thermal Expansion | Significant dimensional changes with temperature, causing leaks or excessive wear. |
| Requires an Energizer | Needs a secondary component (e.g., spring) to maintain sealing force, adding complexity. |
| Installation Complexity | Rigid material is easily damaged during installation, requiring specialized tools and care. |
| Higher Material Cost | More expensive upfront compared to standard elastomers like NBR or EPDM. |
Need a PTFE Seal That Performs Under Pressure?
PTFE's disadvantages—like creep and thermal instability—can be engineered around. KINTEK specializes in designing and manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) that overcome these inherent material weaknesses.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, providing precision production from prototypes to high-volume orders. Don't let material limitations compromise your application.
Contact KINTEK today for a solution tailored to your specific chemical, thermal, and mechanical requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the characteristics of graphite PTFE gland packings? High-Performance Sealing for Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE benefit the electronics industry? Achieve Superior Signal Integrity & Reliability
- What design parameters are specified for PTFE sliding bearings? Ensure Structural Safety and Performance
- What are the medical applications of PTFE coatings? Essential Guide for Safer Medical Devices
- What do the ratings A, B, and C indicate in the chemical resistance table for Filled PTFE? A Guide to Material Safety
- What are PTFE bellows and what are they made of? Solve Tough Chemical & Thermal Challenges
- Why are PTFE coated fasteners used in electronics and telecommunications? Ensure Reliability and Signal Integrity
- What are the operational temperature limits for PTFE-lined diaphragm valves? Understanding the Full System Range



















