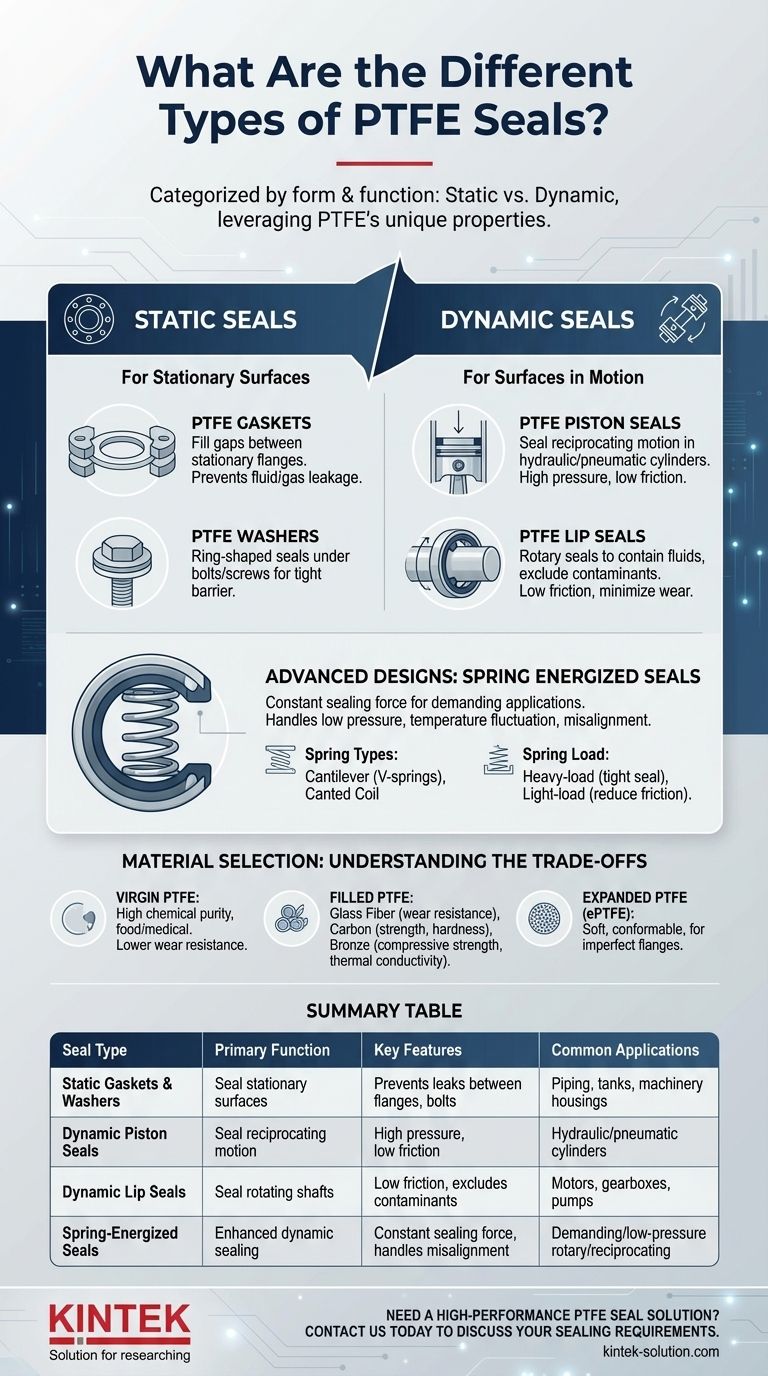
At their core, PTFE seals are categorized by their form and function, most commonly as static gaskets and washers or dynamic piston and lip seals. These designs leverage Polytetrafluoroethylene's unique properties to prevent leaks in a vast range of industrial applications, from stationary pipes to high-speed rotating shafts.
The shape of a PTFE seal answers "what" it is, but its material composition (virgin, filled) and design features (like spring energizing) answer "how" it will perform. True selection requires matching the seal's design and material to the specific operational demands of temperature, pressure, and motion.

The Foundation: Why Choose PTFE for Sealing?
Before diving into the types of seals, it is critical to understand why PTFE is such a sought-after sealing material. Its performance is rooted in a unique combination of chemical and physical properties.
Exceptional Temperature Range
PTFE seals operate effectively across an incredibly wide thermal spectrum, typically from cryogenic temperatures of -200°C (-328°F) up to 260°C (500°F).
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert, resisting almost all industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This makes it the default choice for applications involving aggressive media.
Extremely Low Friction
Known for its slippery, non-stick surface, PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This property is vital for dynamic seals, as it reduces wear, minimizes heat generation, and lowers energy consumption.
Classifying Seals by Function and Form
The most fundamental way to categorize PTFE seals is by whether they are designed for static or dynamic applications.
Static Seals: Gaskets and Washers
Static seals are used between two components that do not move relative to each other.
- PTFE Gaskets: These are flat seals designed to fill the microscopic gaps between two stationary flange faces, such as in piping, tanks, or machinery housings. Their job is to create a barrier and prevent fluid or gas leakage.
- PTFE Washers: These are simple, ring-shaped seals that provide a leak-proof barrier, often used under the head of a bolt or screw to ensure a tight seal against a surface.
Dynamic Seals: Piston and Lip Seals
Dynamic seals are used where one sealing surface is in motion relative to another.
- PTFE Piston Seals: Used in hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders, these seals prevent fluid from bypassing the piston as it reciprocates. They are engineered for high pressure and low friction to ensure efficient cylinder operation.
- PTFE Lip Seals: These are rotary seals designed to contain fluids and exclude contaminants on rotating shafts. The flexible "lip" maintains contact with the shaft, creating a dynamic seal that minimizes friction and wear, making them common in motors, gearboxes, and pumps.
Advanced Designs: The Role of Spring Energizing
For demanding dynamic applications, a standard PTFE lip seal may not provide sufficient sealing force, especially at low pressures or where there is material shrinkage at low temperatures. This is where spring-energized seals excel.
What is a Spring-Energized Seal?
A spring-energized seal is a PTFE seal that incorporates a metallic spring in its jacket. This spring provides a constant, resilient load on the sealing lips, ensuring consistent contact with the sealing surfaces regardless of system pressure, temperature fluctuations, or minor hardware misalignment.
Key Spring Types
The type of spring used directly influences the seal's performance. Common options include cantilever (V-springs) and canted coil springs. Each provides a different load characteristic tailored to the application's needs.
Matching Spring Load to the Application
The spring's force can be customized. Heavy-load springs provide a very tight seal where some friction is acceptable. In contrast, light-load springs are used in high-speed or sensitive applications to reduce friction, minimize wear, and extend the service life of both the seal and the shaft.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Material Selection
The term "PTFE" represents a family of materials, not a single substance. The choice of PTFE grade is a critical trade-off between purity, cost, and mechanical performance.
Virgin PTFE
This is pure, unfilled Polytetrafluoroethylene. It offers the highest chemical resistance and is often required for food, medical, or semiconductor applications. However, it has lower resistance to wear and creep (deformation under load) compared to filled grades.
Filled PTFE
To enhance mechanical properties, PTFE can be blended with fillers.
- Glass Fiber increases wear resistance and stiffness.
- Carbon improves compressive strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
- Bronze significantly enhances compressive strength and thermal conductivity but should not be used with corrosive media.
Choosing a filled grade improves a seal's durability and pressure rating but may slightly reduce its chemical compatibility.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
This material is created by expanding virgin PTFE, resulting in a soft, highly conformable structure. It is excellent for gaskets used on damaged or irregular flanges because it compresses easily into a thin, strong seal under load.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal requires a clear understanding of your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is preventing leaks between stationary flanges: A PTFE gasket is your solution. Consider an expanded PTFE (ePTFE) gasket for older or imperfect flange surfaces.
- If your primary focus is sealing a rotating shaft in aggressive chemicals: A spring-energized PTFE lip seal is necessary. Select a filled PTFE material for durability and ensure the filler is compatible with the media.
- If your primary focus is sealing a reciprocating piston in a high-pressure cylinder: A filled PTFE piston seal designed for wear resistance and low friction is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is minimizing friction in a high-speed dynamic application: A spring-energized seal with a light-load spring is ideal to reduce wear and heat generation.
By aligning the seal's design and material with its intended function, you ensure optimal performance, reliability, and service life.
Summary Table:
| Seal Type | Primary Function | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Static Gaskets & Washers | Seal stationary surfaces | Prevents leaks between flanges, bolts | Piping, tanks, machinery housings |
| Dynamic Piston Seals | Seal reciprocating motion | High pressure, low friction | Hydraulic/pneumatic cylinders |
| Dynamic Lip Seals | Seal rotating shafts | Low friction, excludes contaminants | Motors, gearboxes, pumps |
| Spring-Energized Seals | Enhanced dynamic sealing | Constant sealing force, handles misalignment | Demanding/low-pressure rotary/reciprocating |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Seal Solution?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require a standard static gasket or a custom-designed, spring-energized dynamic seal, we provide expert material selection and fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to ensure reliability, chemical resistance, and long service life in your specific application.
Contact us today to discuss your sealing requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using PTFE bushes? Low-Friction, Chemical-Resistant Performance
- What role does coolant play in PTFE machining? Master Thermal and Chip Management for Precision Parts
- What property does graphite filler provide to PTFE? Achieve Superior Self-Lubrication and Low Friction
- What is the role of Teflon backup rings in sealing technology? Prevent Seal Extrusion & Boost Reliability
- What is the pH range that PTFE Enveloped Gaskets can handle? Achieve Universal Chemical Resistance
- What are the advantages of using PTFE guide strips in industrial applications? Enhance Equipment Life & Efficiency
- What tests are conducted on PTFE sliding rubber bearings? Ensure Your Structure's Safety and Movement
- What are the applications of Teflon rods in CNC machining and 3D printing? Solve Friction, Chemical, and Electrical Challenges



















