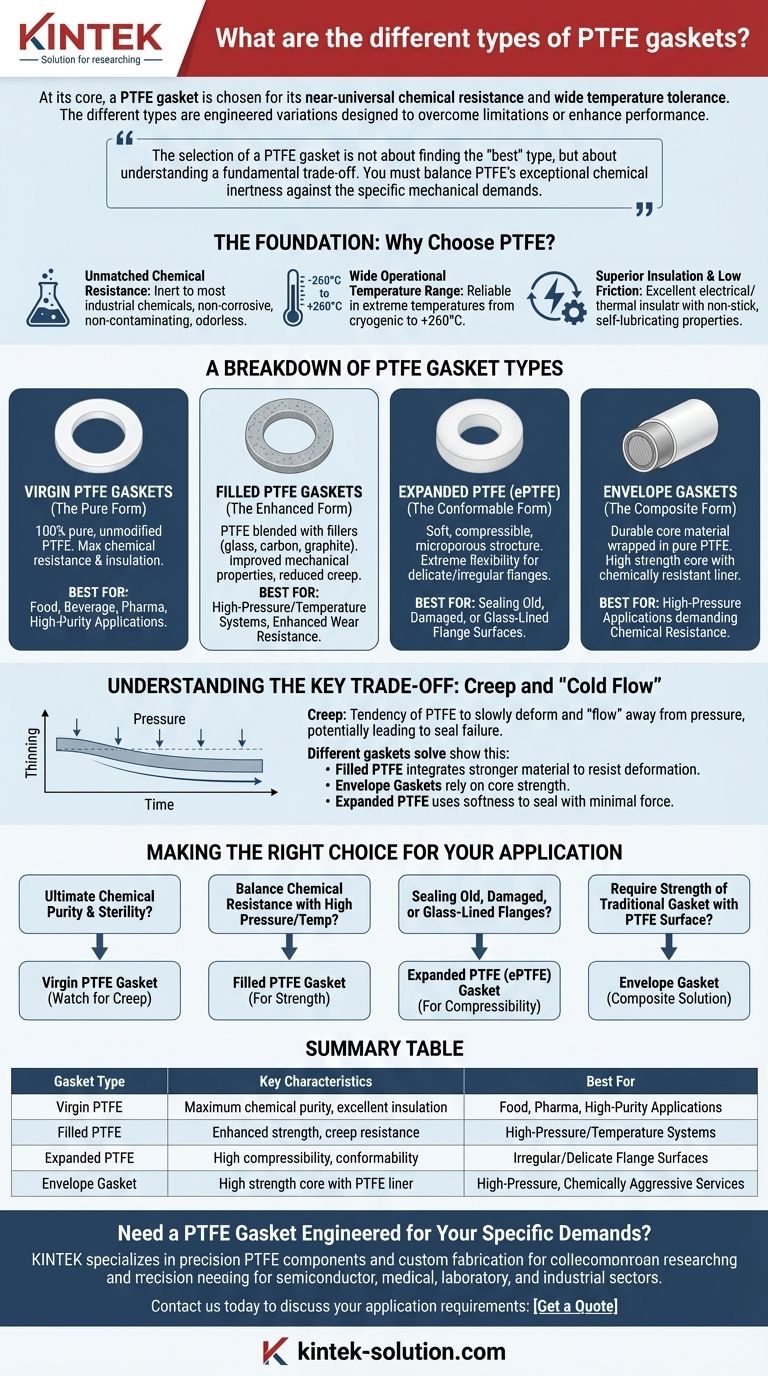
At its core, a PTFE gasket is chosen for its near-universal chemical resistance and wide temperature tolerance. The different types of PTFE gaskets are engineered variations on this theme, each designed to overcome the material's inherent limitations or enhance its performance for specific applications. The main categories are Virgin PTFE, for purity; Filled PTFE, for mechanical strength; Expanded PTFE, for conformability; and Envelope Gaskets, which offer a composite solution.
The selection of a PTFE gasket is not about finding the "best" type, but about understanding a fundamental trade-off. You must balance PTFE's exceptional chemical inertness against the specific mechanical demands of your system, such as pressure, temperature, and flange condition.

The Foundation: Why Choose PTFE in the First Place?
Before comparing types, it's crucial to understand the baseline properties that make PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) an elite gasket material. All variations share these fundamental strengths.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert and does not react with the vast majority of industrial chemicals. This makes it non-corrosive, non-contaminating, and odorless, which is critical for sensitive applications in pharmaceuticals, food processing, and aggressive chemical services.
Wide Operational Temperature Range
Standard PTFE performs reliably in extreme temperatures, from cryogenic conditions up to approximately +260°C (+500°F). This stability allows it to be used in a vast range of processes without degrading.
Superior Insulation and Low Friction
In its pure form, PTFE is an excellent electrical and thermal insulator. It also has an extremely low coefficient of friction, resulting in non-stick, self-lubricating properties that prevent material buildup on the gasket surface.
A Breakdown of PTFE Gasket Types
Each type of PTFE gasket is an engineered solution designed to enhance a specific property, most often to improve its mechanical performance under pressure.
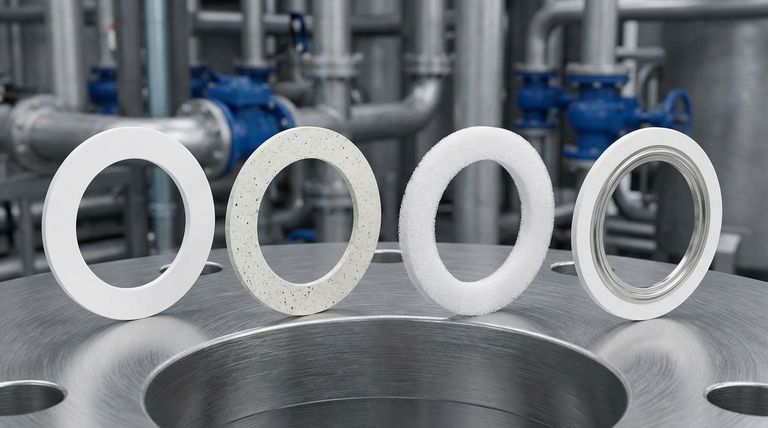
Virgin PTFE Gaskets (The Pure Form)
This is the most basic type, made from 100% pure, unmodified PTFE. It offers the maximum chemical resistance and electrical insulation of any variant.
It is the ideal choice when purity is the absolute priority, such as in food, beverage, or pharmaceutical applications.
Filled PTFE Gaskets (The Enhanced Form)
These gaskets are made by blending PTFE with filler materials like glass, carbon, or graphite. This process significantly improves the gasket's mechanical properties.
The primary goal of fillers is to reduce the material's tendency to creep or deform under load. Glass-filled PTFE offers enhanced wear resistance, while carbon-filled versions provide greater compressive strength.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) (The Conformable Form)
Expanded PTFE is a soft, highly compressible material with a microporous structure. It is produced by rapidly expanding PTFE under specific conditions.
Its extreme flexibility makes it perfect for sealing delicate, damaged, or irregular flange surfaces. It can create a tight seal with very low bolt torque, protecting fragile equipment.
Envelope Gaskets (The Composite Form)
An envelope gasket combines the best of both worlds. It consists of a durable core material (like compressed non-asbestos fiber or stainless steel) wrapped in a thin "envelope" of pure PTFE.
This design provides the high strength and rigidity of the core insert while ensuring only the chemically inert PTFE envelope touches the process fluid. It is an excellent solution for high-pressure applications that also demand PTFE's chemical resistance.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Creep and "Cold Flow"
The primary weakness of pure PTFE is its susceptibility to creep, also known as cold flow. This is the tendency of the material to slowly deform and "flow" away from the point of pressure over time.
The Impact of Cold Flow
Under the compressive load of a flange, a Virgin PTFE gasket can slowly thin out, leading to a loss of bolt torque and, potentially, a failed seal. This effect is accelerated at higher temperatures.
How Different Gaskets Solve This Problem
Filled and Envelope gaskets are direct engineering responses to the problem of cold flow.
- Filled PTFE integrates a stronger material into the PTFE matrix, creating a composite that physically resists deformation.
- Envelope Gaskets rely on the mechanical strength of their core insert to handle the compressive load, using the PTFE only as a chemically resistant liner.
- Expanded PTFE mitigates the issue in a different way; its incredible softness allows it to fill imperfections and seal with minimal force, reducing the stress that causes creep in the first place.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct PTFE gasket requires matching the gasket's strengths to your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is ultimate chemical purity and sterility: Choose a Virgin PTFE Gasket, but be mindful of your system's pressure and temperature to avoid creep.
- If you need to balance chemical resistance with higher pressures or temperatures: A Filled PTFE Gasket provides the necessary mechanical strength and creep resistance.
- If you are sealing old, damaged, or glass-lined flanges: The superior compressibility of an Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) Gasket is the ideal solution.
- If you require the strength of a traditional gasket with the surface inertness of PTFE: An Envelope Gasket offers a robust, high-performance composite solution.
By understanding how each variant modifies PTFE's core properties, you can select a gasket that provides a reliable, long-lasting seal for your specific operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Gasket Type | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | Maximum chemical purity, excellent insulation | Food, Pharma, High-Purity Applications |
| Filled PTFE | Enhanced strength, creep resistance | High-Pressure/Temperature Systems |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | High compressibility, conformability | Irregular/Delicate Flange Surfaces |
| Envelope Gasket | High strength core with PTFE liner | High-Pressure, Chemically Aggressive Services |
Need a PTFE Gasket Engineered for Your Specific Demands?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom gaskets for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical balance between chemical inertness and mechanical performance.
Whether you require a prototype or a high-volume order, our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get a reliable, long-lasting seal solution.
Contact us today to discuss your application requirements: Get a Quote
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is expanded PTFE considered superior for demanding applications? Unlock Superior Sealing Performance
- What are the benefits of 15% graphite-filled PTFE bushings? Enhance Wear Resistance & Thermal Performance
- What design parameters are specified for PTFE sliding bearings? Ensure Structural Safety and Performance
- What are the structural differences between PTFE oil seals and rubber oil seals? A Guide to Lip Design & Performance
- What are the limitations of machining Teflon (PTFE)? Overcome Challenges for Precision Parts
- Can you provide examples of industries where PTFE bars have been successfully applied? Discover Key Applications
- What is PTFE and why is it used in lined valves? Achieve Superior Corrosion Resistance and Purity
- How does CNC machining enhance PTFE part production? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency



















