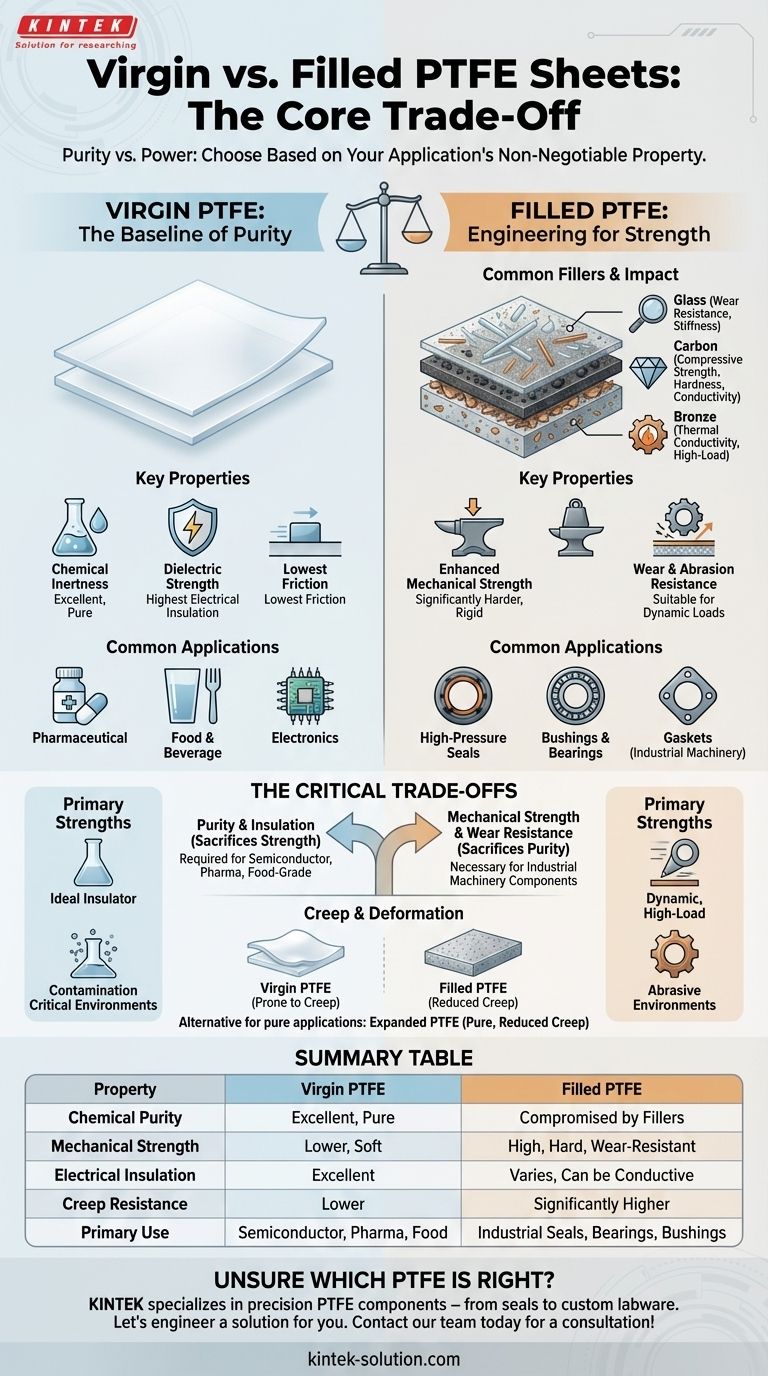
In essence, the choice between virgin and filled PTFE comes down to a single trade-off: purity versus power. Virgin Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is the pure, unmodified material, prized for its exceptional chemical resistance and electrical insulation. Filled PTFE incorporates additives like glass, carbon, or bronze to dramatically improve its mechanical properties, such as hardness and wear resistance, for more demanding industrial applications.
The core decision is not about which material is superior overall, but which property is non-negotiable for your specific application. You must choose between the absolute chemical purity of virgin PTFE and the enhanced mechanical durability of filled PTFE.

What is Virgin PTFE? The Baseline of Purity
The Unmodified Material
Virgin PTFE is the pure, unprocessed form of this high-performance thermoplastic. It contains no fillers or additives.
This purity makes it the most chemically inert and biocompatible version of the material. It also possesses the highest electrical insulation properties and the lowest coefficient of friction in the PTFE family.
Key Properties
Virgin PTFE is defined by its exceptional resistance to chemicals, gases, and moisture. It is soft, flexible, and has a wide operating temperature range.
Its primary strengths are its chemical inertness and dielectric strength, making it an ideal insulator and a perfect choice for environments where contamination is a critical concern.
Common Applications
Due to its purity, virgin PTFE is the standard for critical applications in the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, and electronics industries.
Any application that requires direct contact with sensitive products or demands high electrical insulation—from medical device components to semiconductor manufacturing—relies on virgin PTFE.
Understanding Filled PTFE: Engineering for Strength
The Principle of Reinforcement
Filled PTFE is a composite material created by adding a reinforcing agent to virgin PTFE resin before it's sintered.
This process is designed to overcome the primary weaknesses of virgin PTFE: its relative softness and its tendency to deform or "creep" under a sustained load.
Common Fillers and Their Impact
The properties of filled PTFE are determined by the additive used. The most common fillers include:
- Glass: Improves wear resistance and stiffness.
- Carbon: Increases compressive strength, hardness, and wear resistance, while also providing electrical conductivity.
- Bronze: Enhances compressive strength and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-load applications like bearings.
Key Properties
The defining characteristic of filled PTFE is its enhanced mechanical strength. These materials are significantly harder, more rigid, and far more resistant to wear and abrasion than their virgin counterpart.
This makes them suitable for dynamic, high-load, and abrasive environments where virgin PTFE would fail prematurely.
Common Applications
Filled PTFE is the workhorse of demanding industrial applications. It is commonly found in components like high-pressure seals, bushings, bearings, and gaskets that require exceptional durability and longevity under mechanical stress.
The Critical Trade-offs to Consider
Purity vs. Mechanical Strength
This is the central compromise. By adding a filler, you gain immense mechanical strength but sacrifice the absolute chemical purity and inertness of virgin PTFE.
For an industrial valve seal, strength is paramount. For a food processing gasket, purity is the priority.
Electrical Insulation vs. Wear Resistance
Virgin PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator. However, some fillers, particularly carbon, make the material conductive, completely altering this property.
You must weigh the need for insulation against the need for durability in your specific design.
Creep and Deformation
Virgin PTFE is soft and can deform under pressure over time, a phenomenon known as creep. Fillers significantly reduce this tendency.
For applications requiring dimensional stability under load, such as a structural component or a tight-tolerance seal, a filled grade is almost always the superior choice. An alternative for pure applications is expanded PTFE, which is pure but processed to eliminate creep.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity or electrical insulation: Virgin PTFE is the only choice. It is required for applications in semiconductor, pharmaceutical, or food-grade environments.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance and compressive strength: A filled PTFE is necessary. Use it for mechanical components like bearings, rings, and seals in demanding industrial machinery.
- If your primary focus is pure sealing without deformation: Consider expanded PTFE. It offers the purity of virgin PTFE with significantly improved resistance to creep, making it ideal for critical flange gaskets.
By understanding this fundamental distinction between purity and strength, you can confidently select the precise PTFE sheet engineered to solve your specific challenge.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | Filled PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Purity | Excellent (Pure) | Compromised by fillers |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower (Soft) | High (Hard, Wear-Resistant) |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent | Varies (Can be conductive) |
| Creep Resistance | Lower | Significantly Higher |
| Primary Use | Semiconductor, Pharma, Food | Industrial Seals, Bearings, Bushings |
Unsure which PTFE material is right for your project?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware.
Whether your application in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector demands the absolute purity of virgin PTFE or the enhanced durability of filled PTFE, our experts can help you select the ideal material. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring optimal performance for your specific needs.
Let's engineer a solution for you. Contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability



















