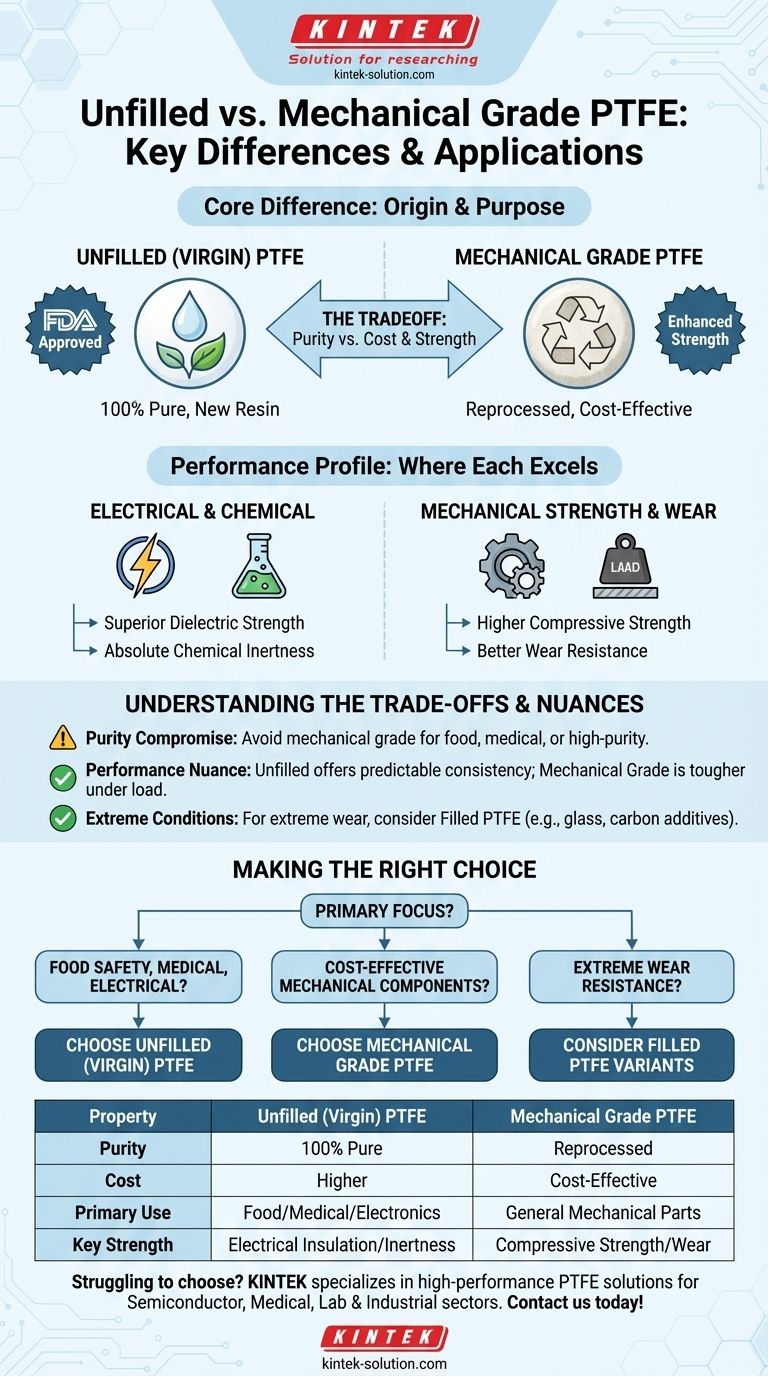
At its core, the difference is one of origin and purpose. Unfilled Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), also known as virgin PTFE, is made from 100% pure, new resin. Mechanical grade PTFE is a more cost-effective option produced from reprocessed or reground PTFE, trading absolute purity for enhanced compressive strength and wear resistance in applications where material cost is a primary driver.
The choice between unfilled and mechanical grade PTFE is a classic engineering trade-off: select unfilled PTFE for its certified purity and superior electrical properties, or opt for mechanical grade PTFE for its economic advantage and robust performance in general industrial applications.

Purity and Composition: The Fundamental Divide
The primary distinction between these two materials lies in what they are made of. This fundamental difference in composition dictates their ideal use cases, performance characteristics, and regulatory compliance.
Unfilled (Virgin) PTFE: The Purest Form
Unfilled PTFE is manufactured directly from pure, unused PTFE resin. It contains no recycled material or fillers of any kind.
Because of this purity, it is often FDA approved and suitable for direct contact with sensitive products. This makes it the default choice for the food, beverage, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Mechanical Grade PTFE: The Recycled Workhorse
Mechanical grade PTFE is produced using reprocessed resin. This recycling process makes it a significantly more cost-effective material.
This composition means it is not suitable for applications requiring high purity or FDA compliance. It is designed specifically for industrial and mechanical parts where performance and cost are more critical than purity.
Performance Profile: Where Each Material Excels
While both materials share core PTFE properties like a low coefficient of friction and high-temperature tolerance, their composition creates key differences in performance.
Electrical and Chemical Properties
Unfilled PTFE offers the highest physical and electrical insulation properties of any PTFE variant. Its chemical inertness is absolute, making it reliable for semiconductor manufacturing or aggressive chemical processing.
Mechanical Strength and Wear
Mechanical grade PTFE exhibits superior compressive strength and wear resistance compared to its unfilled counterpart. The reprocessing consolidates the material, making it harder and more durable for structural components.
This makes it an excellent choice for high-performance parts like bearings, bushings, and seals in non-critical applications where it will be subjected to friction and load.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong material can lead to unnecessary costs or premature component failure. Understanding the compromises is essential.
The Purity Compromise
Opting for mechanical grade PTFE means sacrificing the certified purity and consistency of virgin material. If your application involves food, medical devices, or high-purity electronics, this is not a viable trade-off.
The Performance Nuance
While mechanical grade is tougher under compression, unfilled PTFE provides more predictable and consistent overall properties. For applications demanding the absolute best dielectric strength or the most uniform material structure, virgin PTFE remains the superior choice.
When to Consider Filled PTFE
If your application requires even greater wear resistance or stability under extreme loads, neither of these may be the optimal choice. Filled PTFE, which incorporates additives like glass, carbon, or bronze, is specifically engineered for the most demanding mechanical conditions, offering another level of performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is food safety, medical use, or electrical insulation: Choose unfilled (virgin) PTFE for its unmatched purity and dielectric properties.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mechanical components: Mechanical grade PTFE is the ideal choice for non-critical parts like bearings, seals, or structural elements.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance and load-bearing: You should evaluate filled PTFE variants, which are specifically engineered for these demanding conditions.
Selecting the right grade of PTFE is about aligning the material's inherent strengths with your application's most critical requirements.
Summary Table:
| Property | Unfilled (Virgin) PTFE | Mechanical Grade PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | 100% pure, new resin | Reprocessed/recycled resin |
| Cost | Higher | More cost-effective |
| Primary Use | Food, medical, high-purity electronics | General industrial mechanical parts |
| Key Strength | Superior electrical insulation, chemical inertness | Enhanced compressive strength, wear resistance |
Struggling to choose the right PTFE for your components? At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in both unfilled and mechanical grade PTFE ensures you get the optimal material for your specific application—whether you need certified purity for sensitive environments or cost-effective durability for industrial use. From prototypes to high-volume orders, we deliver precision and reliability. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and get a custom solution! Reach out to our experts
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- How do PTFE gaskets perform under extreme temperatures? Unlock Reliable Sealing from -200°C to +260°C
- What is meant by the percentage of PTFE content? Fine-Tune Material Properties for Your Application
- What are some common applications of machined Teflon? Critical Components for Harsh Environments
- How is a piston seal constructed? A Guide to Dynamic, Pressure-Energized Sealing
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the advantages of using a Teflon sheet for heat press? Protect Your Projects & Achieve Flawless Results
- What is the chemical resistance of Virgin PTFE? Unmatched Inertness for Harsh Chemical Environments
- What are the key benefits of using PTFE for piston rings in oil-free compressors? Achieve Clean, Efficient Compression



















