To successfully manage PTFE's behavior, you must address its two most challenging properties—creep and thermal expansion—through a combination of mechanical design and specialized processing techniques. For creep, the solution is structural containment using backing materials or encapsulation, while managing thermal expansion requires careful control of machining parameters and, in many cases, modifying the material itself with fillers.
PTFE is a uniquely flexible material, but this low stiffness creates challenges. The key to success is either constraining the material mechanically to prevent deformation or fundamentally enhancing its stability by adding reinforcing fillers like glass or carbon.

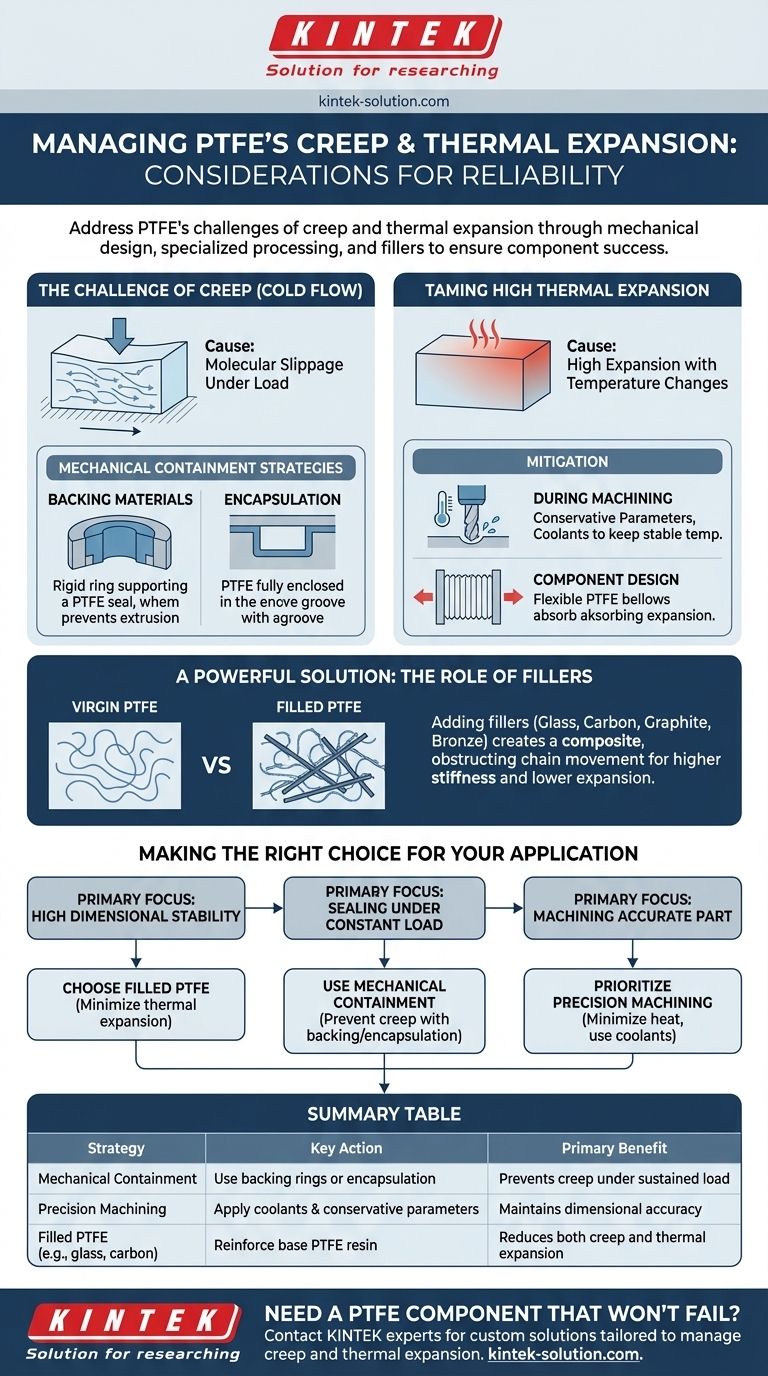
The Challenge of Creep (Cold Flow)
Creep, often called "cold flow," is PTFE's tendency to slowly and permanently deform under a sustained mechanical load, even at room temperature. This occurs because of the material's low inherent stiffness.
What Causes Creep?
PTFE's molecular structure allows polymer chains to slip past one another when pressure is applied over time. This results in a gradual change in the component's shape, which can lead to seal failure or a loss of critical tolerances.
Mechanical Containment Strategies
The most effective way to counteract creep is to prevent the material from being able to move.
Backing materials are rigid components placed behind a PTFE seal or bearing. They provide structural support and stop the PTFE from extruding or flowing away from the high-pressure area.
Encapsulation involves designing a groove or housing that fully contains the PTFE component. By enclosing the material, the housing takes on the mechanical load and constrains the PTFE, preventing it from deforming.
Taming High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a very high coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning it expands and contracts significantly with temperature changes. This can cause major problems during both manufacturing and in the final application if not properly managed.
Why Thermal Expansion Matters
A component machined to precise dimensions at room temperature may be out of tolerance at its operating temperature. This dimensional instability is a primary consideration for any application with temperature fluctuations.
Mitigation During Machining
Heat generated during cutting is the main enemy. The localized heating causes the PTFE to expand, leading to inaccurate cuts.
To prevent this, machinists must use conservative cutting parameters and coolants to keep the material temperature stable. Minimizing clamping force is also critical to avoid introducing stress before machining even begins.
Mitigation in Component Design
In some cases, this property can be an advantage. PTFE expansion bellows, for example, are designed to flex and absorb thermal expansion in pipelines, preventing leaks.
For most applications, however, you must account for this behavior in the design phase to ensure the part maintains its function and fit across the entire operational temperature range.
A Powerful Solution: The Role of Fillers
For applications demanding greater stability, modifying the PTFE itself is the most effective strategy.
How Fillers Improve Stability
Adding fillers like glass fibers, carbon, graphite, or bronze to the base PTFE resin creates a composite material. These fillers act as a reinforcing internal structure.
This structure physically obstructs the movement of the PTFE polymer chains, which dramatically improves performance.
Reduced Creep and Expansion
Filled PTFE grades have significantly higher stiffness and a much lower coefficient of thermal expansion than virgin PTFE. This enhancement directly improves resistance to creep and ensures dimensional stability across a wider range of temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While fillers provide significant mechanical and thermal benefits, they do alter the fundamental properties of the material.
Pure PTFE vs. Filled PTFE
Fillers can sometimes reduce certain desirable properties of virgin PTFE, such as its chemical resistance or its coefficient of friction. The choice of filler must be matched to the specific demands of the application.
Design vs. Material Complexity
Using mechanical containment adds complexity and part count to an assembly. Opting for a filled PTFE grade may simplify the design but requires careful material selection to ensure all performance criteria are met.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final strategy depends entirely on the primary goal of your component.
- If your primary focus is high dimensional stability in varying temperatures: Choose a filled PTFE, such as one with glass or carbon, to minimize thermal expansion and contraction.
- If your primary focus is sealing under a constant mechanical load: Use virgin PTFE but contain it with a rigid backing ring or a fully encapsulated groove design to prevent creep.
- If your primary focus is machining an accurate part: Prioritize minimizing heat buildup through the use of sharp tools, ample coolant, and conservative cutting speeds and feeds.
By understanding and proactively addressing these inherent properties, you can leverage PTFE's unique benefits while ensuring reliable and precise performance.
Summary Table:
| Strategy | Key Action | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Containment | Use backing rings or encapsulation | Prevents creep under sustained load |
| Precision Machining | Apply coolants & conservative parameters | Maintains dimensional accuracy |
| Filled PTFE (e.g., glass, carbon) | Reinforce base PTFE resin | Reduces both creep and thermal expansion |
Need a PTFE component that won't fail?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical balance between PTFE's flexibility and the need for stability. Whether you require the pure chemical resistance of virgin PTFE or the enhanced dimensional stability of a filled grade, our custom fabrication services from prototype to high-volume production ensure your application performs reliably.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a solution tailored to manage creep and thermal expansion.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















