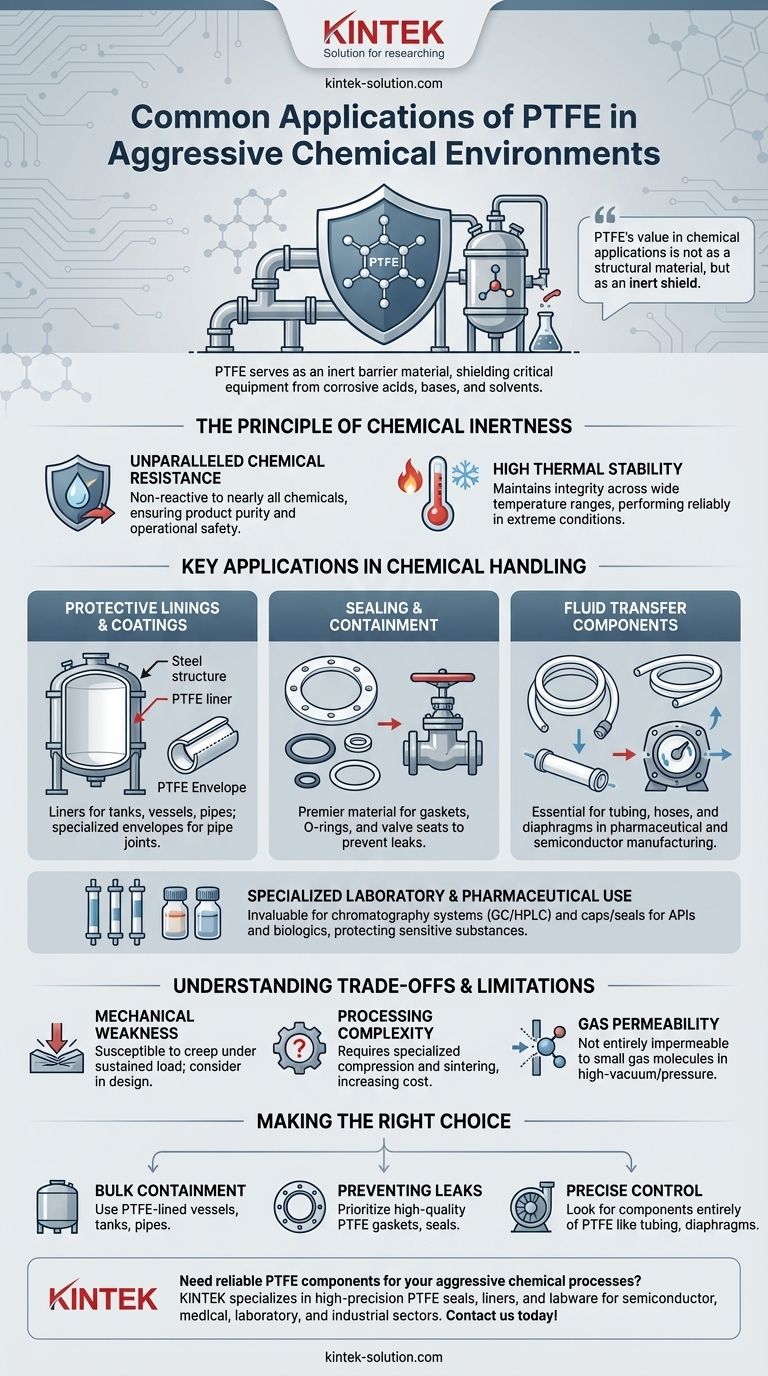
In aggressive chemical environments, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is most commonly used for protective linings, seals, gaskets, and components within fluid transfer systems. Its profound chemical inertness makes it an essential barrier material, shielding pipes, vessels, and valves from corrosive acids, bases, and solvents. This ensures the longevity and safety of critical industrial equipment.
PTFE's value in chemical applications is not as a structural material, but as an inert shield. Its fundamental purpose is to protect the integrity of a system by forming a non-reactive barrier between corrosive media and more vulnerable components.

The Principle of Chemical Inertness: Why PTFE Excels
The unique molecular structure of PTFE is the source of its exceptional performance. Understanding this is key to appreciating its role in harsh environments.
Unparalleled Chemical Resistance
PTFE is non-reactive to nearly all chemicals and solvents. This universal resistance means it can be used in chemical manufacturing, processing, and laboratory settings without risk of degradation or material failure.
It provides a reliable containment solution for everything from highly corrosive acids to reactive organic compounds, ensuring product purity and operational safety.
High Thermal Stability
In addition to its chemical stability, PTFE maintains its integrity across a wide range of temperatures. It does not melt or degrade under the high-heat conditions common in many chemical production processes.
This thermal resilience allows it to perform reliably in applications where both extreme temperatures and corrosive substances are present simultaneously.
Key Applications in Chemical Handling and Processing
PTFE is rarely used as a standalone structural component. Instead, it is integrated into systems specifically where chemical contact occurs.
Protective Linings and Coatings
One of the most common applications is as a liner for tanks, vessels, and pipes. This approach allows for the use of strong, cost-effective structural materials like steel, while the PTFE lining provides the necessary chemical protection.
In pipe joints, specialized PTFE envelopes are used to shield gaskets from chemical attack, preventing leaks at critical connection points.
Sealing and Containment
PTFE is a premier material for creating static and dynamic seals. It is fabricated into gaskets, O-rings, and valve seats that prevent the leakage of hazardous fluids.
Its reliability is so absolute that it was historically used in gaskets for the containment of highly reactive materials, such as uranium hexafluoride gas during the development of the atomic bomb.
Fluid Transfer Components
For the direct transport of aggressive media, PTFE is manufactured into tubing, hoses, and diaphragms. These components are essential in pharmaceutical research, chemical synthesis, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Its low-friction surface is also an advantage in components like valve seats, ensuring smooth operation and a tight seal over many cycles.
Specialized Laboratory and Pharmaceutical Use
In high-precision environments, PTFE is invaluable. It is used extensively in chromatography (GC/HPLC) systems where solvent purity is critical.
It is also used to create caps and seals for vials containing Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) or biologics, protecting sensitive and often reactive substances from contamination and degradation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While chemically robust, PTFE is not without its limitations. Acknowledging these is crucial for proper engineering design.
Mechanical Weakness
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is susceptible to creep, which is the tendency to slowly deform under a sustained mechanical load. This must be accounted for when designing gaskets and seals that will be under constant compression.
Processing Complexity
Unlike many common plastics, PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt-extrusion or injection molding techniques. It must be formed using specialized compression and sintering processes, which can increase manufacturing complexity and cost.
Gas Permeability
While excellent for liquid containment, PTFE is not entirely impermeable to small gas molecules. In high-vacuum applications or when containing certain gases at high pressure and temperature, some degree of permeation can occur and must be considered.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal will determine the ideal form of PTFE for your system.
- If your primary focus is bulk containment of highly corrosive fluids: Utilize PTFE-lined vessels, tanks, and pipes to protect the primary structure.
- If your primary focus is preventing leaks at joints and connections: Prioritize high-quality PTFE gaskets, seals, and O-rings.
- If your primary focus is the precise control or transfer of reactive chemicals: Look to components made entirely of PTFE, such as tubing, valve seats, and pump diaphragms.
Ultimately, selecting PTFE is a decision to prioritize chemical compatibility and operational reliability in the most demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key PTFE Components | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Protective Linings | Tank & Pipe Liners, Envelopes | Shields structural materials from corrosion |
| Sealing & Containment | Gaskets, O-rings, Valve Seats | Prevents leaks of hazardous fluids |
| Fluid Transfer | Tubing, Hoses, Diaphragms | Ensures purity and safe transport of aggressive media |
| Laboratory & Pharma | Vial Seals, Chromatography Components | Protects sensitive substances from contamination |
Need reliable PTFE components for your aggressive chemical processes?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We ensure your equipment operates safely and efficiently in the most demanding environments, from prototyping to high-volume production.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and benefit from our expertise in precision PTFE fabrication.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability
- What are the advantages of hydrophobic PTFE membrane filters? Achieve Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Purity
- How was the slipperiness of Teflon studied in the research? Visualizing Material Transfer at the Molecular Level
- What makes PTFE/Teflon suitable for medical applications? Discover Its Unique Biocompatibility & Performance
- How do Nylon and PTFE compare in terms of durability and strength? Choosing the Right Polymer for Your Application
- What are the common applications of PTFE? Leverage Its Extreme Properties for Your Industry
- How is Teflon used in the chemical industry? Protect Equipment and Ensure Purity
- What are some common household applications of PTFE? Discover Its Hidden Uses Beyond Non-Stick Pans



















