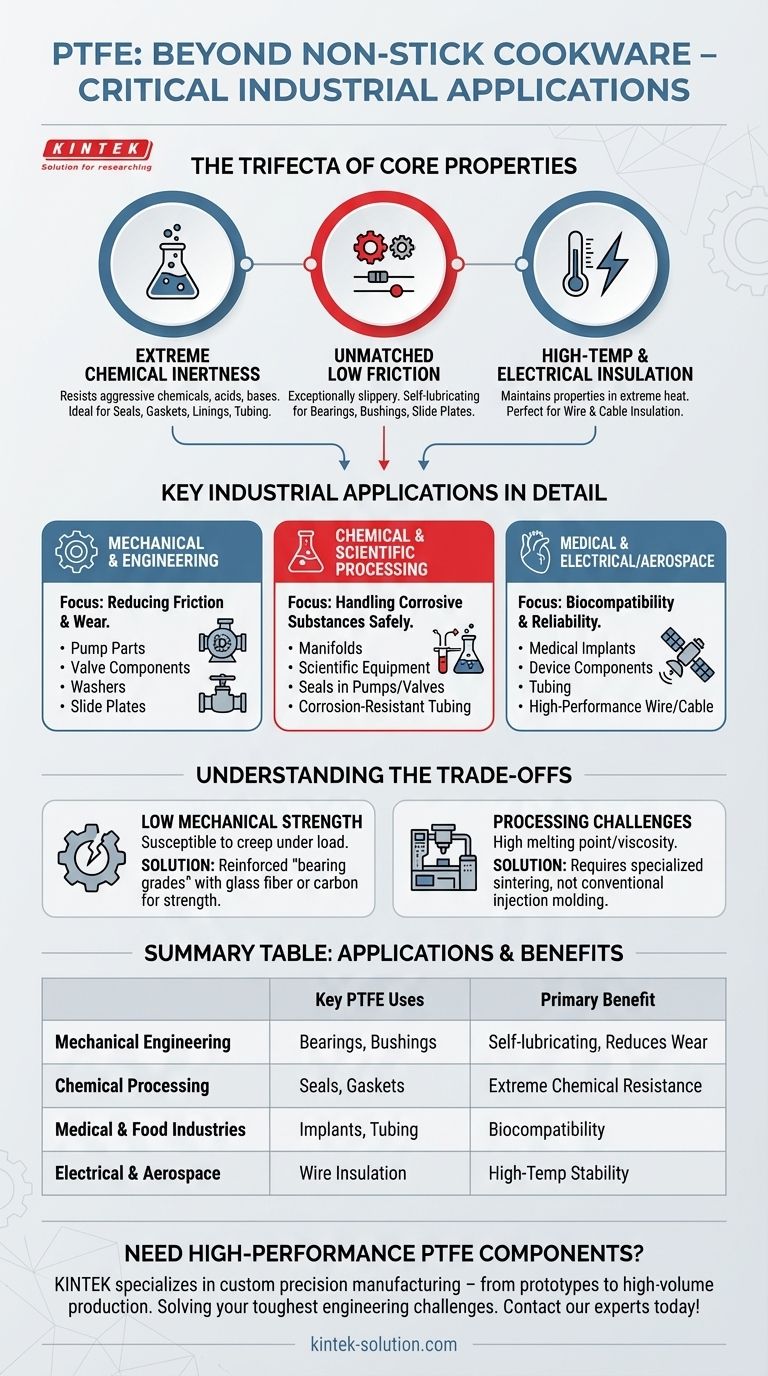
Beyond non-stick pans, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a critical material in nearly every advanced industry, from aerospace to medicine. Its applications include creating self-lubricating bearings, chemically resistant seals for handling corrosive materials, and high-performance electrical insulation for mission-critical wiring.
The true value of PTFE lies not in a single feature, but in a unique combination of three core properties: extreme chemical resistance, an incredibly low coefficient of friction, and high-temperature stability. This trifecta makes it an indispensable problem-solver in demanding engineering environments where other materials would fail.

The Core Properties Driving PTFE's Versatility
To understand where PTFE is used, you must first understand why. Its widespread adoption is a direct result of its remarkable material characteristics.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most non-reactive substances known. It can withstand exposure to a vast range of aggressive chemicals, acids, and bases without degrading.
This makes it the material of choice for components used in the chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and semiconductor industries. It is used to manufacture seals, gaskets, linings, and chemical-resistant tubing.
Unmatched Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, making it exceptionally slippery. This property allows it to function as a superior self-lubricating material.
In mechanical engineering, it is used for plain bearings, bushings, slide plates, and other sliding elements where reducing wear and eliminating the need for liquid lubricants is critical.
High-Temperature and Electrical Insulation
PTFE maintains its properties over a wide temperature range and is an excellent electrical insulator.
This combination makes it vital in the electrical and aerospace industries for insulating high-performance wires and cables, especially in high-temperature applications where reliability is paramount.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
The fundamental properties of PTFE translate directly into specific, high-value applications across multiple sectors.
Mechanical and Engineering
The focus here is on reducing friction and wear.
PTFE is fabricated into pump parts, valve components, and washers that must operate smoothly with minimal maintenance. Its self-lubricating nature ensures longevity and consistent performance.
Chemical and Scientific Processing
The goal in these fields is to handle aggressive or high-purity substances safely.
You will find PTFE used for manifolds, scientific equipment, and seals in pumps and valves that manage corrosive fluids. Its non-reactive surface prevents contamination and material degradation.
Medical and Food Industries
Biocompatibility and inertness are the primary drivers for its use in these sensitive applications.
PTFE is used for certain medical implants, components for medical devices, and tubing. In food processing, its non-stick and non-toxic properties are highly valued for components that come into contact with food.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and PTFE is no exception. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Low Mechanical Strength
Pure PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be susceptible to "creep" or cold flow under a sustained load.
For this reason, it is often reinforced with other materials like glass fiber or carbon to create "bearing grades" with improved strength and wear resistance for more demanding mechanical roles.
Processing Challenges
PTFE has a very high melting point and viscosity, which makes it more difficult to process using conventional polymer techniques like injection molding.
Specialized methods like sintering are required, which can increase manufacturing complexity and cost compared to other plastics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a material depends entirely on the problem you need to solve. PTFE is often chosen when performance cannot be compromised.
- If your primary focus is mechanical performance: Use PTFE for self-lubricating bearings, bushings, and slide plates to dramatically reduce friction and wear.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: PTFE is the industry standard for seals, gaskets, and tubing that must withstand highly corrosive environments.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or medical use: Its inertness makes PTFE an excellent choice for scientific equipment, tubing, and biocompatible device components.
Ultimately, PTFE's role as a high-performance polymer is secured by its ability to function reliably in conditions where most other materials would quickly fail.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key PTFE Uses | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Engineering | Bearings, Bushings, Slide Plates | Self-lubricating, Reduces Friction & Wear |
| Chemical Processing | Seals, Gaskets, Linings, Tubing | Extreme Chemical Resistance & Purity |
| Medical & Food Industries | Medical Implants, Device Components, Tubing | Biocompatibility & Non-Toxic Properties |
| Electrical & Aerospace | Wire & Cable Insulation | High-Temperature Stability & Electrical Insulation |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—from seals and liners to complex labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production, we deliver solutions that meet the most demanding requirements for chemical resistance, low friction, and thermal stability.
Let us help you solve your toughest engineering challenges. Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the limitations when machining Teflon/PTFE? Overcome Dimensional Instability & Creep
- What are some common fillers used in PTFE seal materials? Enhance Performance for Your Application
- How are PTFE rubber seals constructed? Precision Engineering for High-Performance Sealing
- How do PTFE sealed ball bearings perform in terms of durability? Maximize Lifespan with Superior Sealing
- Why is PTFE considered cost-effective for plumbing applications? Maximize Long-Term Value & Reliability
- How does the manufacturing of PTFE expansion joints accommodate industry-specific needs? Tailor-Made Solutions for Your Application
- What medical applications benefit from PTFE's biocompatibility? Ensuring Patient Safety in Critical Devices
- What industries commonly use CNC machined Teflon parts? Key Sectors Relying on PTFE's Performance



















