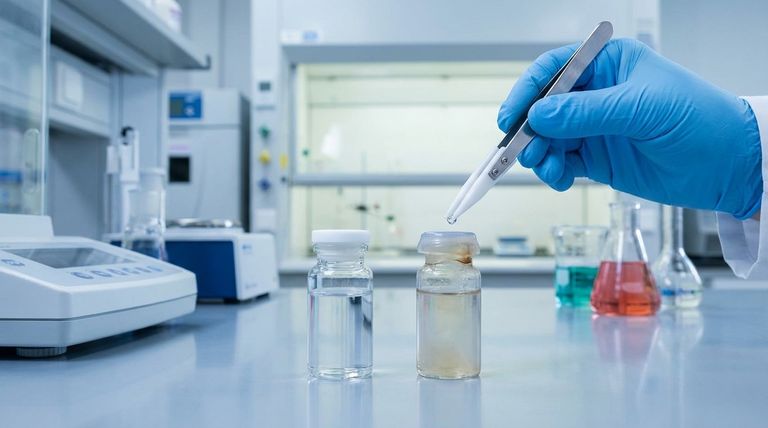
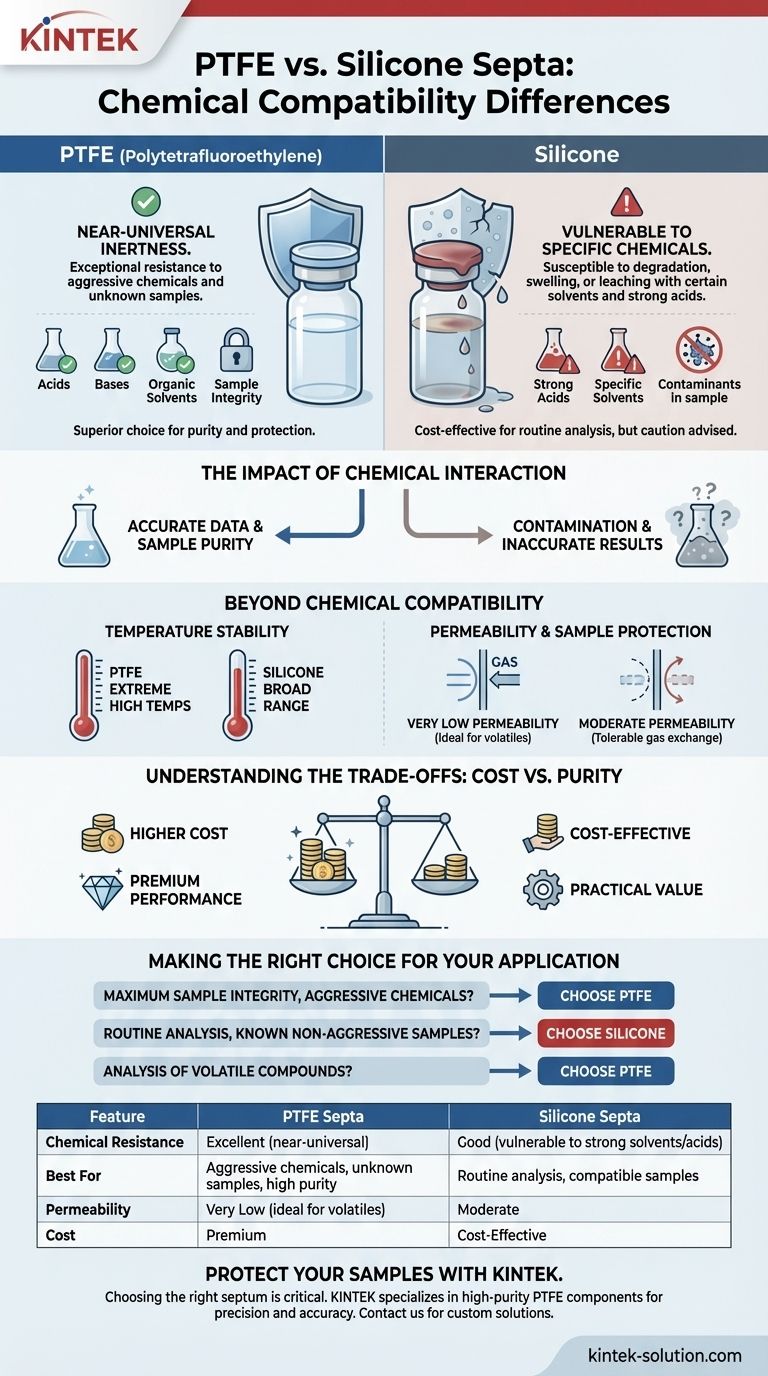
The fundamental difference in chemical compatibility is PTFE's near-universal inertness compared to silicone's vulnerability to specific organic solvents and strong acids. PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) provides exceptional resistance against a vast range of chemicals, making it the superior choice for aggressive or unknown samples. In contrast, silicone may swell, degrade, or leach when exposed to certain compounds, compromising sample integrity and the vial's seal.
Choosing the right septum is a critical decision for analytical integrity. PTFE provides maximum chemical resistance for protecting sensitive samples, whereas silicone offers a cost-effective and practical solution for routine analyses where chemical exposure is limited and well-understood.

The Impact of Chemical Interaction
The choice of septum material directly affects the reliability of your results. An incompatible septum can lead to sample contamination, loss of analyte, and inaccurate data.
The Superior Inertness of PTFE
PTFE is renowned for its exceptional chemical resistance. It remains stable and non-reactive when exposed to most acids, bases, and organic solvents.
This high degree of inertness makes PTFE septa the gold standard for applications involving highly reactive chemicals or when sample purity is paramount.
The Vulnerability of Silicone
Silicone is generally a chemically stable material, but it has known weaknesses. It is susceptible to degradation or swelling when in contact with certain organic solvents and strong acids.
This interaction can compromise the physical integrity of the seal, leading to evaporation or contamination, and may introduce leachables from the silicone material itself into your sample.
Beyond Chemical Compatibility: Other Key Factors
While chemical resistance is often the primary concern, other properties like temperature stability and permeability play a crucial role in performance.
Temperature Stability
Both materials perform well across a broad temperature range. However, PTFE can typically withstand more extreme high temperatures than silicone, making it a better choice for high-temp applications.
Permeability and Sample Protection
PTFE septa have very low permeability to gases. This creates a highly effective barrier that protects samples from atmospheric contamination and prevents the loss of volatile analytes.
Silicone has a moderate level of permeability. While this makes it less ideal for highly sensitive samples, it can be suitable for applications like headspace sampling where some gas exchange is tolerable.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Purity
The decision between PTFE and silicone often comes down to balancing performance requirements with budget constraints.
The Premium for Performance
PTFE's superior chemical resistance and temperature stability come at a higher cost. Its manufacturing process is more complex, making it the premium option.
The Value of Practicality
Silicone septa are significantly more cost-effective. This makes them a practical and widely used choice for routine laboratory procedures where high chemical resistance is not the primary requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific analytical goals should dictate your selection.
- If your primary focus is maximum sample integrity with aggressive chemicals: Choose PTFE for its near-universal inertness and superior protection against contamination.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis with known, non-aggressive samples: Silicone is a reliable and cost-effective option that performs well in many standard procedures.
- If your primary focus is analysis of volatile compounds or gas-sensitive samples: PTFE's low permeability provides a more secure seal, ensuring greater accuracy.
Selecting the correct septum based on these principles is a fundamental step toward achieving accurate and repeatable analytical results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Septa | Silicone Septa |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (near-universal inertness) | Good (vulnerable to strong solvents/acids) |
| Best For | Aggressive chemicals, unknown samples, high purity | Routine analysis with known, compatible samples |
| Permeability | Very Low (ideal for volatiles) | Moderate |
| Cost | Premium | Cost-Effective |
Protect your samples with precision-engineered PTFE components from KINTEK.
Choosing the right septum material is critical for preventing contamination and ensuring the accuracy of your results. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-purity PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact specifications. Whether you need the superior chemical resistance of PTFE or a cost-effective solution for routine analyses, our expertise ensures you get the right part for your application.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and request a quote. Let us help you achieve superior sample integrity and analytical performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- How does chemical compatibility of PTFE silicone septas benefit pharmaceutical research? Ensure Sample Integrity
- How do PTFE lined caps contribute to safety in laboratory testing? Prevent Leaks and Ensure Sample Integrity
- Where are PTFE stirrers typically applied? Essential for Chemical, Pharma & Bioprocessing
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for chromatography septums? Ensure Sample Integrity and Reliable Results
- Why is temperature stability important for PTFE silicone septas in pharmaceutical processes? Ensure Data Integrity & Sample Safety
- What materials are used in PTFE-lined bottle caps? A Guide to PP Caps and PTFE Liners
- How does the non-stick surface of PTFE shovels benefit laboratory work? Enhance Accuracy & Efficiency
- What are the durability benefits of using PTFE/silicone septums in chromatography? Maximize Uptime & Data Integrity



















