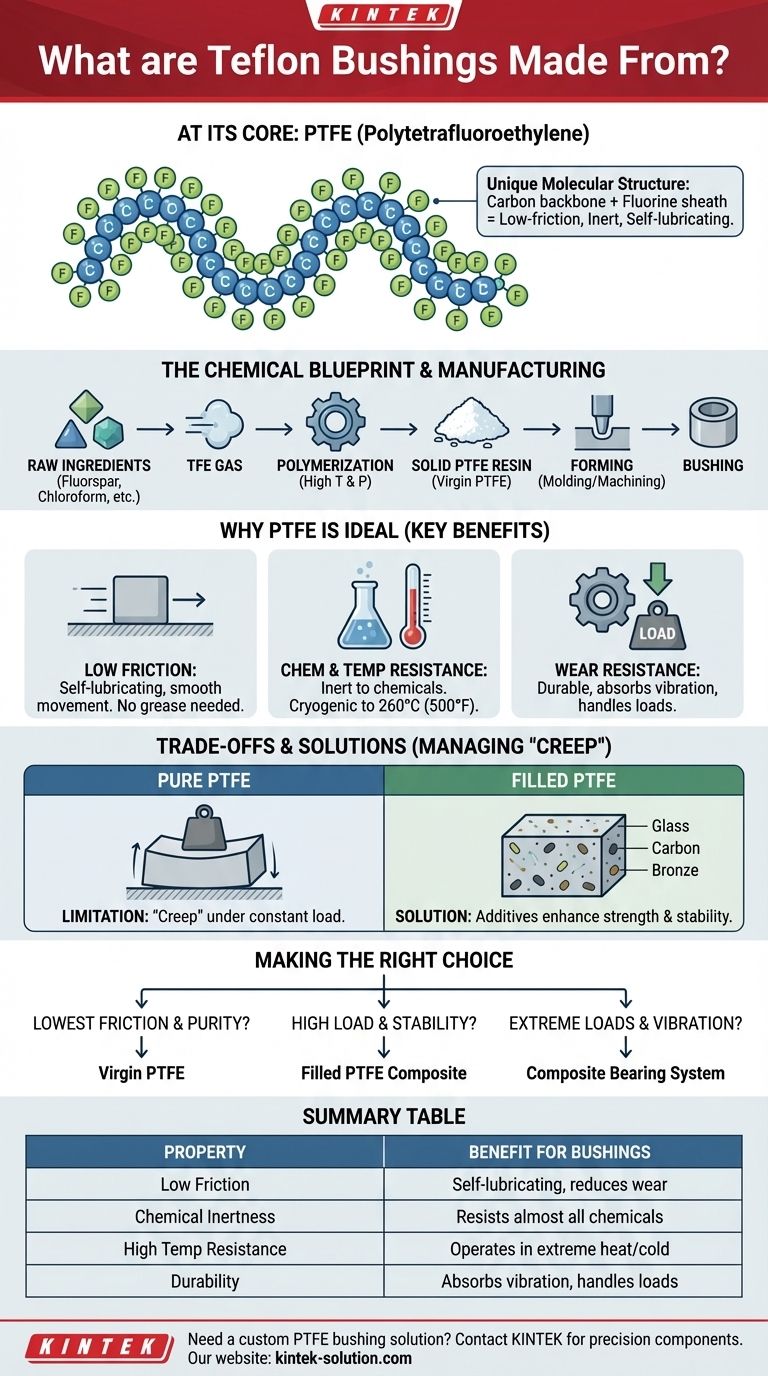
At its core, a Teflon bushing is made from a high-performance fluoropolymer known as Polytetrafluoroethylene, or PTFE. While "Teflon" is a registered trademark of the Chemours company, the name has become synonymous with the material itself due to its widespread use. This solid white material is formed by linking many individual tetrafluoroethylene molecules into long, stable chains.
The true value of a Teflon (PTFE) bushing comes from its unique molecular structure. A strong carbon backbone is completely sheathed by fluorine atoms, creating an incredibly low-friction and chemically inert surface ideal for self-lubricating, maintenance-free mechanical parts.

What Exactly is PTFE?
To understand why PTFE is used for bushings, we must first look at its fundamental composition and how it is manufactured. It is not a simple plastic but a precisely engineered material.
The Chemical Blueprint
The chemical formula for PTFE is (C2F4)n, signifying a long, repeating chain of carbon (C) and fluorine (F) atoms.
Imagine a long chain of carbon atoms forming a spine. In PTFE, every available bonding point on this spine is occupied by a fluorine atom, creating a tight, protective "jacket." This fluorine sheath is the secret to PTFE's properties.
From Raw Ingredients to Solid Polymer
The production process begins by synthesizing tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) gas from raw ingredients like fluorspar, chloroform, and hydrofluoric acid in a high-temperature reaction.
This TFE gas is then subjected to a process called polymerization. Under controlled pressure and temperature, the individual TFE molecules link together to form the long, stable chains of solid PTFE resin.
Forming the Bushing
This raw PTFE resin, often called virgin PTFE, is the base material for the bushing. The resin is then shaped into its final form, typically through methods like compression molding or machining from stock rods and tubes.
Why PTFE is an Ideal Choice for Bushings
The molecular structure of PTFE directly translates into three key performance characteristics that make it exceptionally well-suited for creating bushings and bearings.
Extremely Low Friction
The fluorine atoms that shield the carbon backbone are very stable and don't readily interact with other surfaces. This causes molecules to slide past each other with minimal resistance, giving PTFE one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This property allows for smooth, self-lubricating movement without the need for grease or oil.
Chemical and Temperature Resistance
The carbon-fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry. This makes PTFE exceptionally non-reactive and inert to almost all chemicals and solvents. It also maintains its strength and flexibility across a vast temperature range, from cryogenic levels up to around 260°C (500°F).
Wear Resistance and Durability
While soft compared to metal, PTFE is a tough and durable material. It effectively absorbs vibration and can handle significant loads, preventing wear and tear on the shafts and housings it supports.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While pure PTFE is remarkable, it isn't perfect for every application. Its primary limitation must be understood and is often engineered around.
The Limitation of "Creep"
The primary mechanical weakness of pure, or virgin, PTFE is its tendency to "creep." Under a constant, heavy load, the material can slowly and permanently deform over time.
The Role of Fillers
To counteract creep and enhance mechanical strength, manufacturers often create filled PTFE composites. Additives like glass fiber, carbon, bronze, or graphite are blended with the PTFE resin before it is molded. These fillers significantly improve wear resistance and dimensional stability, though often at the cost of a slightly higher coefficient of friction.
Composite Bearing Systems
In some heavy-duty applications, such as bridge bearings, a thin, dimpled plate of PTFE is bonded to a structural pad made of materials like steel-laminated rubber. Here, the PTFE provides the low-friction sliding surface, while the rubber and steel assembly provides the necessary structural support and load-bearing capacity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct type of PTFE bushing depends entirely on the mechanical and environmental demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible friction and high chemical purity: A bushing made from 100% virgin PTFE is the best choice.
- If your primary focus is high load capacity and dimensional stability: You should specify a filled-PTFE composite bushing with additives like carbon, bronze, or glass.
- If your primary focus is managing extreme loads and vibration: Consider a composite bearing pad that bonds a PTFE surface to a more robust structural material.
Ultimately, understanding that "Teflon" bushings are based on PTFE allows you to select the precise formulation that balances lubricity with the structural strength your project requires.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Bushings |
|---|---|
| Low Friction | Self-lubricating, reduces wear and maintenance |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists almost all chemicals and solvents |
| High Temp Resistance | Performs from cryogenic to 500°F (260°C) |
| Durability | Absorbs vibration and handles significant loads |
Need a custom PTFE bushing solution?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components like seals, liners, and custom bushings for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production ensures you get the exact properties you need—whether it's virgin PTFE for ultimate chemical purity or a filled composite for enhanced load capacity and dimensional stability.
We handle everything from prototypes to high-volume orders, delivering parts that meet your most demanding specifications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What electrical properties do PTFE mechanical seals possess? Superior Insulation for Demanding Applications
- What makes PTFE V-rings suitable for sealing applications? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What affects the thickness tolerance of PTFE gasket sheets? The Critical Role of Manufacturing Process
- What are the advantages of using PTFE bushes? Low-Friction, Chemical-Resistant Performance
- What are other names for Teflon encapsulated silicone o-rings? Find the Right High-Performance Seal
- What precautions should be taken when installing PTFE O-rings? Avoid Permanent Damage and Seal Failure
- What is the recommended method for cleaning Teflon PTFE sheets? A Guide to Preserving Non-Stick Performance
- What are the characteristics of PTFE Lined Gate Valves? Ideal for Full-Bore Flow and Tight Shut-Off



















