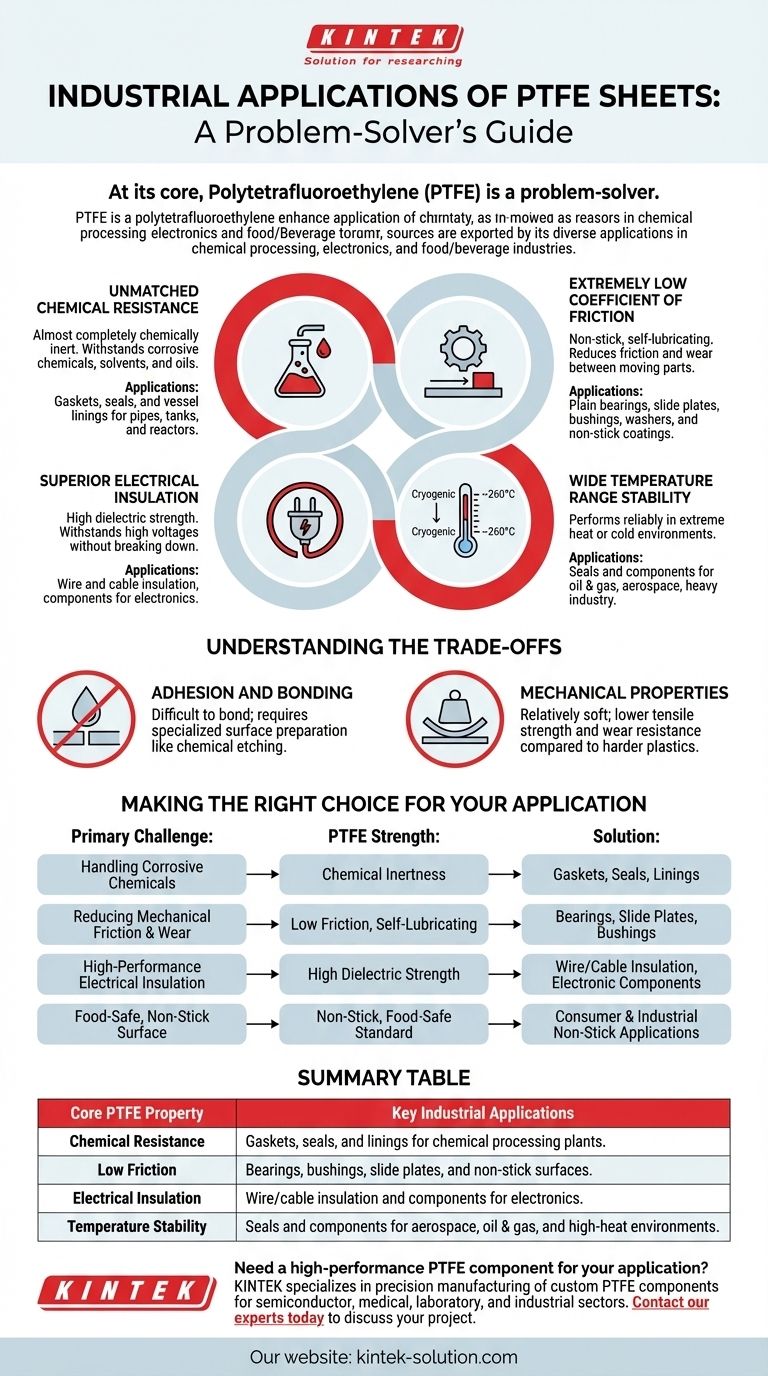
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a problem-solver. Its industrial applications are incredibly diverse, with the most common uses found in chemical processing as gaskets and vessel linings, in electronics as a high-performance electrical insulator, and in food and beverage industries for its unparalleled non-stick surfaces. PTFE sheets are also widely machined into components like bearings, seals, and bushings for industrial machinery.
The immense versatility of PTFE doesn't stem from a single feature, but from a rare combination of four key properties: extreme chemical resistance, a very low coefficient of friction, high-temperature stability, and excellent electrical insulation. Understanding which of these properties is critical for your goal is the key to leveraging this material effectively.

Why PTFE is So Versatile: The Core Properties
The value of PTFE is best understood by examining the fundamental characteristics that drive its adoption across so many different sectors.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is famous for being almost completely chemically inert. It can withstand highly corrosive chemicals, oxidizing media, solvents, and mineral oils that would degrade most other materials.
This makes it an essential material in chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and petrochemical plants. It is fabricated into gaskets, seals, and linings for pipes, tanks, and reactors that handle aggressive substances.
Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest friction coefficients of any known solid material, giving it its signature "non-stick" or self-lubricating quality.
In industrial machinery, this property is used to reduce friction and wear between moving parts. Common applications include plain bearings, slide plates, bushings, and washers. In the food industry, this same property is used for non-stick coatings on cookware and bakeware.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an exceptional electrical insulator with high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand high voltages without breaking down.
This property makes it a critical material in the electrical, electronics, and semiconductor industries. It is frequently used for wire and cable insulation, especially in high-performance or high-frequency applications where signal integrity is paramount.
Wide Temperature Range Stability
PTFE maintains its properties across a very broad range of temperatures, from cryogenic levels up to approximately 260°C (500°F).
This thermal stability allows it to perform reliably in hostile environments found in the oil & gas, aerospace, and heavy industrial sectors, where components are exposed to extreme heat or cold.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, they also present practical considerations that are important to understand.
Adhesion and Bonding
The same low-friction, non-stick surface that makes PTFE so valuable also makes it very difficult to bond to other materials using conventional adhesives. Applying PTFE coatings or bonding sheets often requires specialized surface preparation techniques like chemical etching.
Mechanical Properties
PTFE is a relatively soft material. This softness is advantageous for creating highly effective seals and gaskets that conform to surfaces. However, it also means PTFE has lower tensile strength and wear resistance compared to harder engineering plastics, making it less suitable for high-load structural applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if PTFE is the correct material, map your primary challenge to its core strengths.
- If your primary focus is handling corrosive chemicals: PTFE's chemical inertness makes it the ideal choice for gaskets, seals, and linings.
- If your primary focus is reducing mechanical friction and wear: PTFE sheets machined into bearings, slide plates, or bushings are a top-tier solution.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electrical insulation: PTFE is one of the best materials available for demanding electronic and wiring applications.
- If your primary focus is a food-safe, non-stick surface: PTFE is the established industry standard for both consumer and industrial applications.
Ultimately, selecting PTFE is a decision to leverage a unique combination of high-performance properties to solve a specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Core PTFE Property | Key Industrial Applications |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Gaskets, seals, and linings for chemical processing plants. |
| Low Friction | Bearings, bushings, slide plates, and non-stick surfaces. |
| Electrical Insulation | Wire/cable insulation and components for electronics. |
| Temperature Stability | Seals and components for aerospace, oil & gas, and high-heat environments. |
Need a high-performance PTFE component for your application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and machined parts—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require a prototype or a high-volume production run, we leverage the unique properties of PTFE to solve your specific challenges with corrosion, friction, or insulation.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















