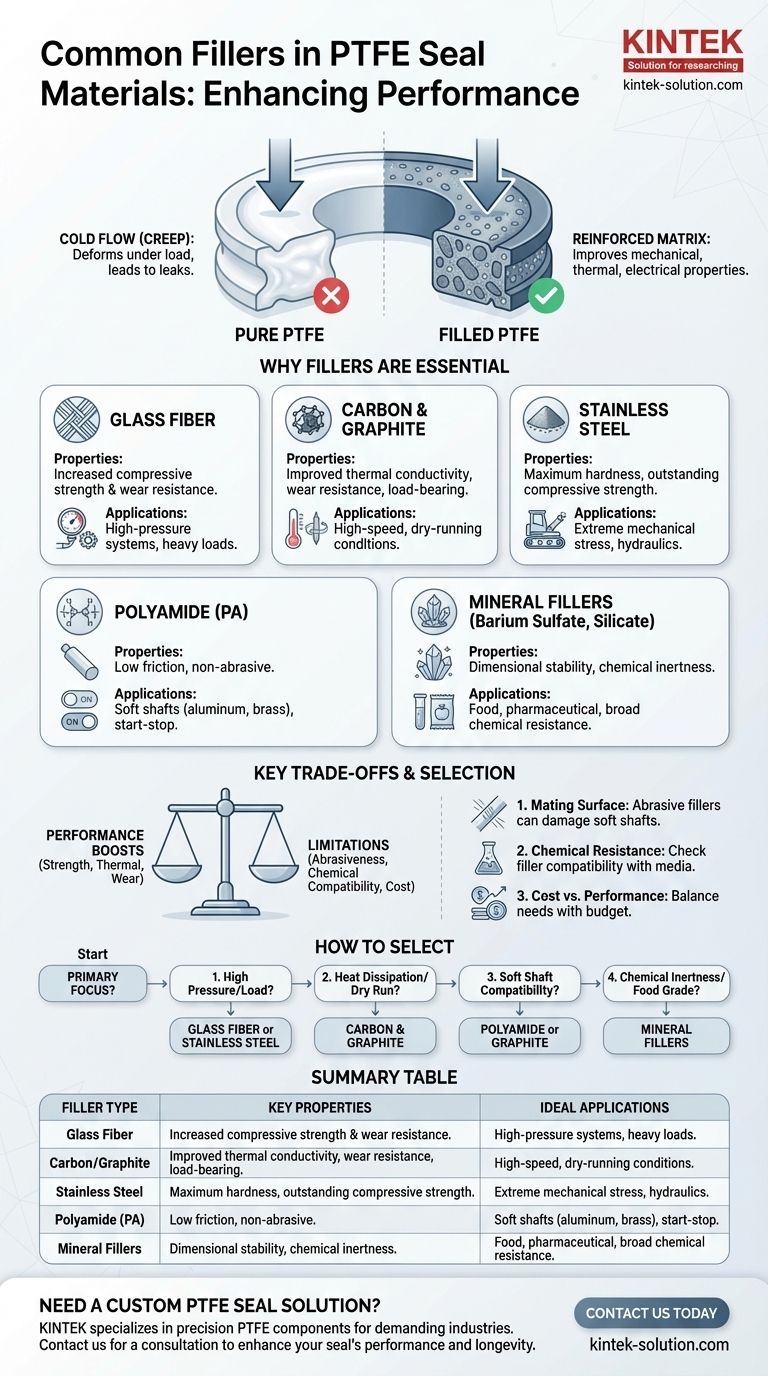
The performance of a PTFE seal is defined by its filler. While pure PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is known for its low friction and chemical inertness, it is rarely used alone in demanding applications. The most common fillers added to the PTFE matrix include glass, carbon, graphite, stainless steel, polyamide, and various minerals like barium sulfate to enhance its mechanical properties.
The central takeaway is that fillers are not just additives; they are essential engineering components. They are used to overcome the inherent limitations of pure PTFE, such as its tendency to deform under load (creep), by improving wear resistance, thermal conductivity, and compressive strength for specific operational demands.

Why Pure PTFE Isn't Always Enough
Before examining specific fillers, it's crucial to understand why they are necessary. Pure, or "virgin," PTFE has remarkable properties but also significant weaknesses that limit its use in dynamic or high-pressure sealing.
The Problem of "Cold Flow"
The most significant limitation of pure PTFE is creep, often called "cold flow." Under sustained pressure, even at room temperature, PTFE will slowly deform and lose its original shape.
This deformation can compromise the integrity of a seal, leading to leaks and eventual failure, especially in critical high-pressure applications.
The Role of Reinforcing Fillers
Fillers are added to the PTFE matrix to create a composite material. These reinforcements provide a rigid structure within the flexible PTFE.
This composite structure dramatically improves mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties, turning a general-purpose polymer into a high-performance sealing material.
A Guide to Common PTFE Fillers
Each filler imparts a unique set of characteristics to the final seal material. The selection process involves matching the filler's properties to the application's specific challenges, such as pressure, temperature, media, and mating surface material.
Glass Fiber
Glass is one of the most common fillers used to enhance PTFE. It is typically added in the form of microspheres or fibers.
Its primary benefit is a significant increase in compressive strength and wear resistance. Glass-filled PTFE is excellent for higher-pressure applications.
Carbon and Graphite
Carbon and graphite are often used together to improve multiple properties simultaneously.
These fillers increase thermal conductivity, which helps dissipate heat from the sealing surface, making them ideal for high-speed or dry-running applications. They also enhance wear resistance and load-bearing capability.
Stainless Steel
For applications requiring maximum hardness and load capacity, stainless steel powder is the filler of choice.
It provides outstanding compressive strength and durability, making it suitable for seals in high-pressure hydraulic systems or components that experience extreme mechanical stress.
Polyamide (PA)
Polyamide is a synthetic polymer that offers a unique set of benefits, particularly related to friction and compatibility.
With a low coefficient of friction, it is ideal for non-lubricated or start-stop applications. Crucially, it is non-abrasive, making it safe for use against softer mating surfaces like stainless steel, aluminum, or brass.
Mineral Fillers (Barium Sulfate, Silicate)
Minerals like barium sulfate or silicate offer a balance of properties.
They improve dimensional stability and chemical resistance without being overly abrasive. Barium sulfate, in particular, is often used in food and pharmaceutical applications due to its inertness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a filler is an exercise in balancing competing requirements. An improvement in one area can often create a limitation in another.
Mating Surface Compatibility
This is a critical consideration. Abrasive fillers like glass can damage softer shaft materials. If your seal is running against an aluminum or bronze shaft, a hard filler can quickly score the surface, leading to leaks. In these cases, a non-abrasive filler like polyamide or graphite is a much safer choice.
Chemical Resistance
While PTFE itself is nearly universally inert, the filler may not be. For example, glass-filled PTFE is not recommended for use with strong alkalis or hydrofluoric acid, as these chemicals can attack the glass fibers.
Cost vs. Performance
High-performance fillers and proprietary blends can significantly increase the cost of the seal. The goal is always to select the most cost-effective material that safely meets the demands of the application without over-engineering the solution.
How to Select the Right Filler for Your Application
Your final choice should be driven entirely by the operational conditions of the seal.
- If your primary focus is high pressure or high load capability: Consider stainless steel or glass fillers for their exceptional compressive strength.
- If your primary focus is heat dissipation in high-speed or dry-running conditions: Carbon and graphite fillers are the standard due to their excellent thermal conductivity.
- If your primary focus is compatibility with soft metal shafts (e.g., aluminum, brass): Opt for non-abrasive fillers like polyamide or graphite to prevent scoring.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical inertness or food-grade standards: Look to mineral fillers like barium sulfate or specially-formulated proprietary blends.
Choosing the correct filler transforms a standard PTFE seal into a precision-engineered component for your specific challenge.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Key Properties | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Fiber | High compressive strength, wear resistance | High-pressure systems, heavy loads |
| Carbon/Graphite | Improved thermal conductivity, wear resistance | High-speed, dry-running conditions |
| Stainless Steel | Maximum hardness, load capacity | Extreme mechanical stress, hydraulics |
| Polyamide (PA) | Low friction, non-abrasive | Soft shafts (aluminum, brass), start-stop |
| Mineral Fillers | Dimensional stability, chemical inertness | Food, pharmaceutical, chemical resistance |
Need a Custom PTFE Seal Solution?
Choosing the right filler is critical for your seal's performance and longevity. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Our expertise ensures you get a seal tailored to your exact operational demands, whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders. Let us help you enhance wear resistance, thermal management, and compatibility with your mating surfaces.
Contact us today for a consultation and discover how our custom PTFE solutions can solve your specific challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency



















