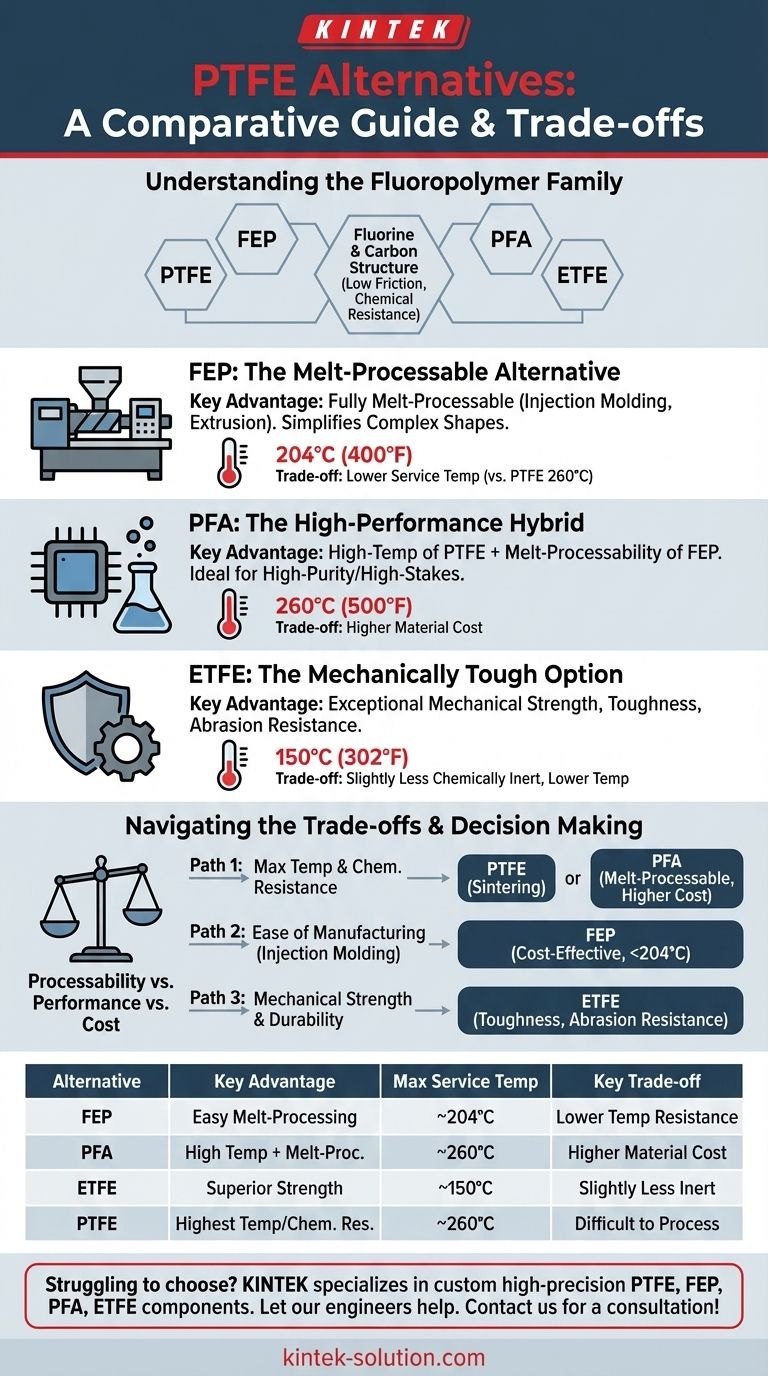
While PTFE is the benchmark for non-stick, high-temperature applications, several key alternatives exist within the same fluoropolymer family. The most common are Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene (FEP), Perfluoroalkoxy (PFA), and Ethylene Tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE). Each offers a unique balance of properties, with the primary trade-offs centering on thermal performance, mechanical strength, and ease of manufacturing.
The decision to choose an alternative to PTFE is rarely about finding a superior material overall. Instead, it is a strategic choice to gain a specific advantage—such as easier melt-processing with FEP or superior toughness with ETFE—while accepting a calculated compromise in another area, like ultimate temperature resistance.

Understanding the Fluoropolymer Family
Think of PTFE and its alternatives not as entirely different materials, but as siblings in the fluoropolymer family. They all share a core chemical structure based on fluorine and carbon, which gives them their characteristic low friction, high chemical resistance, and non-stick surfaces.
However, subtle differences in their molecular makeup create distinct advantages and disadvantages, making one a better fit than another for a specific job.
FEP: The Melt-Processable Alternative
Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene (FEP) is often the first alternative considered when moving away from PTFE. Its primary advantage is that it is fully melt-processable.
Unlike PTFE, which must be compressed and sintered (a process similar to ceramics), FEP can be easily processed using conventional methods like injection molding and extrusion. This dramatically simplifies manufacturing complex shapes.
It retains the excellent chemical resistance and low-friction properties of PTFE. The main compromise is a lower service temperature, as it begins to soften and degrade at temperatures where PTFE remains stable (around 204°C for FEP vs. 260°C for PTFE).
PFA: The High-Performance Hybrid
Perfluoroalkoxy (PFA) effectively bridges the gap between PTFE and FEP. It combines the high-temperature performance of PTFE with the melt-processability of FEP.
This makes PFA an ideal choice for high-stakes applications, such as semiconductor or chemical processing equipment, that demand both extreme purity and the ability to be molded into intricate parts. It shares PTFE's near-universal chemical resistance and excellent electrical properties.
The trade-off for this "best of both worlds" profile is typically a higher material cost compared to both PTFE and FEP.
ETFE: The Mechanically Tough Option
Ethylene Tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE) stands out for its exceptional mechanical properties. It is significantly tougher, stiffer, and more abrasion-resistant than PTFE, FEP, or PFA.
While still a fluoropolymer with excellent chemical resistance, it is slightly less inert than the others, as noted by its "slightly more reactive" nature. This strength and durability make it a premier material for architectural membranes, protective coatings, and demanding wire and cable insulation in the aerospace industry.
Its thermal performance is lower than that of PTFE, but its combination of strength, chemical resistance, and relatively low density creates a unique and valuable profile.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a fluoropolymer is a balancing act. Your decision will almost always hinge on which property you are willing to compromise to gain an advantage elsewhere.
The Processing Hurdle of PTFE
The single biggest driver for seeking PTFE alternatives is its difficult processing. The sintering process is slower, more complex, and less suitable for creating intricate, thin-walled parts than melt-processing. If your part design requires injection molding, PTFE is simply not an option.
Temperature vs. Manufacturability
FEP is the clearest example of this trade-off. By accepting a ~60°C reduction in maximum service temperature compared to PTFE, you gain the immense manufacturing advantages of melt extrusion and injection molding.
Performance vs. Cost
PFA offers a way to overcome PTFE's processing limits without sacrificing temperature performance, but this comes at a premium price. The choice between PFA and FEP often comes down to a simple question: is the higher service temperature worth the additional cost for your application?
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires aligning its strengths with your project's most critical need.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature and chemical resistance: PTFE remains the gold standard, but PFA is the clear choice if you also require melt-processability for your part design.
- If your primary focus is ease of manufacturing via injection molding: FEP offers a cost-effective solution with excellent non-stick and chemical properties, as long as your application operates below its 204°C (400°F) limit.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength, durability, and abrasion resistance: ETFE is the superior choice, providing toughness that other fluoropolymers cannot match for applications like durable films or wire insulation.
By understanding these key differences, you can select the precise fluoropolymer that meets your project's unique performance and manufacturing requirements.
Summary Table:
| Alternative | Key Advantage | Max Service Temp | Key Trade-off | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FEP | Easy melt-processing (injection molding) | ~204°C (400°F) | Lower temperature resistance | Cost-effective, complex parts below 204°C |
| PFA | Combines PTFE's high temp with melt-processability | ~260°C (500°F) | Higher material cost | High-purity, high-temp applications (e.g., semiconductor) |
| ETFE | Superior mechanical strength & toughness | ~150°C (302°F) | Slightly less chemically inert | Durable films, wire insulation, abrasion resistance |
| PTFE | Highest temperature & chemical resistance | ~260°C (500°F) | Difficult to process (sintering) | Maximum performance when processability is not critical |
Struggling to choose the right fluoropolymer for your specific application? At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE, FEP, PFA, and ETFE components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get the optimal material and design for your project's unique requirements. Let our engineers help you navigate the trade-offs and select the perfect solution. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of Teflon balls? Unlock Superior Performance in Demanding Environments
- What temperature range can PTFE balls withstand? Unlock Extreme Thermal Stability from -200°C to 260°C
- What are the properties of Teflon balls? Unlock Elite Chemical & Friction Resistance
- What are PTFE balls made of and what are their key properties? Unlock Superior Chemical & Thermal Performance
- What are the tolerances for PTFE balls based on size? Precision vs. Standard Grade Explained



















