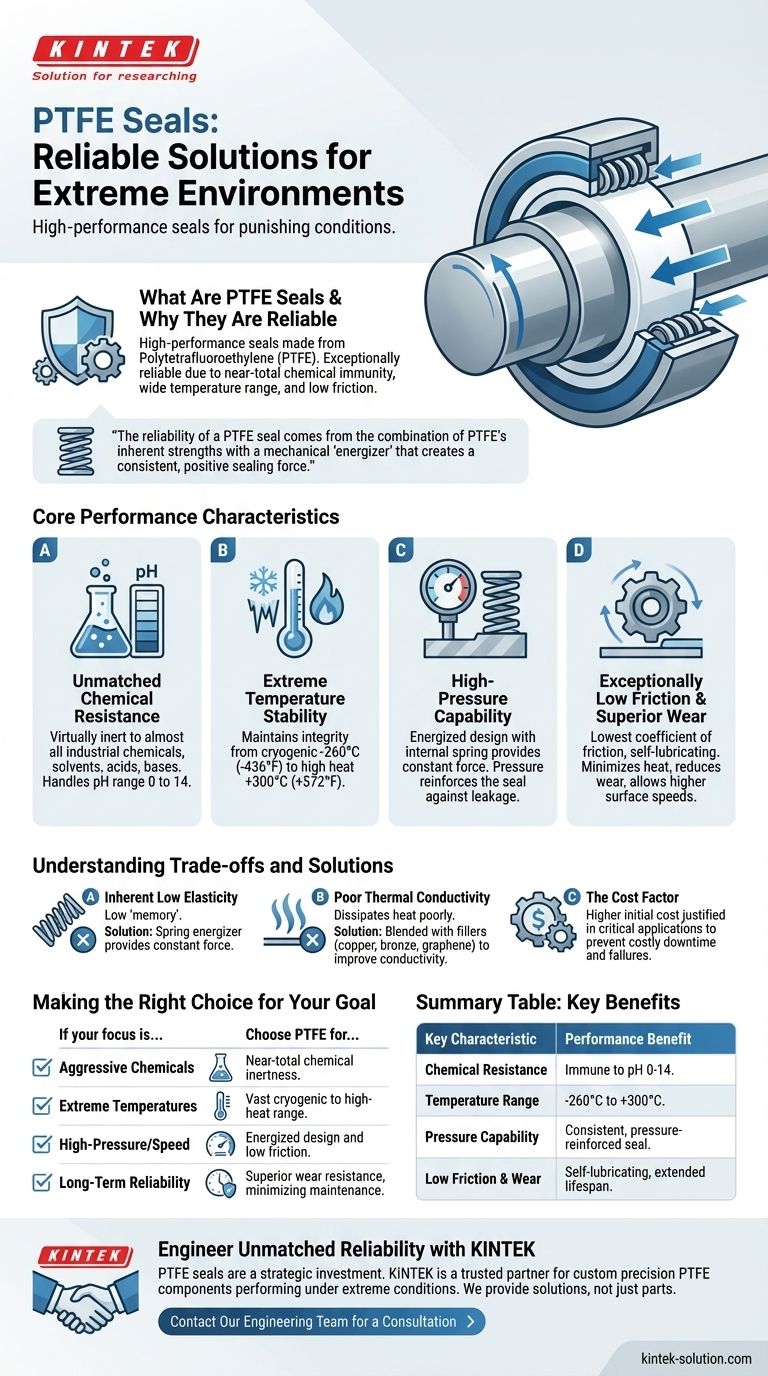
At their core, PTFE seals are high-performance sealing components made from Polytetrafluoroethylene, a material widely known by the brand name Teflon. They are considered exceptionally reliable for extreme environments because their fundamental material properties—near-total chemical immunity, an incredibly wide operating temperature range, and an extremely low coefficient of friction—allow them to function where traditional rubber or elastomer seals would quickly fail.
The reliability of a PTFE seal doesn't come from the material alone. It's the combination of PTFE's inherent strengths with a mechanical "energizer" (like a spring or O-ring) that creates a consistent, positive sealing force across punishing conditions of extreme temperature, pressure, and chemical exposure.

The Core Characteristics of PTFE Seal Performance
To understand why PTFE seals are specified for the most demanding jobs, it's necessary to analyze their key performance attributes. These characteristics work in concert to provide a sealing solution that is both robust and efficient.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert, making it immune to attack from almost all industrial chemicals, solvents, acids, and bases. It can effectively handle fluids across the entire pH range of 0 to 14.
This makes it the default choice for applications in petrochemical plants, chemical processing, and any system handling aggressive or corrosive media where a lesser material would degrade and cause a leak.
Extreme Temperature Stability
PTFE seals maintain their integrity and sealing properties across a vast temperature spectrum, typically from cryogenic lows of -260°C (-436°F) to high heat of +300°C (+572°F).
This allows them to be used in applications as varied as liquefied natural gas (LNG) systems at frigid temperatures and high-temperature systems in industrial manufacturing. Traditional elastomers would become brittle and crack in the cold or soften and degrade in the heat.
High-Pressure Capability
The design of an energized PTFE seal is one of its most significant advantages. The seal consists of a machined PTFE jacket and an internal energizer, often a corrosion-resistant metal spring.
When installed, the energizer is compressed, applying a constant outward force to the PTFE jacket, creating the initial seal. As system pressure increases, that pressure acts on the seal, reinforcing the energizer's force and creating an even tighter barrier against leakage.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material. This self-lubricating property is critical in dynamic applications, such as rotating shafts or reciprocating rods.
The low friction minimizes heat generation, reduces wear on both the seal and the hardware, and allows for higher surface speeds without the risk of seal failure, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and the lifespan of the equipment.
Superior Wear Resistance
The combination of low friction and material toughness gives PTFE seals excellent wear resistance. This makes them ideal for dynamic sealing and reduces the need for frequent maintenance and replacement.
In applications with constant motion, this longevity translates directly into lower operating costs and increased system uptime.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, PTFE seals are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to using them cost-effectively.
Inherent Low Elasticity
Compared to rubber or other elastomers, PTFE has very low "memory" or elasticity. It does not spring back into shape well on its own after being compressed.
This potential weakness is overcome by the inclusion of the spring energizer, which provides the constant force needed to maintain seal contact when system pressure is low or absent.
Poor Thermal Conductivity
The base material does not dissipate heat well. In very high-speed applications, friction can generate heat faster than the seal can shed it, potentially causing issues.
To mitigate this, PTFE can be blended with fillers like copper, bronze, or graphene. These additives dramatically improve thermal conductivity while often enhancing wear resistance as well.
The Cost Factor
PTFE seals are generally more expensive than standard rubber O-rings or oil seals due to more complex manufacturing processes and material costs.
Their use is justified in critical applications where the cost of failure—due to downtime, safety risks, or environmental damage—far outweighs the initial investment in a superior sealing solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing the right seal requires aligning the material's strengths with your application's primary challenges. PTFE is a strategic choice when performance requirements exceed the capabilities of conventional materials.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE is the definitive choice for its near-total chemical inertness, ensuring seal integrity.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperatures (cryogenic or high heat): PTFE's vast operating range makes it one of the few materials that will not become brittle or degrade.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure or high-speed dynamics: The energized design and low-friction surface provide a reliable, long-lasting seal that won't wear out or overheat.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability in a critical system: The superior wear resistance and durability of PTFE justify its higher cost by minimizing maintenance and preventing costly failures.
Ultimately, specifying a PTFE seal is a strategic decision to engineer reliability into environments where conventional materials cannot survive.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Performance Benefit |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Immune to virtually all industrial chemicals, acids, and bases (pH 0-14). |
| Temperature Range | Stable from cryogenic -260°C (-436°F) to high heat +300°C (+572°F). |
| Pressure Capability | Energized design provides a consistent seal that improves with system pressure. |
| Low Friction & Wear | Self-lubricating for high-speed dynamics, reducing wear and extending lifespan. |
Engineer Unmatched Reliability into Your Critical Systems with KINTEK
PTFE seals are a strategic investment for applications where failure is not an option. For over [X] years, KINTEK has been a trusted partner to the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, manufacturing precision PTFE components that perform under extreme pressure, temperature, and chemical exposure.
We don't just supply parts; we provide solutions. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from initial prototypes to high-volume production—ensures you get a seal perfectly tailored to your specific operational challenges.
Ready to eliminate downtime and prevent costly failures? Let's discuss how our PTFE seals can enhance your equipment's performance and longevity.
Contact our engineering team today for a consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What design parameters are specified for PTFE sliding bearings? Ensure Structural Safety and Performance
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- What are the key properties of PTFE Teflon washers? Unlock Superior Chemical & Temperature Resistance
- What advantages do 40% bronze-filled PTFE bushings provide? Boost Load Capacity, Wear Resistance & Heat Dissipation
- What are the nonstick properties of PTFE? Unlocking Superior Performance for Demanding Applications
- Why are PTFE seals suitable for high-velocity applications? Superior Performance at Extreme Speeds
- What are the operational temperature limits for PTFE-lined diaphragm valves? Understanding the Full System Range
- What alternatives to PTFE are available for sealing applications? Find the Right Material for Your Sealing Needs



















