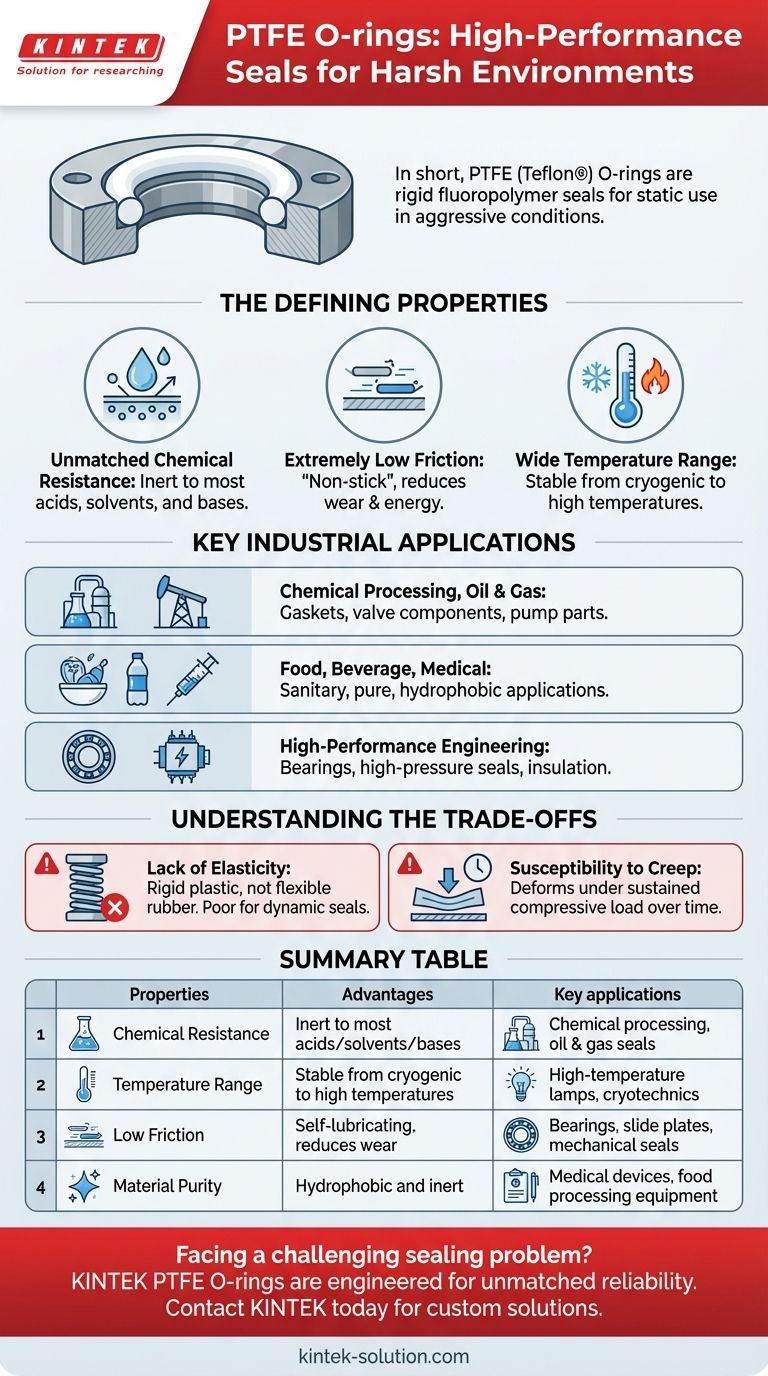
In short, PTFE O-rings are high-performance seals known for their exceptional resistance to aggressive chemicals, extreme temperatures, and friction. Made from the synthetic fluoropolymer polytetrafluoroethylene—commonly known by the trade name Teflon®—they are primarily used in static applications where standard rubber O-rings would fail, such as in pumps, valves, and flanges within the chemical processing, medical, and engineering industries.
The core reason to choose a PTFE O-ring is for its chemical and thermal stability, not its flexibility. Unlike rubber, PTFE is a rigid plastic, making it a superior choice for static sealing in harsh environments but generally unsuitable for dynamic applications that require elasticity.

The Defining Properties of PTFE
To understand where PTFE O-rings are used, you must first understand the material's fundamental characteristics. Its unique molecular structure, composed of carbon and fluorine atoms, gives it a combination of properties that are unmatched by most other polymers.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is a fluoropolymer, making it almost completely inert. It can withstand exposure to the most aggressive acids, solvents, and bases without degrading.
This chemical inertia is why it's a default choice for equipment that handles corrosive fluids.
Extremely Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, giving it a "non-stick" or self-lubricating quality.
In mechanical systems, this reduces wear and energy consumption, making it ideal for components like slide plates, bearings, and seal rings.
Wide Temperature Range
The material remains stable and functional across a vast temperature spectrum, from cryogenic conditions up to high-temperature applications.
This thermal stability allows it to be used in everything from cryotechnics to components in high-temperature lamps and engines.
Where PTFE Excels: Key Industrial Applications
The unique properties of PTFE make it a critical problem-solver across a wide range of demanding industries. Its use is almost always tied to overcoming challenges that would destroy lesser materials.
Chemical Processing and Oil & Gas
In this sector, equipment is constantly exposed to corrosive materials. PTFE is used for gaskets, valve components, pump parts, and vessel linings to ensure long-term integrity.
It is specified for any seal, such as on a pipe flange or valve stem, that must contain aggressive chemicals under pressure.
Food, Beverage, and Medical
Because PTFE is inert and hydrophobic (resists water), it is considered a very pure material suitable for sanitary applications.
It is commonly found in food processing equipment, medical devices like catheters, scientific instruments, and even implants.
High-Performance Engineering
In mechanical, transport, and electrical engineering, PTFE's low friction and temperature resistance are invaluable.
Applications include plain bearings, high-pressure seals, washers, and electrical insulation for wiring and transformers where performance and reliability are non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. While PTFE offers elite performance in certain areas, its physical nature creates clear limitations that are critical to understand.
Lack of Elasticity
The most significant trade-off is that PTFE is a rigid plastic, not a flexible elastomer like rubber. It does not compress and rebound.
This makes it an excellent choice for static, face-seal applications but a poor choice for dynamic seals that need to accommodate movement and maintain a constant squeeze.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under sustained compressive load, especially at higher temperatures, PTFE can slowly deform over time. This phenomenon, known as "creep," must be accounted for in joint and seal design.
Installation Challenges
Because it is not flexible, a solid PTFE O-ring cannot be stretched over a component during installation like a standard rubber O-ring. Designs must accommodate this by using split rings or specially designed glands.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right sealing material requires a clear understanding of your primary operational goal. PTFE is a specialized solution for specific, demanding problems.
- If your primary focus is sealing against aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures: PTFE is an ideal choice for static applications where its inertness provides unmatched reliability.
- If your primary focus is a dynamic seal that requires flexibility and memory: You should look to elastomeric materials like FKM (Viton®) or EPDM, as PTFE's rigidity is a disadvantage here.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction in a mechanical system: PTFE, used in components like bearings, washers, or coatings, is one of the best-performing options available.
Ultimately, choosing PTFE is a decision to prioritize chemical and thermal resilience above all else.
Summary Table:
| Property | Advantage | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to most acids, solvents, and bases | Chemical processing, oil & gas seals |
| Temperature Range | Stable from cryogenic to high temperatures | High-temperature lamps, cryotechnics |
| Low Friction | Self-lubricating, reduces wear | Bearings, slide plates, mechanical seals |
| Material Purity | Hydrophobic and inert | Medical devices, food processing equipment |
Facing a challenging sealing problem in a harsh environment?
PTFE O-rings from KINTEK are engineered to provide unmatched reliability where standard seals fail. We specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Our expertise ensures precision production, from initial prototypes to high-volume orders, delivering the chemical and thermal stability your application demands.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and let our experts provide a sealing solution built for durability and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the overall operating temperature range for PTFE seals, gaskets, and O-rings? Achieve Sealing Integrity from -200°C to +260°C
- How do PTFE seals perform under pressurized conditions? Achieving Reliable Sealing in Demanding Environments
- What makes PTFE stand out among materials used in sealing technology? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for sealing applications? | High-Performance Seals for Extreme Conditions
- What are the benefits of using PTFE seals in demanding industries? Solve Extreme Sealing Challenges



















