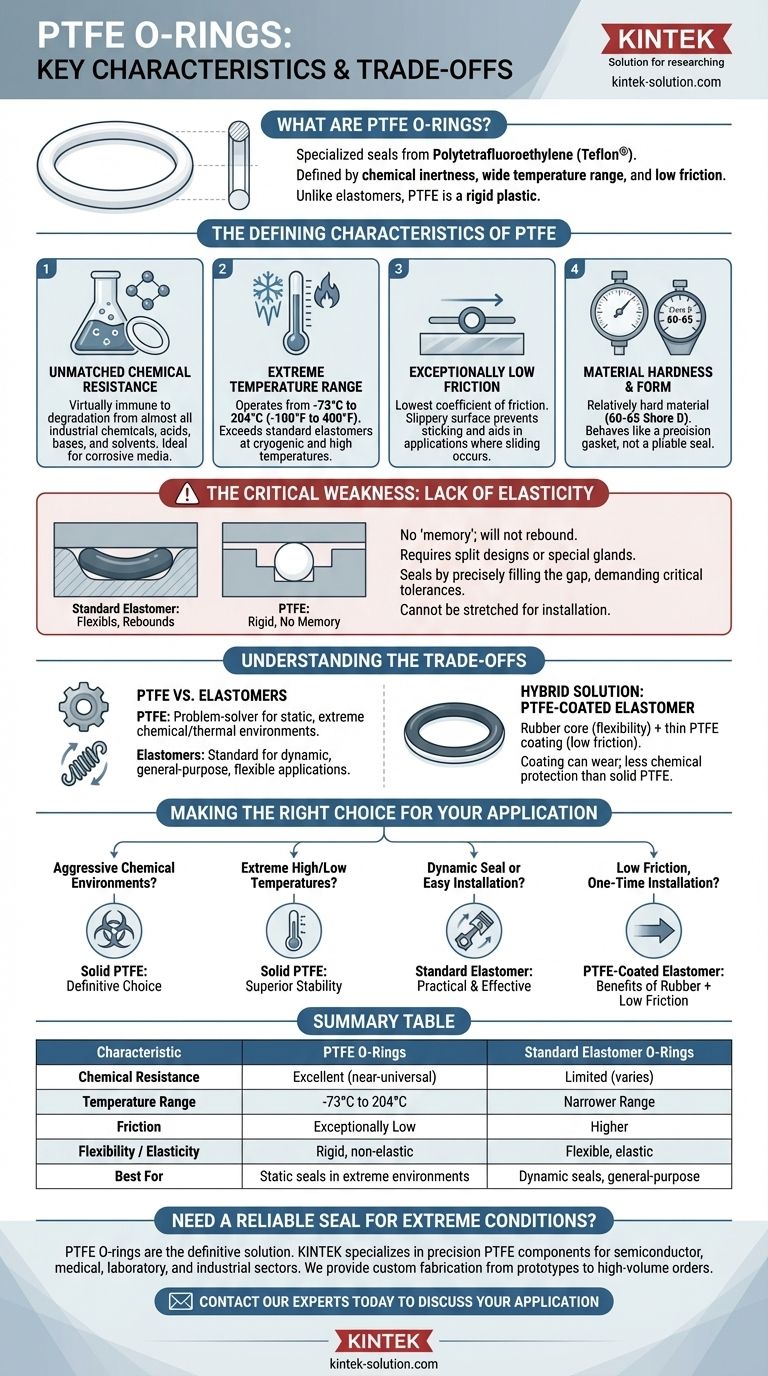
PTFE O-rings are specialized seals made from polytetrafluoroethylene, a fluoropolymer most people know by the brand name Teflon®. They are defined by their near-universal chemical inertness, exceptionally wide temperature range, and very low friction. Unlike common rubber O-rings, PTFE is a rigid plastic, which means it lacks elasticity and does not compress to form a seal in the same way.
The central decision to use a PTFE O-ring is a trade-off: you gain unparalleled resistance to chemicals and extreme temperatures, but you sacrifice the flexibility and ease of installation inherent in standard elastomer O-rings.

The Defining Characteristics of PTFE
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is one of the most chemically inert materials available. It is virtually immune to degradation from almost all industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids, bases, and solvents.
This makes it the default choice for sealing applications in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and other industries where corrosive media are present.
Extreme Temperature Range
PTFE maintains its integrity and sealing properties across an exceptionally broad temperature spectrum. A common operating range is from -73°C to 204°C (-100°F to 400°F).
This stability at both cryogenic lows and high temperatures far exceeds the capabilities of most standard elastomers.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. Its surface is incredibly slippery, which is a major advantage in applications where it must slide against another surface.
This property also aids in preventing the O-ring from sticking to flange surfaces, making disassembly and cleaning easier.
Material Hardness and Form
PTFE is a relatively hard material, typically measuring 60-65 on the Shore D hardness scale. This is in sharp contrast to flexible elastomers like Nitrile or Viton®, which are measured on the softer Shore A scale.
This hardness is a direct result of its rigid, non-elastic nature. It does not stretch or compress easily, behaving more like a precision gasket than a pliable seal.
The Critical Weakness: Lack of Elasticity
The most important factor to understand about PTFE is its lack of "memory." It is not an elastomer and will not rebound after being compressed or stretched.
Installation Challenges
Because PTFE O-rings do not stretch, they cannot be installed in grooves in the same way as rubber O-rings. They often require split designs or specially designed glands that allow the O-ring to be seated without deformation.
Attempting to stretch a PTFE O-ring over a shaft will likely damage it permanently.
Sealing Mechanism
An elastomer O-ring seals by being compressed in a groove, creating a constant force against the mating surfaces. A PTFE O-ring, being non-compressible, seals by precisely filling the gap it occupies.
This means that surface finish and dimensional tolerances of the hardware are much more critical for achieving a reliable seal with PTFE.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a solid PTFE O-ring and a traditional elastomer involves understanding the primary demand of your application.
PTFE vs. Elastomers
Elastomers are the standard choice for general-purpose and dynamic sealing applications where flexibility, resilience, and ease of use are paramount.
Solid PTFE is a problem-solver reserved for static applications where the environment (chemical or thermal) is too extreme for any elastomer to survive.
A Note on PTFE-Coated O-rings
A hybrid solution also exists: an elastomer O-ring (like Viton® or Silicone) with a thin PTFE coating. This design attempts to offer the best of both worlds.
It provides the flexibility and sealing energy of the rubber core with the low-friction surface of PTFE. However, the coating is porous and can wear away, meaning it does not provide the same level of chemical protection as a solid PTFE ring.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection must be driven by the most critical factor in your design.
- If your primary focus is sealing in aggressive chemical environments: Solid PTFE is the definitive choice due to its near-universal inertness.
- If your primary focus is stability at high or cryogenic temperatures: PTFE's exceptionally wide operating range makes it the superior material.
- If your primary focus is a dynamic seal or easy installation: A standard elastomer O-ring is almost always the more practical and effective solution.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction for a one-time installation: A PTFE-coated elastomer O-ring can provide the benefits of rubber with a low-friction surface.
Ultimately, choosing the right sealing material requires matching its unique properties to the specific challenges of your application.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | PTFE O-Rings | Standard Elastomer O-Rings |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (near-universal inertness) | Limited (varies by material) |
| Temperature Range | -73°C to 204°C (-100°F to 400°F) | Narrower range |
| Friction | Exceptionally low | Higher |
| Flexibility / Elasticity | Rigid, non-elastic | Flexible, elastic |
| Best For | Static seals in extreme environments | Dynamic seals, general-purpose use |
Need a Reliable Seal for Extreme Conditions?
PTFE O-rings are the definitive solution for applications where aggressive chemicals, extreme temperatures, or low friction are critical. Choosing the right material and design is essential for performance and safety.
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the unique demands of your industry and provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring you get a seal that meets your exact specifications.
Let us help you solve your most challenging sealing problems. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application



















