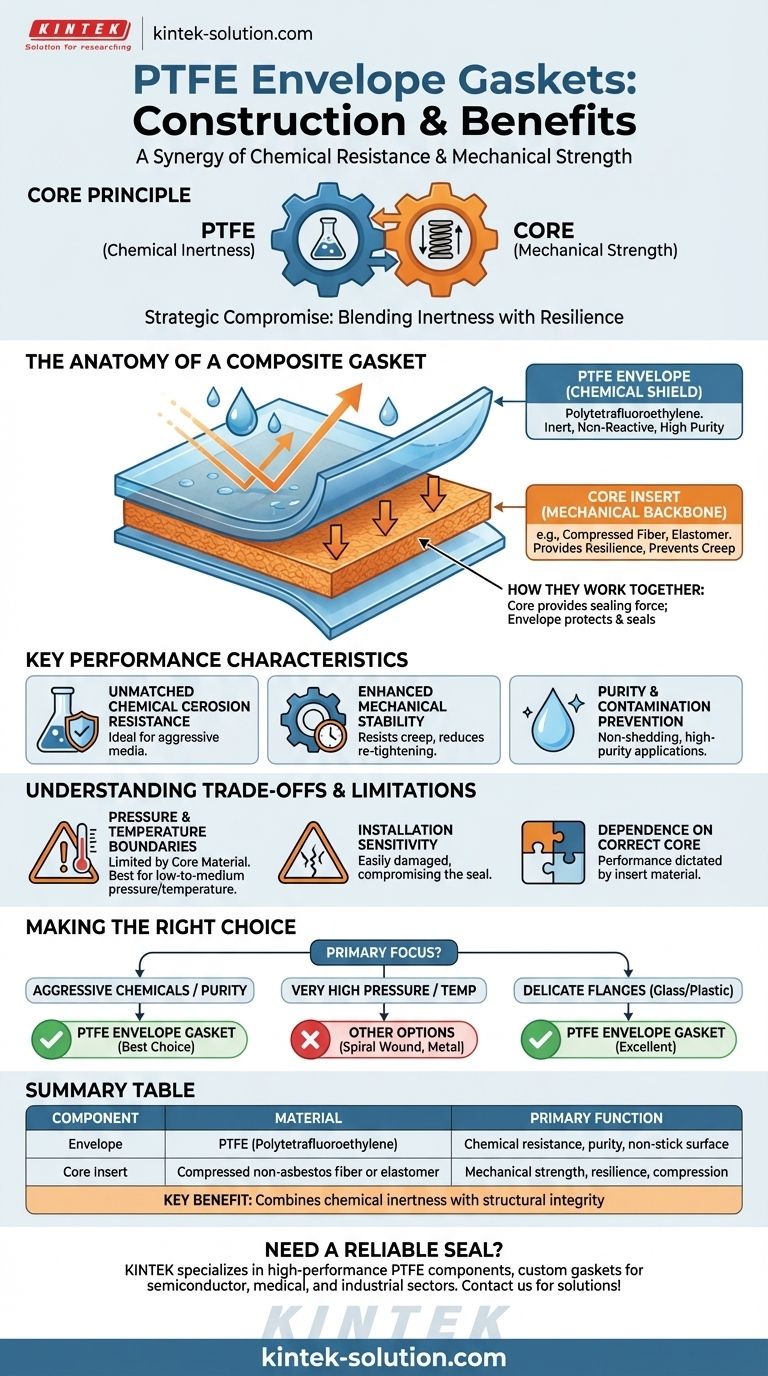
In essence, a PTFE envelope gasket is a composite seal designed to deliver the exceptional chemical resistance of PTFE without its mechanical drawbacks. It achieves this by using a core insert material to provide mechanical strength and resilience, all wrapped within a protective PTFE outer layer. This construction creates a highly versatile gasket for demanding industrial applications.
The core principle behind a PTFE envelope gasket is strategic compromise. It combines the chemical inertness of a PTFE shell with the mechanical strength of a separate core material, creating a seal that is both highly resistant and structurally robust.
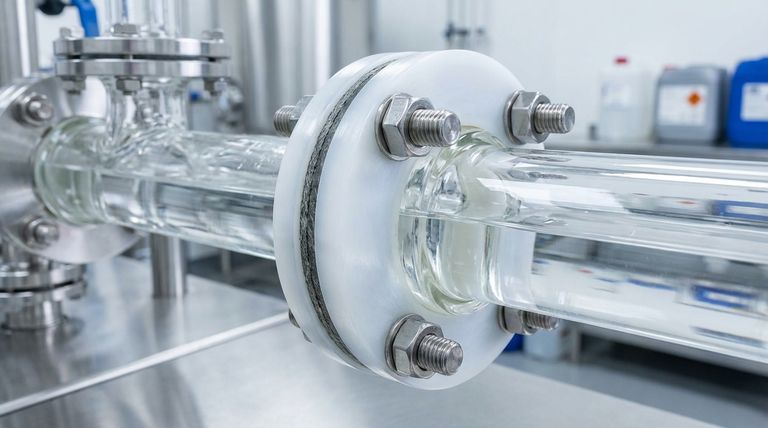

The Anatomy of a Composite Gasket
A PTFE envelope gasket is not a single material but a two-part system. Understanding both components is key to understanding its function and proper application.
The PTFE Envelope: The Chemical Shield
The outer layer, or "envelope," is made from Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This material is selected for its unique properties.
PTFE is almost universally inert, meaning it will not react with or degrade when exposed to the vast majority of industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents.
This non-reactive surface also prevents process media from being contaminated by the gasket material, which is critical in industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing.
The Core Insert: The Mechanical Backbone
The insert material sits inside the PTFE envelope and provides the gasket's structural integrity and sealing force. The core is what allows the gasket to be compressed and maintain a tight seal over time.
Common core materials include compressed non-asbestos fiber, which offers good general-purpose sealing, or various elastomers (rubbers) that provide excellent compressibility for uneven flanges.
The core counteracts PTFE's natural tendency to "creep" or "cold flow" under pressure, ensuring the seal remains tight throughout thermal cycles and pressure fluctuations.
How They Work Together
The design creates a synergy between the two materials. The core provides the robust mechanical force needed to create and hold a seal.
The PTFE envelope protects this core from chemical attack and provides a clean, non-stick, and highly compliant sealing face against the pipe flanges.
Key Performance Characteristics
The composite design results in a unique set of benefits tailored for specific challenges.
Unmatched Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Because the process fluid only ever touches the PTFE envelope, the gasket can be used in the most aggressive chemical services without fear of degradation.
Enhanced Mechanical Stability
The insert material provides the elastic recovery and creep resistance that solid PTFE gaskets lack. This leads to a more reliable, long-lasting seal with minimal need for re-tightening bolts.
Purity and Contamination Prevention
The non-stick, inert surface of the PTFE does not shed particles into the process stream. This makes it an ideal choice for high-purity applications where contamination is not an option.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, PTFE envelope gaskets are not a universal solution. Objectively assessing their limitations is crucial for proper selection.
Pressure and Temperature Boundaries
The performance of the gasket is ultimately limited by its core material. An elastomeric core will have a much lower maximum temperature rating than a compressed fiber core.
Furthermore, these gaskets are generally best suited for low-to-medium pressure applications. In very high-pressure systems, the PTFE envelope can be forced or extruded out of the flange joint.
Installation Sensitivity
The protective benefit of the PTFE envelope is lost if it is damaged. Scratches, cuts, or folds that occur during handling or installation can create a leak path and expose the vulnerable core material to chemical attack.
Dependence on the Correct Core
The gasket's overall performance in terms of temperature, pressure, and compressibility is dictated entirely by the core material. Choosing the wrong insert for your application's demands will lead to premature failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if a PTFE envelope gasket fits your specific operational goal.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals or ensuring product purity: A PTFE envelope gasket is an industry-standard choice, offering unparalleled chemical resistance.
- If your primary focus is sealing very high pressures or temperatures: You should evaluate other options, such as spiral wound or corrugated metal gaskets, which are designed for more extreme mechanical loads.
- If your primary focus is sealing delicate or easily damaged flanges (like glass or plastic): The soft, compliant nature of the PTFE surface makes it an excellent choice to prevent flange damage.
By understanding its composite nature, you can deploy the PTFE envelope gasket as a precise solution for challenging sealing environments.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Envelope | PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) | Chemical resistance, purity, non-stick surface |
| Core Insert | Compressed non-asbestos fiber or elastomer | Mechanical strength, resilience, compression |
| Key Benefit | --- | Combines chemical inertness with structural integrity |
Need a reliable seal for aggressive chemicals or high-purity processes?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom envelope gaskets, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production ensures your gaskets deliver unmatched chemical resistance and mechanical stability, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and get a solution tailored to your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What makes ePTFE gaskets effective against gas leakage? The Key to Superior Gas Sealing
- What is the water transmission rate of Teflon encapsulated O-rings? A Guide to Superior Moisture Sealing
- What are the key advantages of using PTFE valves in the chemical industry? Enhance Safety and Purity
- How are PTFE sheets used in industrial plants? Solve Leaks, Friction & Contamination
- How do PTFE impellers compare to traditional impeller materials? Maximize Efficiency in Corrosive Applications
- What are the future development trends for PTFE seal technology? Advanced Materials & Precision Manufacturing
- Why are PTFE gaskets suitable for the food and beverage industry? Ensure Purity, Hygiene & Performance
- What industries commonly use Teflon encapsulated O-rings for chemical resistance? Protect Critical Processes from Corrosion



















