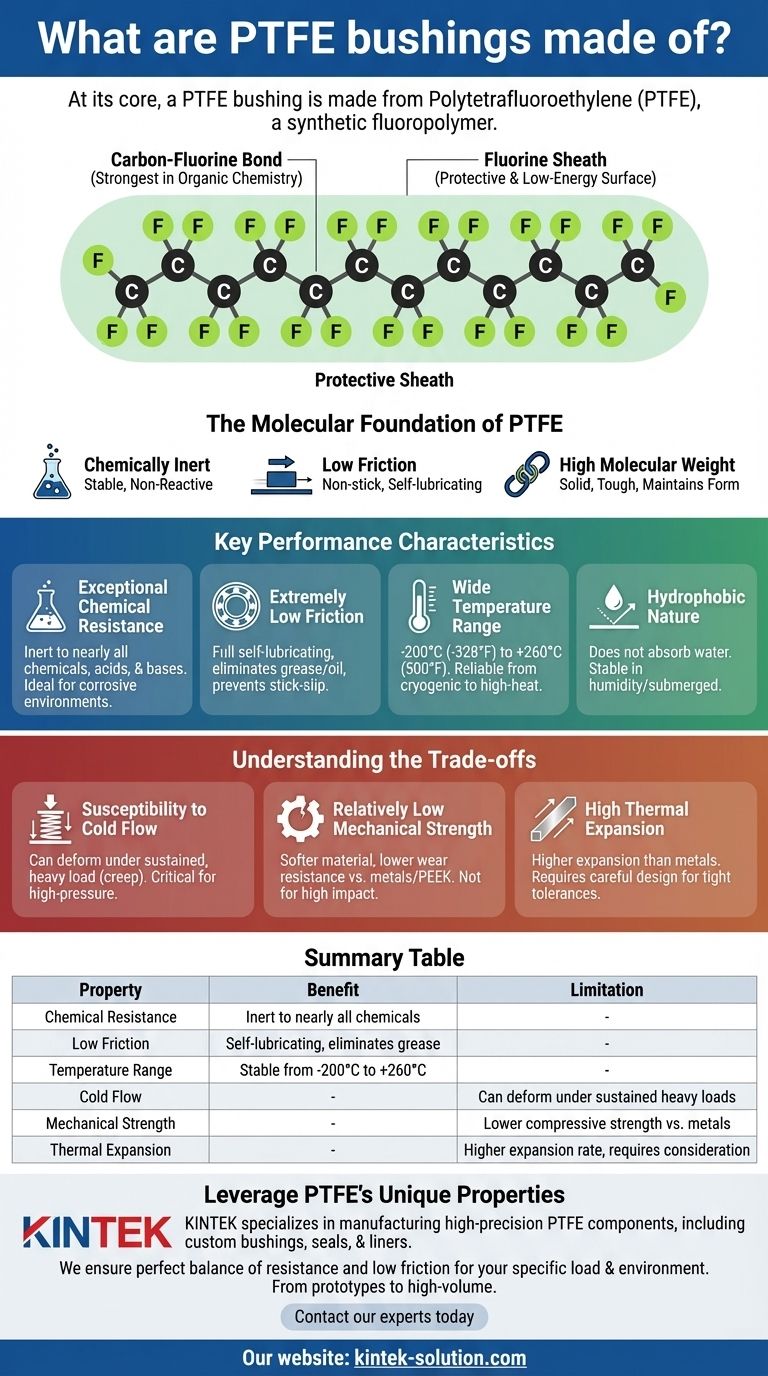
At its core, a PTFE bushing is made from Polytetrafluoroethylene. This is a synthetic fluoropolymer, a high-molecular-weight compound composed exclusively of carbon and fluorine atoms. The remarkably strong bond between these atoms is what gives the material its signature properties, making it far more than just a simple plastic.
The true value of a PTFE bushing lies not just in what it's made of, but in how its unique molecular structure—a chain of carbon atoms shielded by fluorine—creates a material with an unmatched combination of chemical inertness, temperature resistance, and an extremely low-friction surface.

The Molecular Foundation of PTFE
To understand why PTFE bushings perform the way they do, we must look at their fundamental chemistry. The material's properties are a direct result of its simple but incredibly robust atomic structure.
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond
PTFE consists of a long, linear chain of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom in this backbone is bonded to two fluorine atoms.
This arrangement creates a dense "sheath" of fluorine atoms protecting the carbon chain. The bond between carbon and fluorine is one of the strongest known in organic chemistry.
Why This Structure Is So Effective
This powerful molecular structure makes the material exceptionally stable and non-reactive. The fluorine sheath effectively prevents other chemicals from attacking the vulnerable carbon backbone.
Furthermore, the fluorine atoms create a very low-energy surface that repels almost everything, which is the source of its famous non-stick and low-friction characteristics.
High Molecular Weight
PTFE is also a polymer of very high molecular weight. This contributes to its solidity, toughness, and ability to maintain its form under stress, distinguishing it from lower-weight oils and waxes.
Key Performance Characteristics Explained
The molecular structure of PTFE directly translates into a set of highly desirable engineering properties that define its use in bushings.
Exceptional Chemical Resistance
Because the carbon-fluorine bonds are so difficult to break, PTFE is inert to nearly all chemicals, acids, and bases. This makes it an ideal choice for bushings used in corrosive environments.
Extremely Low Friction
The fluorine sheath gives PTFE one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This allows PTFE bushings to operate with full self-lubricating capabilities, eliminating the need for external grease or oil and preventing stick-slip motion.
Wide Temperature Range
The molecular stability of PTFE allows it to perform reliably across an exceptionally broad temperature spectrum. It remains functional and stable from cryogenic conditions of -200°C (-328°F) up to high-heat applications of +260°C (500°F).
Hydrophobic Nature
PTFE does not absorb water. This hydrophobic property ensures that the bushing's dimensions and physical properties remain stable even in high-humidity or submerged applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not the solution for every problem. An objective assessment requires understanding its limitations.
Susceptibility to Cold Flow
Under a sustained, heavy load, pure PTFE can slowly deform over time, a phenomenon known as "creep" or "cold flow." This is a critical design consideration for high-pressure applications.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals or other engineering plastics like PEEK, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It has lower compressive strength and wear resistance, making it less suitable for applications involving high impact or severe abrasion unless it is reinforced with fillers like glass or carbon.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than most metals. In designs with very tight tolerances that will experience significant temperature swings, this expansion and contraction must be carefully managed to avoid failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right bushing material requires matching its core properties to the demands of your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is chemical inertness and low friction: PTFE is an unparalleled choice, ideal for corrosive environments or systems where external lubrication is impossible.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical load or abrasion resistance: Consider a filled-PTFE composite (e.g., glass or carbon-filled) or an entirely different high-strength polymer, as pure PTFE may deform or wear too quickly.
- If your primary focus is precision in a variable-temperature environment: You must account for PTFE's higher thermal expansion rate in your design to maintain critical tolerances.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental carbon-fluorine chemistry of PTFE is the key to correctly leveraging its unique strengths for your engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to nearly all chemicals, acids, and bases. | - |
| Low Friction | Self-lubricating, eliminates need for grease/oil. | - |
| Temperature Range | Stable from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to 500°F). | - |
| Cold Flow | - | Can deform under sustained heavy loads (creep). |
| Mechanical Strength | - | Lower compressive strength vs. metals or PEEK. |
| Thermal Expansion | - | Higher expansion rate than metals; requires design consideration. |
Leverage PTFE's Unique Properties for Your Application
Understanding the fundamental chemistry of PTFE is the first step. Implementing it effectively in a critical component like a bushing is the next. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom bushings, seals, liners, and labware.
Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise ensures you get a component that perfectly balances PTFE's exceptional chemical resistance and low friction with the structural integrity required for your specific load, temperature, and environmental conditions.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Ready to solve your engineering challenge with a precisely engineered PTFE solution?
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications



















