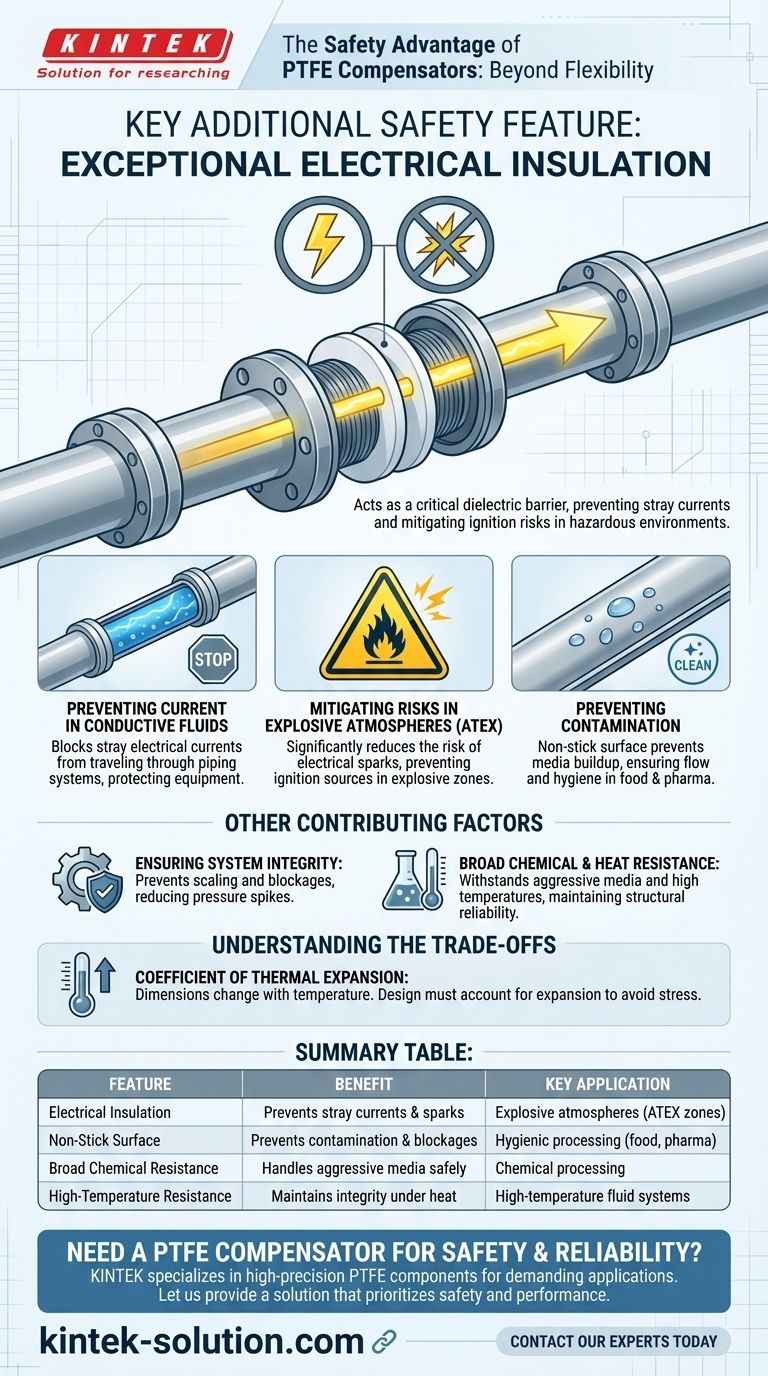
The key additional safety feature of a PTFE compensator is its exceptional electrical insulation. In applications involving conductive fluids or potentially explosive atmospheres, this property acts as a critical electrical break in a metallic piping system, preventing the flow of stray currents and mitigating ignition risks.
While known for chemical and heat resistance, PTFE's role as a dielectric insulator provides a unique and vital layer of safety. This feature is not a minor benefit but a decisive factor for ensuring system integrity in hazardous environments.

The Core Safety Advantage: Electrical Insulation
A compensator, or expansion joint, is designed to absorb movement and vibration. However, when made of PTFE and installed in a metal pipeline, it serves a dual purpose.
Why Electrical Insulation Matters
Most industrial piping is made of conductive metals. This creates a continuous electrical path throughout the system.
A PTFE compensator is a dielectric material, meaning it does not conduct electricity. Inserting it into a metal pipeline effectively isolates one section from another.
Preventing Current in Conductive Fluids
When electrically conductive fluids (like many acids or salt solutions) flow through a pipeline, they can carry stray electrical currents.
A PTFE compensator acts as a barrier, stopping this current from traveling through the entire system and potentially damaging sensitive equipment or creating a safety hazard.
Mitigating Risks in Explosive Atmospheres
This is the most critical application for PTFE's insulating properties. In environments classified as potentially explosive (such as ATEX zones), preventing ignition sources is paramount.
Stray electrical currents or the buildup of static electricity can create a spark, which could lead to a catastrophic explosion. By breaking the electrical continuity of the pipeline, a PTFE compensator significantly reduces the risk of an electrical spark.
Other Contributing Safety & Performance Factors
While electrical insulation is a standout feature, other properties of PTFE contribute to overall system safety and reliability.
Preventing Contamination
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction, resulting in a non-stick surface.
This property prevents process media from building up inside the joint, which is crucial for maintaining flow and preventing contamination in hygienic applications like food, beverage, and pharmaceutical production.
Ensuring System Integrity
The prevention of scaling and deposit buildup also means there is less risk of a blockage that could lead to dangerous pressure spikes within the system.
This inherent cleanliness reduces the need for aggressive chemical cleaning, further enhancing operational safety and component longevity.
Fundamental Chemical and Heat Resistance
Of course, the primary reasons PTFE is chosen are its broad chemical compatibility and high-temperature resistance.
These fundamental properties ensure the compensator will not degrade when exposed to aggressive media or high temperatures, which is the first line of defense for system safety.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every scenario. To specify PTFE correctly, you must be aware of its operational limitations.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion compared to metals.
This means its dimensions change significantly with temperature. System designers must account for this expansion and contraction to avoid undue stress on the compensator or its connecting flanges.
Specialized Chemical Compatibility
While PTFE is resistant to most chemicals, certain highly reactive agents or conditions can pose a challenge.
For specialized or high-purity applications, it is always recommended to consult the manufacturer's compatibility data to ensure the specific grade of PTFE is suitable for the intended service.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires aligning its properties with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is safety in explosive atmospheres: The electrical insulation of PTFE is a critical, non-negotiable feature for preventing ignition.
- If your primary focus is hygienic processing: PTFE's non-stick surface and availability in FDA-compliant grades are essential for preventing contamination.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical handling: The combination of near-universal chemical resistance and electrical insulation provides a uniquely robust safety buffer.
By understanding these distinct properties, you can specify a material not just for performance, but for comprehensive and reliable system safety.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | Prevents stray currents and ignition sparks | Explosive atmospheres (ATEX zones) |
| Non-Stick Surface | Prevents contamination and blockages | Hygienic processing (food, pharma) |
| Broad Chemical Resistance | Handles aggressive media safely | Chemical processing |
| High-Temperature Resistance | Maintains integrity under heat | High-temperature fluid systems |
Need a PTFE compensator that ensures safety and reliability?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom compensators designed for demanding applications in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial settings. Our expertise ensures your system is protected against electrical hazards, contamination, and chemical degradation.
Let us provide you with a solution that prioritizes safety and performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements for prototypes or production orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection



















