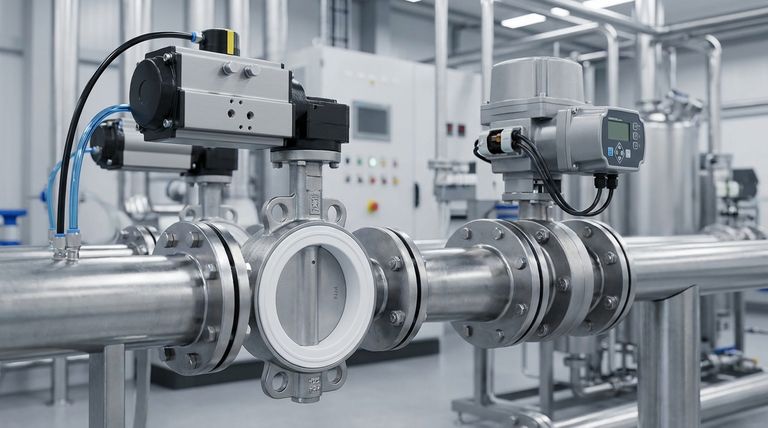
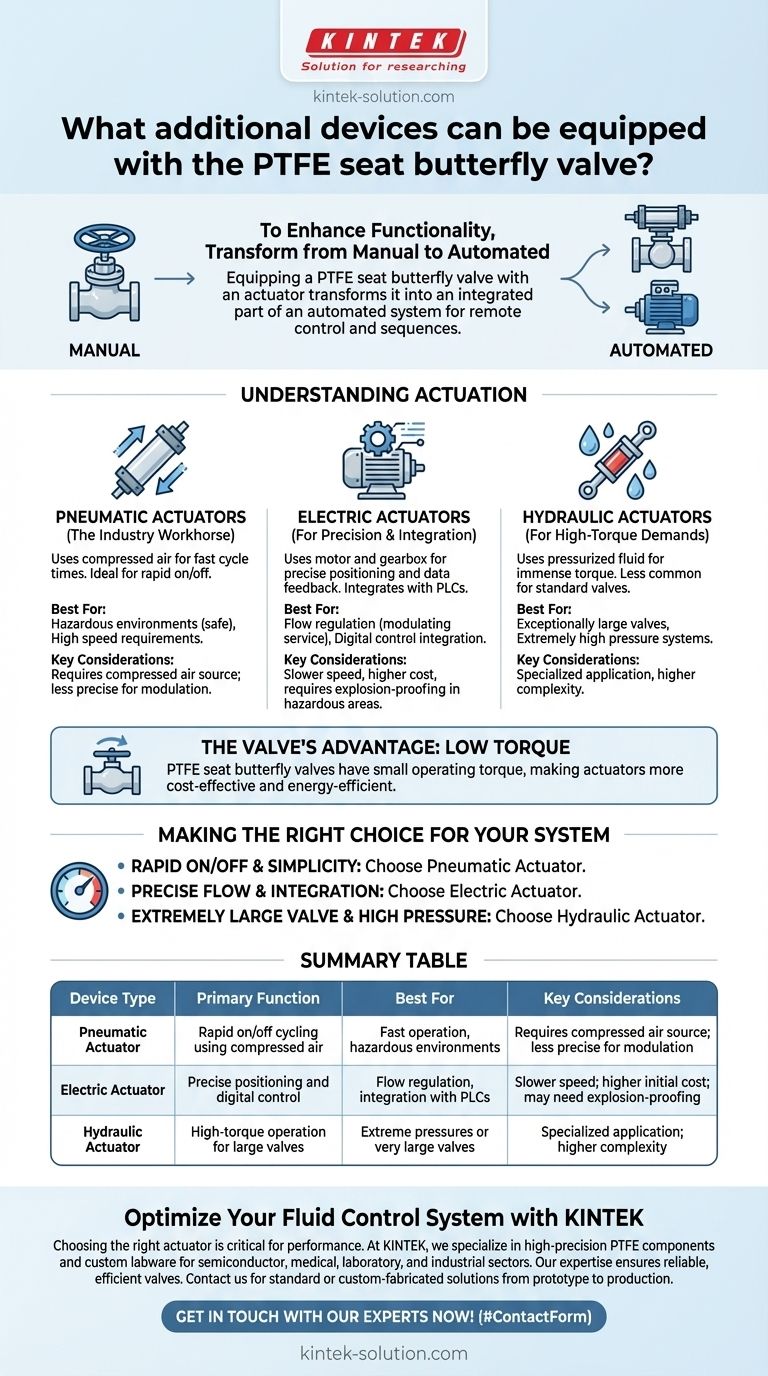
To enhance functionality, a PTFE seat butterfly valve is most commonly equipped with pneumatic or electric actuators. These devices replace manual operation, allowing the valve to be integrated into automated systems for remote control and programmed sequences.
Equipping a PTFE seat butterfly valve with an actuator transforms it from a manual component into an integrated part of an automated system. The choice between pneumatic, electric, or even hydraulic actuation depends entirely on your system's specific needs for speed, power, and control precision.

Understanding Actuation: From Manual to Automated Control
The primary purpose of adding a device to a butterfly valve is to provide a method of actuation—the force that opens and closes the disc. While manual operation is the baseline, automation unlocks significant process efficiencies.
The Default: Manual Operation
Most butterfly valves come standard with a simple lever or a geared handwheel for manual control. This is reliable and straightforward but requires an operator to be physically present at the valve.
Pneumatic Actuators: The Industry Workhorse
A pneumatic actuator uses compressed air to generate the force needed to turn the valve stem. They are widely used due to their reliability and simplicity.
These devices are known for their fast cycle times, making them ideal for applications requiring rapid opening and closing. They are also inherently safe for use in hazardous or explosive environments where an electric spark would be a risk.
Electric Actuators: For Precision and Integration
An electric actuator uses a motor and gearbox to operate the valve. This is the preferred choice for systems that require precise control and data feedback.
They excel at "modulating" service, where the valve must be held at specific positions (e.g., 25% open) to regulate flow. Electric actuators integrate seamlessly with modern control systems like a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), enabling sophisticated program control.
Hydraulic Actuators: For High-Torque Demands
Though less common for standard PTFE butterfly valves, hydraulic actuators are another option. They use pressurized fluid (like oil) to generate immense torque.
This makes them suitable for exceptionally large valves or systems with extremely high pressures where pneumatic or electric actuators might not provide sufficient force.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an actuator is not just about function; it's about balancing cost, complexity, and performance within your specific operational context.
Pneumatic Actuator Limitations
The primary requirement is a source of clean, dry compressed air, which represents a significant infrastructure cost if not already available. While great for on/off service, they offer less precise positioning for modulating control compared to electric actuators.
Electric Actuator Limitations
Electric actuators typically have a slower operating speed than their pneumatic counterparts. They also tend to have a higher initial purchase price and may require more complex wiring and setup. In hazardous locations, they require expensive explosion-proof enclosures.
The Valve's Advantage: Low Torque
A key feature of PTFE seat butterfly valves is their small operating torque. This inherent efficiency means they do not require excessively large or powerful actuators, making both pneumatic and electric options more cost-effective and energy-efficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Selecting the correct device depends on a clear understanding of your process goals.
- If your primary focus is rapid on/off cycling and operational simplicity: A pneumatic actuator is the most reliable and common choice.
- If your primary focus is precise flow control and integration with a digital control system: An electric actuator provides the necessary accuracy and communication capabilities.
- If your primary focus is managing an extremely large valve or very high system pressures: A hydraulic actuator delivers the necessary torque, though this is a specialized application.
Choosing the correct device transforms your valve from a simple component into a responsive, intelligent part of your overall process.
Summary Table:
| Device Type | Primary Function | Best For | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pneumatic Actuator | Rapid on/off cycling using compressed air | Fast operation, hazardous environments | Requires compressed air source; less precise for modulation |
| Electric Actuator | Precise positioning and digital control | Flow regulation, integration with PLCs | Slower speed; higher initial cost; may need explosion-proofing |
| Hydraulic Actuator | High-torque operation for large valves | Extreme pressures or very large valves | Specialized application; higher complexity |
Optimize Your Fluid Control System with KINTEK
Choosing the right actuator is critical for maximizing the performance of your PTFE seat butterfly valves. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures that your valves operate with the reliability and efficiency your processes demand.
Whether you need a standard solution or a custom-fabricated component from prototype to high-volume production, we are here to help. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your system's automation and performance.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Which contact surfaces provide the best wear resistance for PTFE piston rings? Design a High-Performance System
- How do PTFE spring-energized seals perform in defense and nuclear environments? Engineered for Extreme Reliability.
- How is TFE (tetrafluoroethylene) produced? A Guide to the High-Temperature Synthesis Process
- What material is used to make PTFE flange gaskets? Choose the Right PTFE for Your Sealing Needs
- What precautions should be taken when drilling PTFE? Master Clean, Accurate Holes Every Time
- What are the processing methods for PTFE? A Guide to Compression Molding and Machining
- How does PTFE's low friction performance benefit industrial applications? Enable Clean, Reliable Movement Without Lubricants
- In which industries are PTFE heat press sheets commonly used? Essential for Textile Printing & Custom Apparel



















