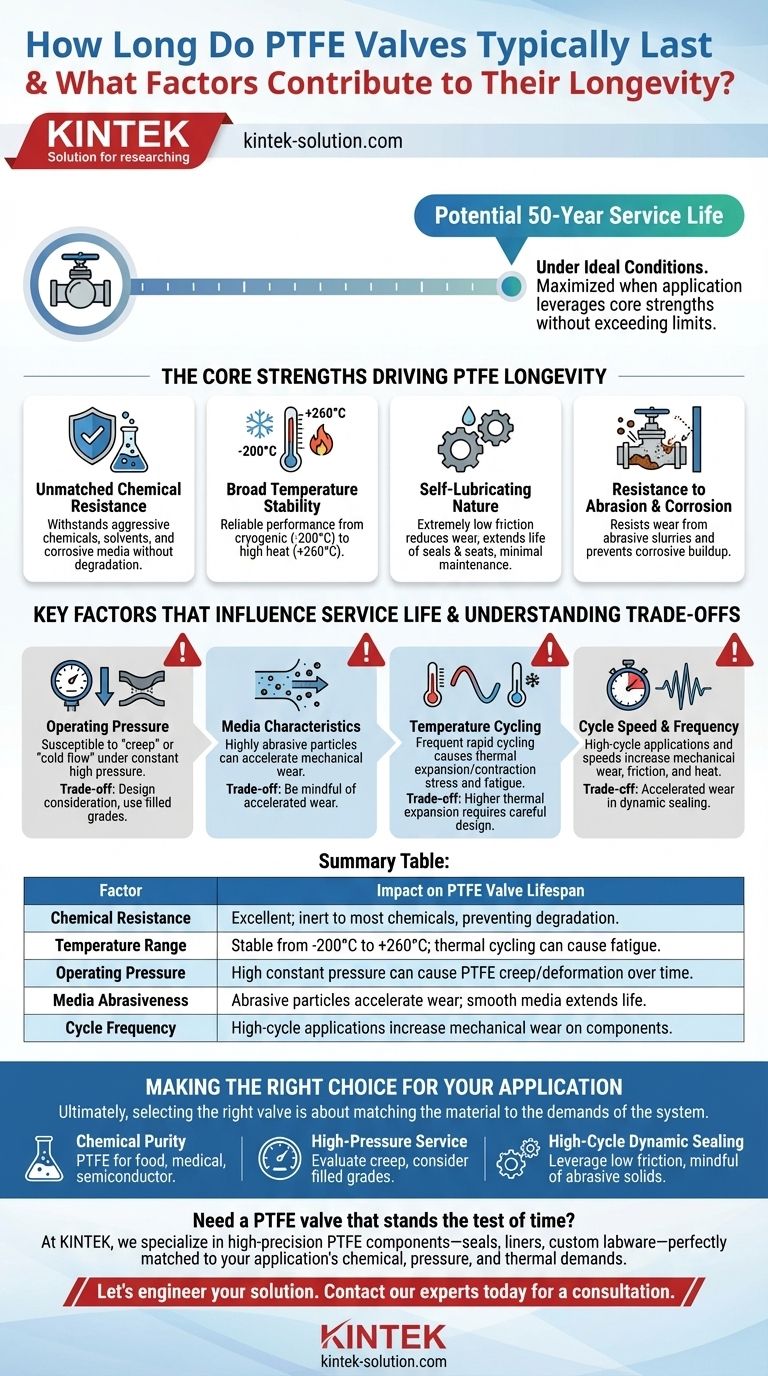
Under ideal conditions, PTFE valves are engineered for an exceptionally long service life, capable of lasting up to 50 years. This remarkable longevity is not guaranteed; it is a direct result of PTFE's unique material properties and the degree to which the operating environment aligns with its strengths.
The lifespan of a PTFE valve is less about a fixed timeline and more about a fundamental principle: its durability is maximized when the application leverages its inherent chemical inertness, low-friction surface, and wide temperature tolerance without exceeding its mechanical limits for pressure and wear.

The Core Strengths Driving PTFE Longevity
To understand why PTFE valves can last so long, we must first understand the core properties of the material itself. These characteristics make it a default choice for demanding applications.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is one of the most chemically inert polymers known. It can withstand a vast range of aggressive chemicals, solvents, and corrosive media without degrading, which is the primary reason for its long life in processing plants.
Broad Temperature Stability
The material remains highly stable and performs reliably across an impressive temperature range, from cryogenic conditions at -200°C (-328°F) up to high heat at +260°C (+500°F).
Self-Lubricating Nature
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction, one of the lowest of any solid material. This self-lubricating quality means valve components move smoothly with minimal wear, significantly reducing the need for maintenance and extending the life of seals and seats.
Resistance to Abrasion and Corrosion
Beyond its chemical inertness, PTFE physically resists wear from abrasive slurries and prevents the corrosive buildup that can seize other types of valves, ensuring consistent operational performance over decades.
Key Factors That Influence Service Life
The theoretical 50-year lifespan is a best-case scenario. In practice, several operational factors dictate the actual service life of a PTFE valve.
Operating Pressure
While PTFE handles pressure well, it is susceptible to a phenomenon called "creep" or "cold flow." Constant, high pressure can cause the material to slowly deform over time, which may compromise the integrity of a seal.
Media Characteristics
The fluid or gas passing through the valve has a major impact. While PTFE is self-lubricating, the presence of highly abrasive particles can accelerate mechanical wear over millions of cycles.
Temperature Cycling
While stable at extreme temperatures, frequent and rapid cycling between hot and cold can cause thermal expansion and contraction. This stress can eventually fatigue the material and surrounding valve components.
Cycle Speed and Frequency
Valves in high-cycle applications (opening and closing many times a day) will experience more mechanical wear than those in simple open/close service. Higher actuation speeds can also increase friction and heat, contributing to faster degradation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. Acknowledging the limitations of PTFE is critical for proper application and realistic life-cycle expectations.
Susceptibility to Creep
As mentioned, PTFE can deform under sustained loads, especially at elevated temperatures. In applications requiring a constant, high-pressure seal, this must be a design consideration. Modified or "filled" PTFE grades are often used to mitigate this.
Lower Radiation Resistance
While generally robust, standard PTFE is not the ideal choice for high-radiation environments. Excessive exposure can break down the polymer chains, leading to a loss of mechanical strength and embrittlement.
Higher Thermal Expansion
PTFE expands and contracts with temperature changes more than metals do. Valve designers must account for this difference in the coefficient of thermal expansion to ensure seals remain tight and parts do not bind across the entire operating temperature range.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, selecting the right valve is about matching the material to the demands of the system.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity and compatibility: PTFE is an unparalleled choice for applications in food, beverage, medical, or semiconductor manufacturing due to its inert nature.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure service: Carefully evaluate the potential for creep and consider filled PTFE grades or alternative materials if the pressure is both high and constant.
- If your primary focus is high-cycle, dynamic sealing: PTFE's low friction is a significant advantage, but be mindful of accelerated wear if the media contains abrasive solids.
Properly matching the valve's capabilities to the operational environment is the single most important factor in achieving a long and reliable service life.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on PTFE Valve Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent; inert to most chemicals, preventing degradation. |
| Temperature Range | Stable from -200°C to +260°C; thermal cycling can cause fatigue. |
| Operating Pressure | High constant pressure can cause PTFE creep/deformation over time. |
| Media Abrasiveness | Abrasive particles accelerate wear; smooth media extends life. |
| Cycle Frequency | High-cycle applications increase mechanical wear on components. |
Need a PTFE valve that stands the test of time?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your valves are perfectly matched to your application's chemical, pressure, and thermal demands, maximizing longevity and performance from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let's engineer your solution. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of Teflon balls? Unlock Superior Performance in Demanding Environments
- What are the tolerances for PTFE balls based on size? Precision vs. Standard Grade Explained
- What industries commonly use PTFE balls? Essential for Chemical, Pharma, and Food Processing
- What are the properties of Teflon balls? Unlock Elite Chemical & Friction Resistance
- What are the common applications of PTFE balls? Leverage Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Low Friction



















