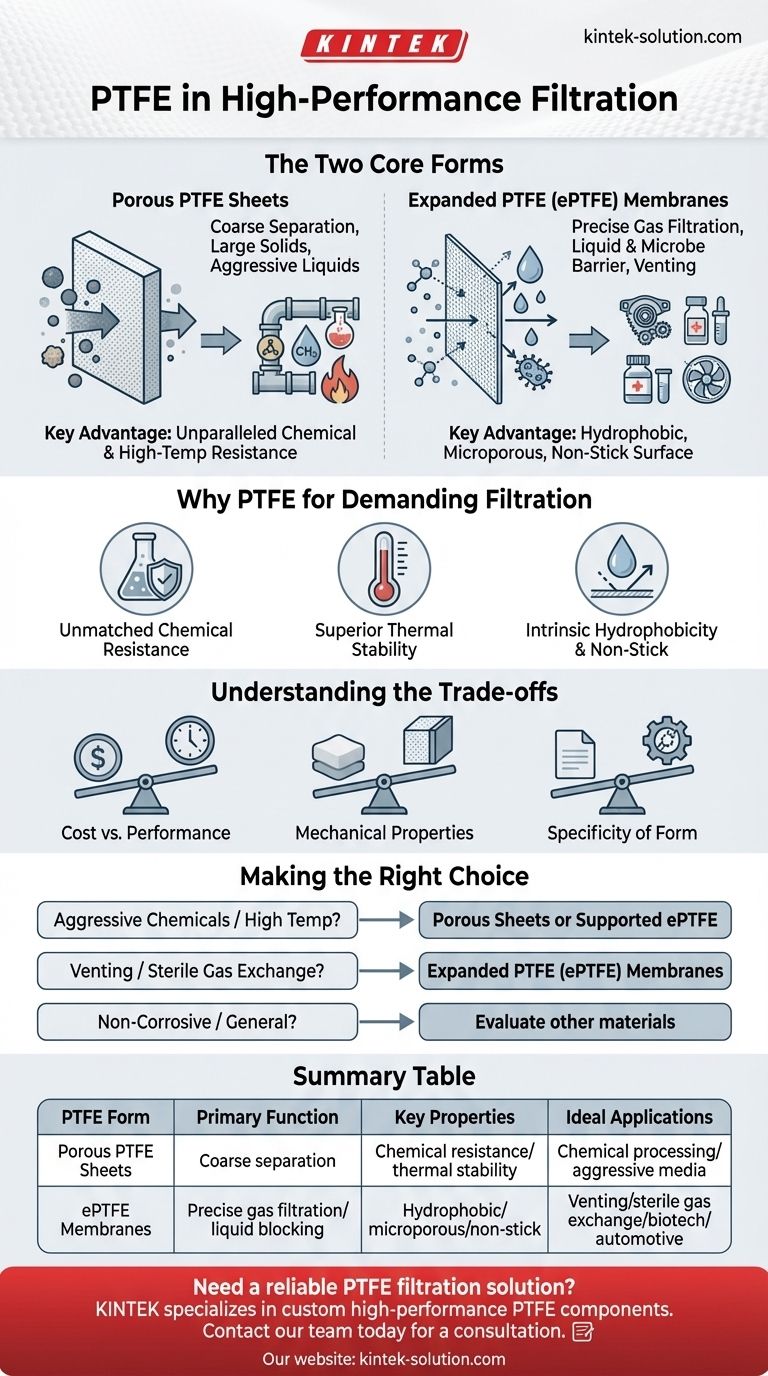
In the world of high-performance filtration, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) serves two distinct roles based on its physical form. It is used as thick, porous sheets for coarse separation of large solids from corrosive liquids, and as thin, microporous membranes known as expanded PTFE (ePTFE) for the precise filtration of gases while completely blocking liquids.
The core value of PTFE in filtration comes from its unique combination of extreme chemical inertness and its engineered ability to form a microporous, water-repelling barrier, making it indispensable for applications where other materials would fail.

The Two Core Forms of PTFE Filtration
PTFE's versatility allows it to be manufactured into two fundamentally different types of filter media, each suited for a specific set of challenges.
Porous PTFE Sheets: The Bulk Separator
Porous PTFE sheets are engineered for heavy-duty, coarse filtration tasks. These are relatively thick materials designed for physical strength and durability.
Their primary function is to separate larger solid particles from a liquid stream. The key advantage here is PTFE's unparalleled resistance to corrosive chemicals and high temperatures, making these sheets ideal for aggressive industrial processes.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) Membranes: The Precision Filter
Expanded PTFE, or ePTFE, is a highly engineered material created by stretching PTFE under specific conditions, forming a web-like, microporous structure.
This structure contains millions of tiny, precisely defined pores. The membrane is naturally hydrophobic, meaning it repels water. This allows gases and vapors to pass through the pores easily while creating a reliable barrier to liquids and microbes. This property is critical in automotive, pharmaceutical, and biotech venting applications.
Why PTFE is Uniquely Suited for Demanding Filtration
Several inherent properties of PTFE make it a superior choice for filtration in critical environments. It's not just one feature, but the combination of them, that sets it apart.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, solvents, acids, and bases. This makes it the default choice for filtering aggressive media in the chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and semiconductor industries where material degradation is not an option.
Superior Thermal Stability
With a very high melting point and a wide operating temperature range, PTFE filters can function reliably in high-temperature applications, such as hot gas filtration, where many other polymers would melt or degrade.
Intrinsic Hydrophobicity and Non-Stick Properties
As mentioned, ePTFE membranes are inherently water-repelling. This is crucial for venting applications that must prevent liquid intrusion while allowing air to escape.
Furthermore, PTFE's famous non-stick surface reduces the tendency for particles or microbes to adhere to the filter, a phenomenon known as fouling. This leads to more consistent flow rates and a longer operational lifetime for the filter.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE offers exceptional performance, it's important to approach its selection with a clear understanding of the practical considerations.
Cost vs. Performance
PTFE is a premium, high-performance polymer. Its manufacturing process is more complex than that of common plastics, resulting in a higher material cost. The decision to use PTFE is a strategic trade-off, balancing its higher upfront cost against its extended lifespan, reduced maintenance, and unmatched reliability in harsh conditions.
Mechanical Properties
In its pure form, PTFE can be relatively soft. For high-pressure applications or environments requiring greater structural integrity, PTFE membranes are often laminated onto a stronger support material. This composite structure combines the filtration properties of PTFE with the mechanical strength of the backing layer.
Specificity of Form
The choice between a porous sheet and an ePTFE membrane is not interchangeable. Porous sheets are unsuited for microbial or fine particulate filtration, while delicate ePTFE membranes would be inappropriate for coarse, high-solids bulk separation. The correct form must be matched precisely to the application's demands for pore size, flow rate, and pressure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct PTFE filter requires aligning the material's properties with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is filtering aggressive chemicals or at high temperatures: Porous PTFE sheets or supported ePTFE membranes are ideal due to PTFE's unmatched chemical and thermal resilience.
- If your primary focus is venting, sterile gas exchange, or aerosol filtration: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) membranes are the definitive choice because their hydrophobic, microporous structure effectively blocks liquid and microbial contaminants.
- If your primary focus is general solid-liquid separation in non-corrosive environments: While PTFE works, you should also evaluate less expensive materials, as its high performance may be unnecessary for your needs.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently specify the right PTFE material to ensure the reliability and longevity of your critical filtration system.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Form | Primary Function | Key Properties | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porous PTFE Sheets | Coarse solid-liquid separation | Chemical resistance, thermal stability | Chemical processing, aggressive media filtration |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) Membranes | Precise gas filtration, liquid blocking | Hydrophobic, microporous, non-stick | Venting, sterile gas exchange, biotech, automotive |
Need a reliable PTFE filtration solution for your demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and specialized filtration elements—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production and custom fabrication services ensure you get a component perfectly tailored to your specific chemical, thermal, and performance requirements, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let's discuss how our PTFE expertise can enhance your system's reliability and longevity. Contact our team today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry



















