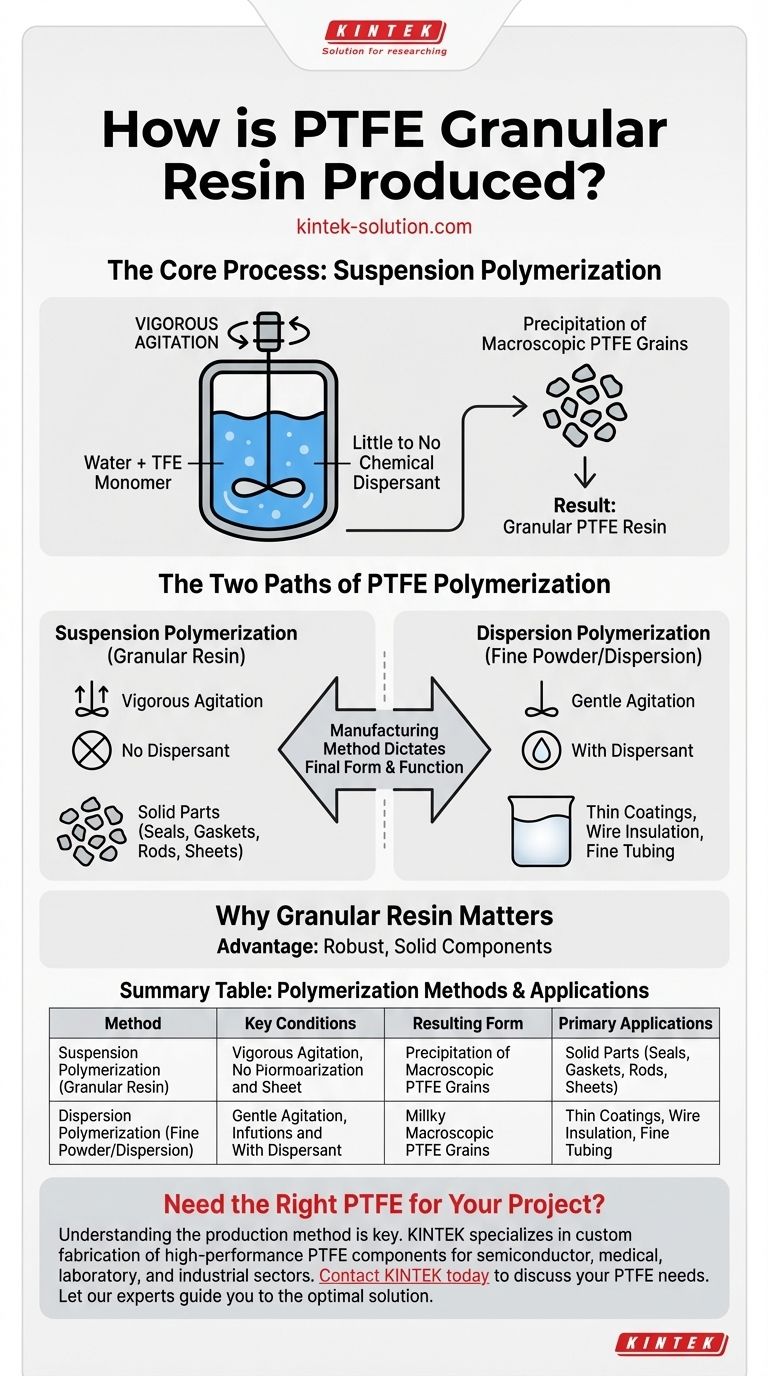
In short, PTFE granular resin is produced through a process called suspension polymerization. This method involves polymerizing tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) monomer in water with vigorous stirring and little to no chemical dispersant, which causes the resulting solid polymer to precipitate out of the water as macroscopic grains.
The manufacturing method is the defining factor for a PTFE resin's final form and function. Whether you get a moldable granular solid or a fine powder for coatings is determined entirely by the conditions of the polymerization reaction—specifically, the agitation level and the presence of a dispersant.

The Two Paths of PTFE Polymerization
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is created using one of two fundamental methods. The choice between them dictates the physical characteristics of the final resin and, therefore, its suitable applications.
Suspension Polymerization: The Origin of Granular Resin
This is the direct method for producing granular PTFE. The process involves polymerizing the TFE monomer directly in an aqueous (water-based) medium.
The two critical conditions are vigorous agitation and the use of little or no dispersant. Without a dispersant to keep the polymer particles separated and suspended, they agglomerate and precipitate out of the water.
The result is a collection of solid PTFE grains, which are then dried. These particles are relatively large and are intended for subsequent molding processes.
Dispersion Polymerization: The Alternative Path
To understand why granular resin is different, it's essential to know its alternative. Dispersion polymerization is used to create PTFE fine powder and aqueous dispersions.
This method uses gentle agitation along with a specific type and amount of dispersant. The dispersant stabilizes the newly formed polymer particles, preventing them from clumping together.
The result is a milky, paste-like substance where tiny colloidal PTFE particles remain suspended. This can be processed into a fine powder or used as a liquid coating.
Why the Production Method Matters
The distinction between suspension and dispersion polymerization isn't just a technical detail; it's the reason why PTFE can be used for both solid mechanical parts and non-stick coatings.
Characteristics of Granular PTFE
The grains produced via suspension polymerization are specifically designed for consolidation. Their size and morphology are optimized for processes like compression molding and ram extrusion.
This is the starting material for creating solid PTFE stock shapes, such as rods, sheets, and billets, which are often machined into final components like seals, gaskets, and bearings.
Characteristics of Fine Powder PTFE
The fine powder derived from dispersion polymerization has a much smaller particle size. This form is not suitable for compression molding in the same way as granular resin.
Instead, it is mixed with a lubricant to form a paste, which is then used for paste extrusion to create thin-walled products like tubing and wire insulation. It is also the basis for the liquid dispersions used in coating applications, such as non-stick cookware.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a PTFE resin is a choice between two distinct material forms designed for entirely different manufacturing outcomes. You cannot substitute one for the other.
The Advantage of Granular Resin
Granular PTFE is the workhorse for creating robust, solid components. Its particle structure is engineered to fuse under heat and pressure into a dense, void-free solid block. This makes it the only choice for producing thick, machinable stock shapes.
The Advantage of Fine Powder and Dispersions
Fine powder excels where granular resin cannot be used. Its ability to be extruded into a paste allows for the creation of complex, thin-walled profiles and delicate insulation for wires. As a liquid dispersion, it's the only way to apply a thin, uniform PTFE film onto a surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The initial polymerization process directly dictates the material's end-use. Your application will determine which type of resin is required.
- If your primary focus is creating solid, machinable parts like billets, rods, or thick sheets: You must use granular PTFE resin, which is produced via suspension polymerization.
- If your primary focus is developing thin coatings, wire insulation, or fine tubing: You require fine powder PTFE, which originates from the dispersion polymerization method.
Understanding this fundamental manufacturing distinction is the key to selecting the correct form of PTFE for any engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Polymerization Method | Key Conditions | Resulting PTFE Form | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Suspension Polymerization | Vigorous agitation, little/no dispersant | Granular Resin | Solid, machinable parts (seals, gaskets, rods, sheets) |
| Dispersion Polymerization | Gentle agitation, with dispersant | Fine Powder / Dispersion | Thin coatings, wire insulation, paste extrusion |
Need the Right PTFE for Your Project?
Understanding the production method is the first step to selecting the perfect PTFE material. Whether your application requires robust, machinable components from granular resin or specialized coatings from fine powder, KINTEK has the expertise and manufacturing capability to deliver.
We specialize in custom fabrication of high-performance PTFE components—from prototypes to high-volume orders—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production ensures your parts meet the highest standards.
Contact KINTEB today to discuss your PTFE needs and let our experts guide you to the optimal solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the hardness of PTFE on the Shore scale? A Guide to Its Softness and Performance
- What are the industrial applications of PTFE? Unlock High-Performance in Extreme Environments
- What are the key features of PTFE laminated fabric? Unmatched Protection & Breathability
- In which industries is PTFE/Teflon commonly used? Discover Its Critical Role in High-Performance Applications
- What are some common uses of Teflon? Discover Its Critical Role in Engineering
- How is PTFE used in industrial applications? Solve Extreme Chemical, Thermal & Friction Challenges
- How does the electronegativity of fluorine affect PTFE's structure? The Key to Its Unmatched Chemical Resistance
- What are the performance characteristics of PTFE? Unmatched Chemical Inertness and Low Friction



















