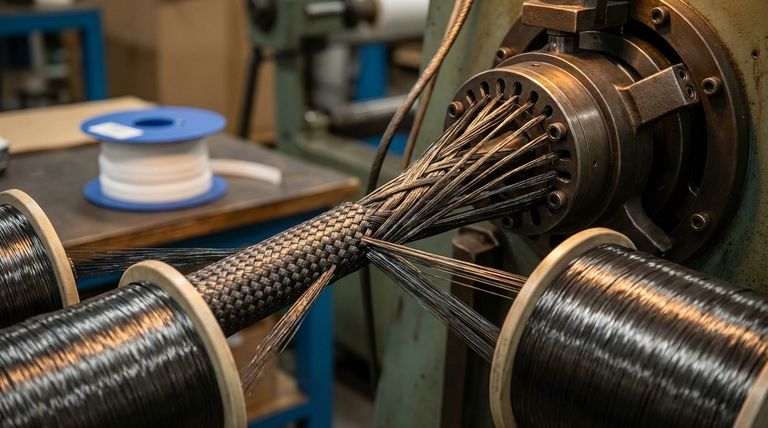
At its core, graphite packing is made by twisting multiple high-purity graphite filaments into a yarn. This yarn is then woven or braided into its final, dense form, a process that significantly increases its tensile strength and durability for industrial sealing applications.
The simple braiding of graphite yarn creates a packing material whose true value lies not just in its strength, but in graphite's inherent ability to manage extreme heat and friction, making it a critical component in high-performance machinery.

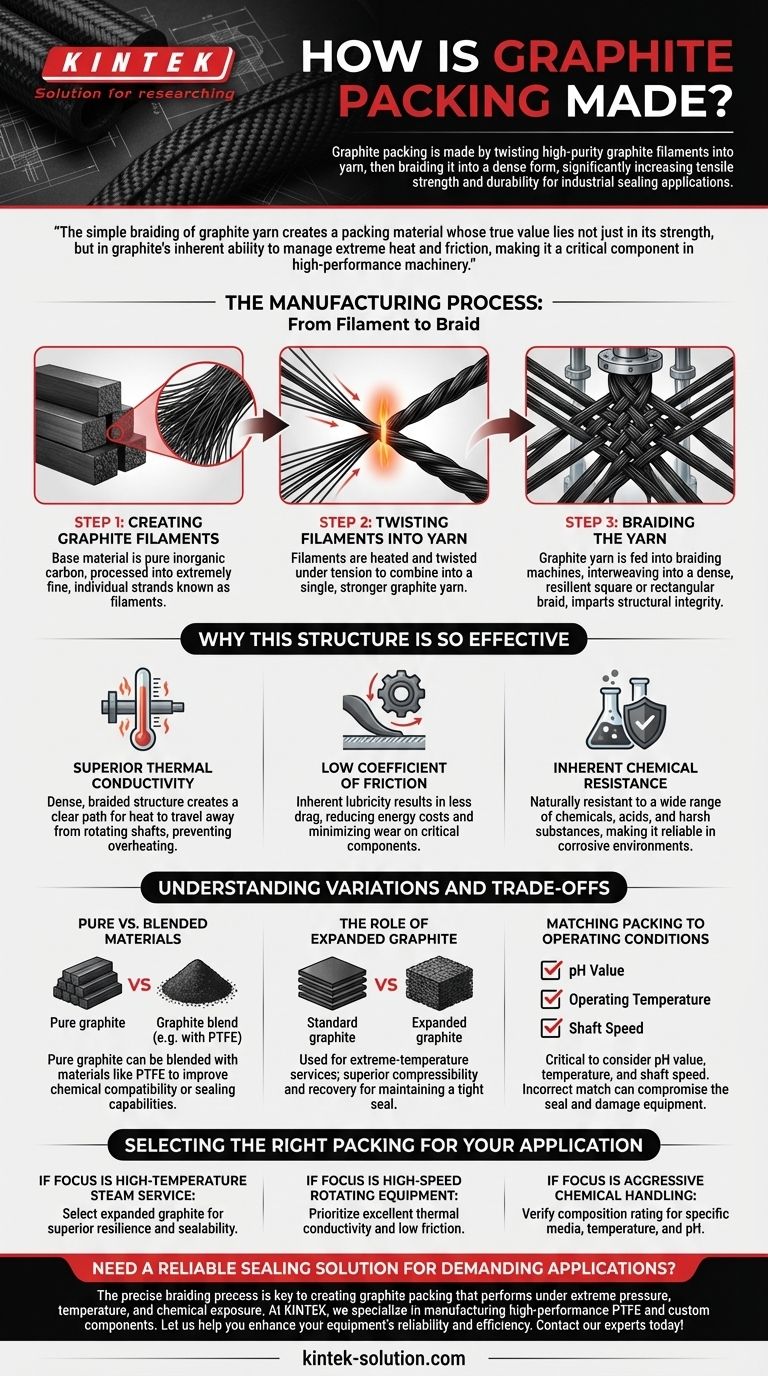
The Manufacturing Process: From Filament to Braid
Understanding how graphite packing is made reveals why it performs so well under pressure. The process is a straightforward mechanical transformation that builds upon the fundamental properties of carbon.
Step 1: Creating Graphite Filaments
The base material is a pure, inorganic form of carbon. This carbon is processed into extremely fine, individual strands known as filaments, which serve as the foundational building blocks of the packing.
Step 2: Twisting Filaments into Yarn
Multiple filaments are heated and twisted together under tension. This action combines the individual strands into a single, cohesive, and much stronger graphite yarn, which is the direct precursor to the final product.
Step 3: Braiding the Yarn
The graphite yarn is then fed into braiding machines. These machines interweave multiple strands of yarn into a dense, square, or rectangular braid. This final step imparts the packing with its structural integrity, resilience, and consistent shape.
Why This Structure Is So Effective
The braided construction is not just for strength; it directly contributes to the key performance characteristics that make graphite packing essential in demanding industrial environments.
Superior Thermal Conductivity
Graphite is an excellent thermal conductor. The dense, braided structure creates a clear path for heat to travel away from the rotating shaft, preventing overheating and extending the life of both the packing and the equipment.
Low Coefficient of Friction
The inherent lubricity of graphite results in a very low coefficient of friction. This means less drag on shafts and valve stems, reducing operational energy costs and minimizing wear on critical components.
Inherent Chemical Resistance
As a form of pure carbon, graphite is naturally resistant to a wide range of chemicals, acids, and other harsh substances. This makes it a reliable sealing solution in chemical processing and other corrosive environments.
Understanding Variations and Trade-offs
Not all graphite packing is the same. The choice of material depends entirely on the specific demands of the application, and selecting the wrong type can lead to premature failure.
Pure Graphite vs. Blended Materials
While pure graphite is highly effective, its properties can be enhanced for specific tasks. It is often blended with other materials, such as PTFE, to improve its chemical compatibility or sealing capabilities in certain applications.
The Role of Expanded Graphite
For extreme-temperature services, such as high-pressure steam turbines and valves, expanded graphite is used. This form has superior compressibility and recovery, allowing it to maintain a tight seal despite significant thermal cycling.
Matching Packing to Operating Conditions
It is critical to consider the application's specific requirements. Factors like pH value, operating temperature, and shaft speed will dictate which type of graphite packing is suitable. An incorrect match can compromise the seal and damage equipment.
Selecting the Right Packing for Your Application
Choosing the correct packing is about aligning the material's properties with the operational goal.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature steam service: Select an expanded graphite packing for its superior resilience and sealability under thermal stress.
- If your primary focus is high-speed rotating equipment: Prioritize a graphite packing with excellent thermal conductivity and low friction to prevent shaft scoring and heat buildup.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical handling: Verify that the packing's composition is rated for the specific media, temperature, and pH to ensure a stable, long-lasting seal.
By understanding the link between its simple construction and its powerful properties, you can confidently select the right material for the job.
Summary Table:
| Manufacturing Step | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Filament Creation | Processing pure carbon into fine strands. | Creates the foundational building blocks. |
| 2. Yarn Formation | Twisting filaments under heat and tension. | Produces a strong, cohesive graphite yarn. |
| 3. Braiding | Interweaving yarns on a braiding machine. | Forms the final dense, resilient packing structure. |
Need a Reliable Sealing Solution for Demanding Applications?
The precise braiding process is key to creating graphite packing that performs under extreme pressure, temperature, and chemical exposure. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production and custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get a sealing solution perfectly matched to your operational requirements.
Let us help you enhance your equipment's reliability and efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the five outstanding characteristics of PTFE seals? Engineered for Extreme Performance
- How do PTFE seals perform under pressurized conditions? Achieving Reliable Sealing in Demanding Environments
- What are the benefits of PTFE seals in terms of prototyping and production? Accelerate R&D and Ensure Elite Performance
- What are the benefits of using PTFE seals in demanding industries? Solve Extreme Sealing Challenges
- What are the key steps for properly installing PTFE seals? Ensure a Leak-Free, Long-Lasting Seal

















